Immunohistochemistry in wholemounts and cryostat sections in rat stomach
Martin Stebbing, John Furness, Madeleine Di Natale, Jamie JL Liew, Billie Hunne
Abstract
This protocol describes the methods used to evaluate neuronal target and population density in wholemount preparations and cryostat sections. In brief, stomachs from Sprague-Dawley rats were collected, fixed, cleared, and processed before being immunohistochemically stained with primary antibody and fluorescent secondary antibodies. Neuronal density and neuronal target analysis were completed using Zen Blue analysis software.
Steps
Immunohistochemistry for neuronal NOS in wholemounts and cryostat sections
Tissue preparation
Fresh stomachs were collected from rats that were deeply anesthetised with an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (100mg/kg), placed into PBS (phosphate-buffered saline: 0.15 M NaCl in 0.01 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.2) containing nicardipine (1 μM), and opened and pinned to balsa board before being immersed in fixative (2% paraformaldehyde and 0.2% picric acid in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) overnight at 4°C. Fixative was washed out with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 3 x 10 min, followed by PBS, 3 x 10 min, and tissue was stored in PBS-azide (0.1% sodium azide in PBS) at 4°C until being prepared for wholemounts or sections.
Wholemounts
Wholemounts of the longitudinal muscle and myenteric plexus were created by dissecting away the mucosa, submucosa and most of the circular muscle. Wholemounts of the submucosa were also prepared. Preparations were blocked with 10% normal horse serum (NHS) with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS at 37°C for 2 hours. Samples were then incubated with a mixture of primary antibodies (eg sheep anti-nNOS and human anti-Hu), diluted in PBS-azide with 0.3% Triton X-100, 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), and 1% NHS, overnight at 37°C followed by 2 nights at room temperature (RT). The preparations were then washed with PBS, 3 x 10 min before a 5-hour incubation with mixtures of Alexa Fluor labelled secondary antibodies diluted in PBS-azide with 0.3% Triton X-100 at 37°C. Samples were washed in PBS, 3 x 10 min before being mounted with Dako fluorescence mounting medium.
Sections
For tissue that was to be prepared for cryostat sections, after fixative was washed out, regions of stomach to be sectioned were placed in PBS-sucrose-azide (30% sucrose in PBS-azide) overnight at 4°C, followed by an overnight incubation in a mixture of OCT (Optimal Cutting Temperature compound; Trajan Scientific and Medical, Ringwood, Australia) and PBS-sucrose-azide in a 1:1 ratio. Tissue blocks were embedded in 100% OCT medium and frozen in isopentane cooled by liquid nitrogen. Cryostat sections (12μM) were cut and mounted onto SuperFrostPlus microscope slides (Menzel-Glaser; Thermo Fisher, Scoresby, Australia). Sections were air-dried for 1 hour, blocked with 10% NHS with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min at RT and then incubated in a mixture of primary antibodies: (eg sheep anti-nNOS and rabbit anti-α smooth muscle actin) diluted in PBS-azide 0.1% Triton X-100, overnight at 4°C. Sections were then washed with 3 x 10 min PBS followed by a 1.5-hour incubation in a mixture of Alexa Fluor labelled secondary antibodies diluted in PBS-azide at RT. Sections were washed in PBS, 3 x 10 min before being cover slipped with Dako fluorescence mounting media.
Imaging
Wholemounts and sections were imaged using an AxioImager or an LMS800 confocal microscope.
Quantitation of NOS immunoreactive neurons
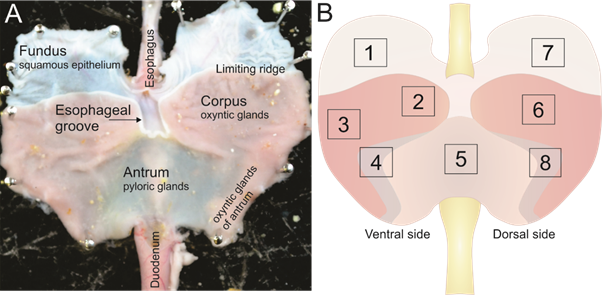
To determine proportion of total neurons that are positive for nNOS, the ratio of nNOS neurons to Hu neurons were counted from wholemount preparations from 8 regions of the rat stomach (Fig 1). These regions were the ventral fundus (1), ventral corpus closer to the lesser curvature (2), ventral corpus closer to the greater curvature (3), ventral antrum closer to the greater curvature which includes the region of transition from corpus to antrum (4), ventral antrum at the lesser curvature (5), dorsal corpus (6), dorsal fundus (7), and dorsal antrum (8).
From each region from each animal, a cohort of 200 Hu positive cells were counted. Hu cells were located, without knowledge of their being nNOS positive. Of the Hu positive cells, the number of nNOS positive cells was then counted to obtain the proportions of nNOS neurons in that region.
The cell profile areas (μm2) of nNOS immunoreactive neurons were determined using Zen Blue software (Zeiss, Sydney, Australia). The Draw-Spline Contour tool was used to trace a border around the edges of nNOS positive cells, including the cell body and dendrites, to obtain measurement data.