WATER PRODUCTION FOR AWARE (Organic Contaminants)
Antonio Cobelo
water sampling
water processing
water analysis
waste water treatment
advanced tertiary treatment SOP
Abstract
The protocol summarises the procedures used for analytical control. The protocol describes the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the optimization of advanced tertiary treatment of water, based on a comprehensive quality and risk assessment.
Steps
Organic Contaminants:
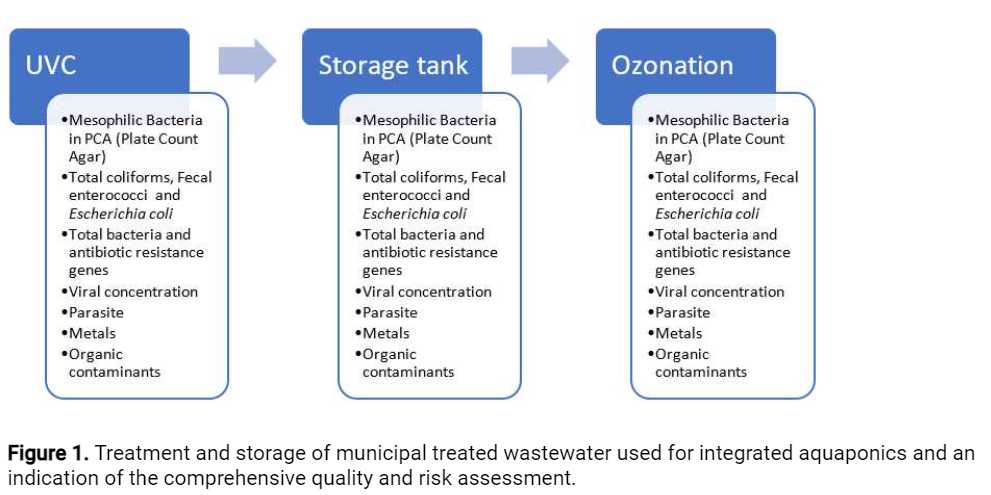
The water production for AWARE main activities includes three stages – disinfection by ultraviolet C radiation (UVC), storage for12h 0m 0s-24h 0m 0s(according to water load and season) and ozonation. The water quality is monitored at these three stages, for the parameters indicated in Figure 1 below.
Sampling, Processing, and Analyses
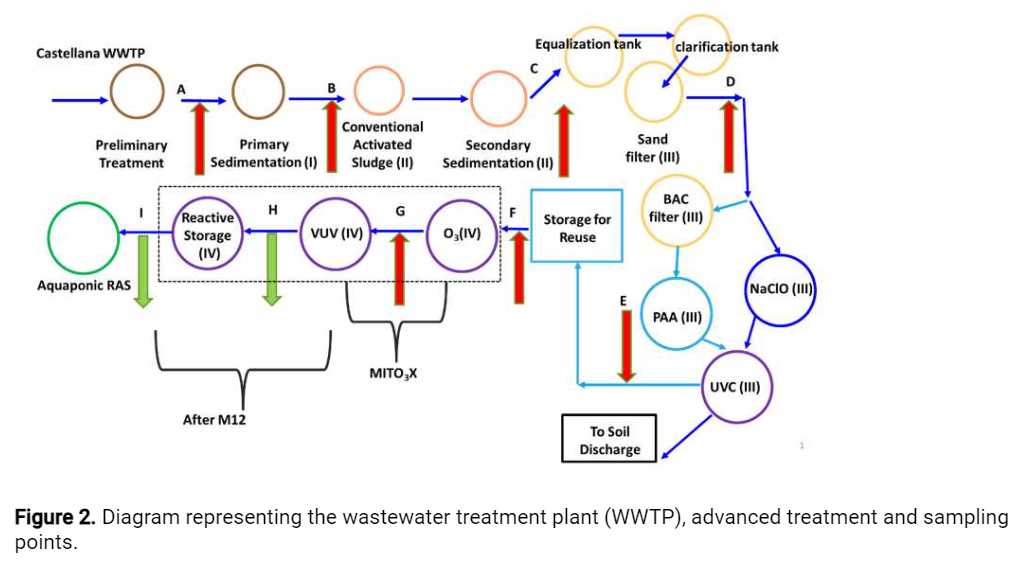
Water samples are collected (see Figure 2) and processed within a6h 0m 0sinterval, before being shipped for the partner responsible for the analyses (Table 1). In case no processing is needed, samples are frozen and stored at-80°Cwithin3h 0m 0s.
For each sampling event, the date, day of the week and hour; the temperature and rain. Sampling points, indicated in Figure 2 were designated from A to I:
-
Influent of primary treatment (A)
-
Influent of biological treatment (activated sludge) (B)
-
Treated secondary effluent (C)
-
Sand filter effluent (D)
-
UVC effluent (E)
-
Storage for reuse tank effluent (F)
-
Ozonation effluent (1 dose, e.g.,
5mgO3) - MITO3X technology - (G) -
Effluent of the vacuum UV oxidation (VUV) (H)
-
Effluent of reactive storage / Influent of the recirculation aquaculture system (RAS) (I) ù
Methods: The section below summarises the procedures used for analytical control – detailed protocols are annexed to this protocol.
Organic Contaminants: Organic Contaminants:
Analysis: s: Screening of Organic Contaminants in Water.
Methods: Solid-phase extraction
2.1 Sample filtration 0.45um um PVDF).
Collect200mLof the filtered water sample (e.g. volumetric flask or beaker) and spike with 50µL of an internal standard solution. Produce two200mLreplicates per sample. Mix well after the internal standard is added.
Cleaning/Conditioning of the cartridges (OASIS HLB200mg)
3.1. Pa5mLs of MeOH
3.2. 5mLass of ultrapure water
Pass the200mLof sample
Rinse the volumetric flask or beaker that contained the sample with 2x10mLof ultrapure water, which are then passed through the cartridege
Drying the cartridge resin (e.g. N2 flow for0h 30m 0s)
Store the cartridges in a freezer (-20°C)
All samples are to be processed in duplicate.
For the cartridge blanks (n=2): star with , and then spike directly on the cartridge the same amount of internal standard as for sam50µLles ( mLix de ). Then go direcly to .
For the ultrapure water blanks (n=2), the same type of sampling flasks are filled with ultrapur24h 0m 0s water before sampling. Then they are treated using the same protocols as for samples.
Elution of the loaded cartridges was carried out by gra10mLity using of methanol f10mLllowed by of dichloromethane. The eluates were concentrated approximat0.5mLly to ca. using a Turbovap II concentrator (Zymark, Hopkinton, MA, USA), then to dryness under a gentle nitrogen stream and finally recons500µLituted in of methanol and filte1ugmLed w13 mm th a GHP‱ syringe filter (Pall Corporation). The extracts were injected in an Agilent 1290 LC coupled with and Agilent 550 QTOF system.
Parameters framed by Legal and Regulatory Requirements:
Using the EU Drinking Water Directive:
Organic contaminants - DIRECTIVE 2008/105/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE
COUNCIL of 16 December 2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy.

