Intratibial implantation of tumor cells
Shubhangi Agarwal, donna.peehl, Renuka Sriram
Abstract
This protocol describes the steps required for the successful implantation of small cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) cells in the bone. Bone is one of the most common sites for the development of metastatic prostate cancer and its study is important for evaluating the tumor characteristics and response to therapy.
This protocol can be used for the implantation of any tumor cell line in the bone.
Steps
Preparation before surgery
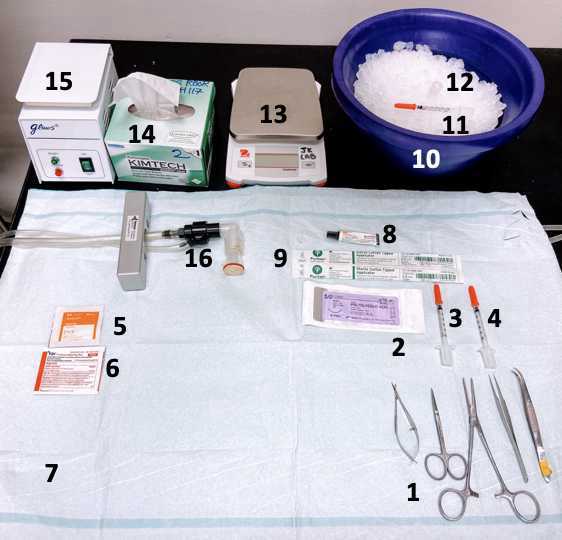
Preparation of surgical instruments and supplies: All of the instruments and supplies should be sterilized.
Surgery record sheets
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| PI | ||
| Personnel | ||
| Date | ||
| Procedure name | Intratibial Implantation | |
| Protocol # | ||
| Type | Survival Surgery | |
| Species | Mouse | |
| Experimental agents administered | Tumor cells | |
| Anesthetics | Isoflurane | Dosage: (1-5 % or mg/kg; mL) |
| Analgesics | (1) Lidocaine | Dosage |
| (2)Buprenorphine | Dosage | |
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse ID | ||
| Mouse weight | ||
| Anesthesia start time | ||
| Analgesics | (1) Lidocaine | Time administered: |
| (2) Buprenorphine | Time administered: | |
| Tumor cells administration time | ||
| Anesthesia end time |
Preparation of the PDX cells for implantation
Preparation of cells for implantation from frozen biobank
Prepare DMEM medium: Prepare fresh DMEM media supplemented with
10% volume FBS and
100ug/ml Gentamicin.
Retrieve cryovials containing cells from liquid nitrogen storage. Thaw the cell-containing cryovial by placing it in 37 degrees water bath. Move the vial into a BSL2 hood and transfer the contents of the vial in a 15 ml conical tube containing fresh DMEM media (9mL DMEM per 1mL of the cell mixture) and mix gently.
Perform live/dead assay using trypan blue and note the live and total cell count.
Centrifuge the 15 ml tube containing cells at 300x g,0h 0m 0s and aspirate the supernatant. Resuspend the cells in fresh DMEM to a final concentration of 1M live cells/10 ul and transfer this mixture into an eppendorf tube.
Transfer the cell suspension into a 31G 0.3 ml syringe right before beginning the surgery.
Preparation of surgical space
Place a disposable sterile pad on a heating pad.
Aseptically sterilize the surgical area by spraying with 70% ethanol.
Station 2: Surgery
Place a disposable sterile pad on a heating pad.
Aseptically sterilize the surgical area by spraying with 70% ethanol.
Place all the autoclaved surgical instruments within the sterilized surgical area.
Heat: Animal should be kept on a heating pad or circulating water blanket/pad during the entire procedure and, after the surgery is over for approx. 2-4 hrs.
Anesthetization and fur removal of mouse
Place the animal in a knock-down box circulating with a gas mixture of Isoflurane @ 1.4-2.0% and O2 @ 1-1.2 lt/min inhalant, maintained via a bain-closed system.
Note the start time for anesthesia.
Move the animal to the station 1 nose cone and apply ophthalmic ointment on the animal’s eyes to prevent them from drying out during the procedure.
Determine the anesthetic depth by pinching the animal’s foot for a reflex response.
Depilate right or left knee.
Administer buprenorphine subcutaneously. Note the time of administration.
Prep the shaved area with povidone-Iodine prep pads, rubbing in a circular motion. Apply 70% alcohol pads to the surgical area to remove the betadine and loose hair. Repeat this process 2 or more times.
The animal is now ready to be moved to station 2 for surgery.
Surgical procedure (Station 2)
Gently grasp lateral malleolus, medial malleolus, and lower half of tibia with forefinger and thumb, then bend leg such that the knee is visible and accessible.
Wet the skin with 70% ethanol to increase the visibility of the underlying patellar ligament, which should be visible as a distinct, thick, white line.
Transfer the cell suspension into a syringe
While firmly grasping the ankle/leg of the mouse insert the syringe with cells suspension under the patella, through the middle of the patellar ligament, and into the anterior intercondylar area in the top of the tibia.
When inserting the needle into the tibia, guide carefully through the growth plate using steady, firm pressure with slight drilling action.
The needle will encounter markedly less resistance upon penetration of the tibial growth plate.
Use a gentle, lateral movement of the needle to ensure the needle is in the tibia and through the growth plate. The movement will be limited if the needle is in the proper place within the tibia.
Slowly depress the plunger to inject 10 μl of cell solution. Little to no resistance should be felt at this point.
Slowly extract the needle.
Administer lidocaine in the flank. Note the time of administration
Start prepping the next mouse for surgery.
Post-Op care and monitoring
Place the animal in a clean cage on a warm heating pad to aid in regaining its body temperature.
Observe the animal until it has regained full consciousness and is walking around in the cage
Observe the animal on a daily basis until sacrificed.