Handling and Sampling Birds - ISL Peru
Gideon Erkenswick, Mrinalini Watsa, Jorge Luis Mendoza-Silva, Giancarlo Inga Diaz, Roberto Salazar, Cristian Tirapelle
Disclaimer
This protocol is actively used by Field Projects International at the Estación Biológico Los Amigos, Madre de Dios, Peru. It is revised annually to reflect improved capture, handling, marking, and sampling methodology. It has been reviewed by the ethics committees of multiple institutions. No author nor affiliated institution takes responsibility or bears any liability for the use of this protocol by others. The protocol is listed as having sensitive content since it involves biosampling from wildlife. Note: these procedures should be carried out only by trained personnel, and are not recommended for use without first obtaining all required permissions.
Abstract
Program Timing :
Sample collection occurs annually during the rainforest dry season (June - August). Sample transport and analyses occur between September and April.
Program Overview :
Mist nets are set up at multiple locations encompassing major habitat types surrounding the field station (terra firme, flood plain, swamp, bamboo, successional forest, primary forest, edge forest, etc). Mist netting occurs over 3 consecutive days at each location throughout the sample collection period.
Team Composition
This protocol is intended to be carried out by a team of no less than 3 individuals, including at least 2 trained personnel. Roles include (1) designated handler (2) sampling assistant (3) data recorder.
Capture Overview:
Mist nets are opened between 0500 and 1000 hours, and captures occur spontaneously throughout (~ 5 - 25 animals/event) -> animals are extracted from the net (1-2 minutes) -> transferred into a light and breathable cloth bag and held in order-of-capture in a nearby tent until processing (0 - 30 minutes) -> one-by-one animals are processed for morphometric measurements, photographs, nonlethal tissue collection, and placement of leg bands (~10 minutes) -> animals are immediately released at the site of capture, but away from mist nets.
Before start
The Team Leader is in charge of coordinating the bird capture activities, selecting specific capture sites, and determining net placement. The sites tend to be changed every 3-4 days to avoid high recapture rates.
Steps
ROLES
Team Composition
This protocol is intended to be carried out by a team of no less than 3 individuals, including at least 2 trained personnel. Roles include (1) designated handler (2) sampling assistant (3) data recorder.
Designated Handler
This is a trained and senior researcher/veterinarian that is experienced with every step of the bird capture process. They are responsible for animal mist-net removal, as well as direct handling during processing and release.
Sampling Assistant
will assist the designated handler with:
- Passing tools, bags and tubes needed for processing
- Reading aloud the serial codes that identify each sample bag and tube.
- Taking all images listed in the processing sheet.
Data Recorder:
Will perform data recording on the animal PROCESSING SHEET (see MATERIALS):
- Write down the weight of the animal and any other measurements, sample codes, important time stamps.
- Recording notes from the handler
- Storing samples in the dedicated sample boxes.
PREPARATORY PHASE
Day before capture
- install 4-12 nylon mist nets (6 - 12 x 2.7 m, 4 - 5 shelves, mesh size 15 - 20 mm) in selected areas. The number of mist nets used should reflect the size of the bird team and frequency of capture at that particular site. Nets are activated from sunrise until around 11:00.
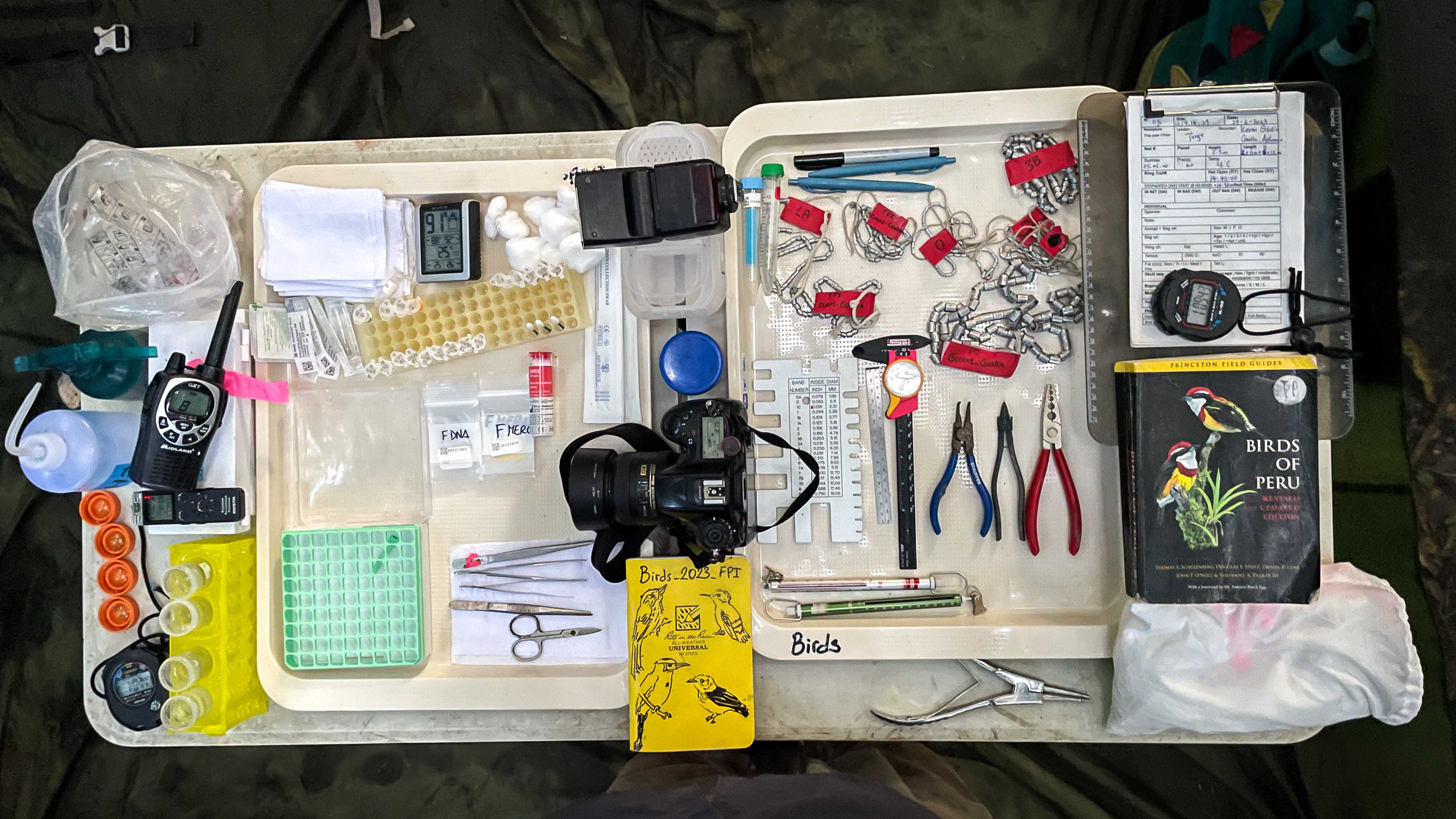
- pack and double-check all capture and processing materials needed for the next morning (refer to the MATERIALS section).
Video on how to place a mist-net
Day of capture
the team will leave the station early in the morning to reach the net site and open the nets before sunrise. A screened-in tent with a table is setup within 25 - 50 meters of the mist nets, which will be used for processing animals.

CAPTURE
The nets are opened at sunrise (05:00 - 11:00 hrs) and left open until 1000 hrs. Nets must be checked regularly:
- Every 20 minutes for the first 2 hours.
- Every 30 minutes for the following hours.
- Every 15 minutes if it is a cold day (below 20 degrees Celsius).
Start the STOPWATCH and VOICE RECORDER, which should be running during the entire session. Say aloud: (1) the full date and time; (2) the weather and temperature; (3) the capture site; (4) the team members participating; (5) the number of open net.
Any time that has to be recorded in the PROCESSING SHEET BirdForm_hardcopy.pdf , refers to the time indicated on the STOPWATCH.

NET INSPECTION:
The person(s) inspecting the nets carry a walkie-talkie to communicate with the rest of the team waiting inside the tent. As soon as a captured bird is discovered the team is informed so that DISCOVERY TIME, NET NUMBER and PANEL NUMBER may be recorded.
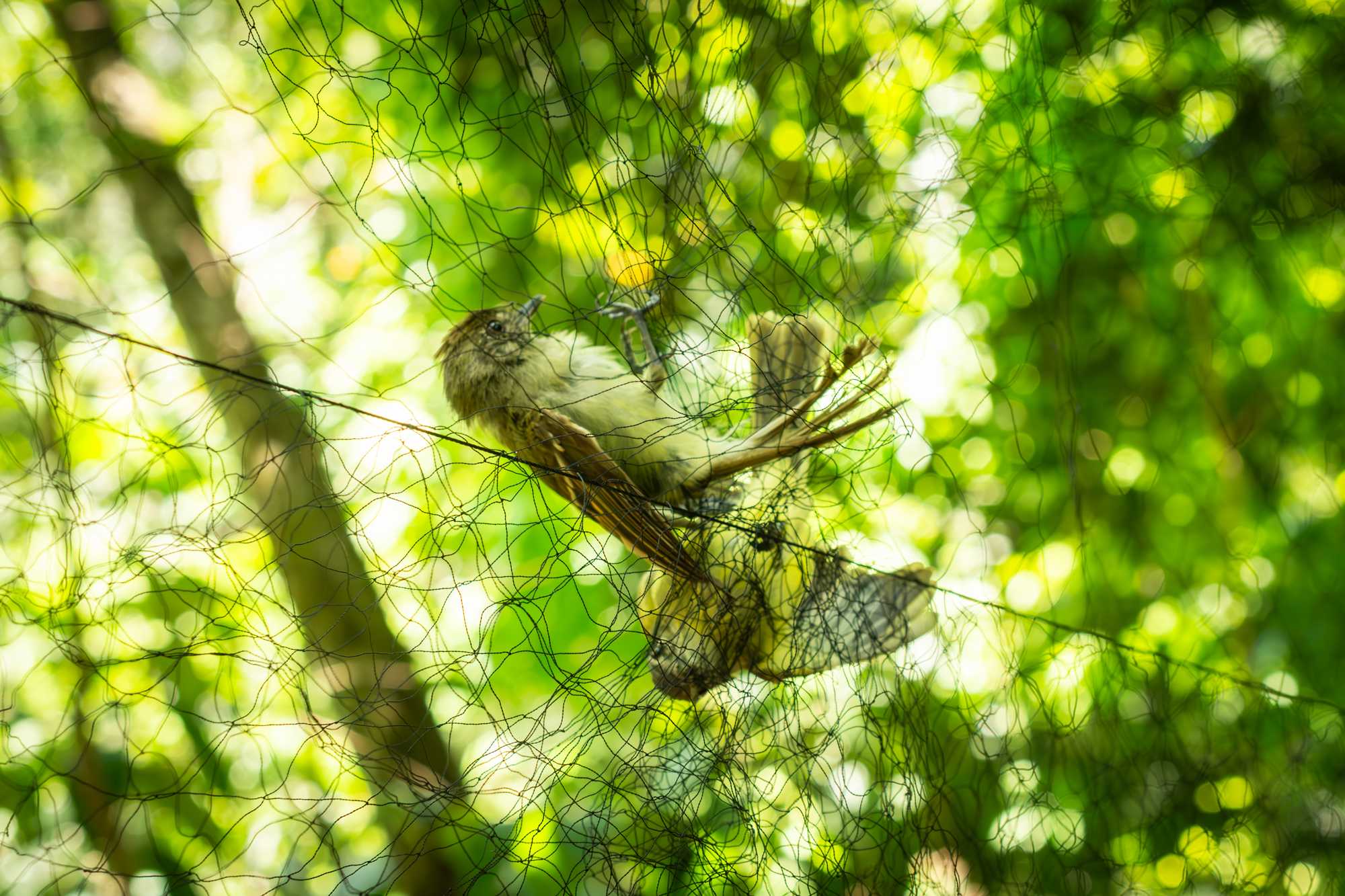

NET REMOVAL
An experienced team member will carefully remove the bird from the net:
Video on how to restrain the bird and remove it from the net.
In case of multiple captures at once, start with birds that are most tangled, near to the ground and in lowest panel, or the smallest species.
- First identify in which panel and from which side the bird was captured.
- The head should be checked first to confirm that the tongue is not tangled and the neck is not strangled.
- Hold the bird with the non-dominant hand.
- Hold the bird with its neck near the base of the gap between your forefinger and middle finger. With these two fingers close gently around the bird's neck, the wings can be contained against the palm of your hand. The remaining fingers and thumb are loosely gripping the bird's body, forming a kind of "cage."
- Using the dominant hand, gently pull the mesh of the net away from the toes and legs first, untangle the wings and finally the head.
- The head of the bird should be freed from the net last
- This type of fastening is called "bird banding position". which should be taken into account in holding the bird's neck firm enough so that the bird cannot remove its head from between its fingers, but at the same time not so tight to avoid suffocating or stressing the bird, as described in the bander's guide (https://nabanding.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Guia-de-Estudio-del-Anillador-de-NorteAmerica-2001.pdf))
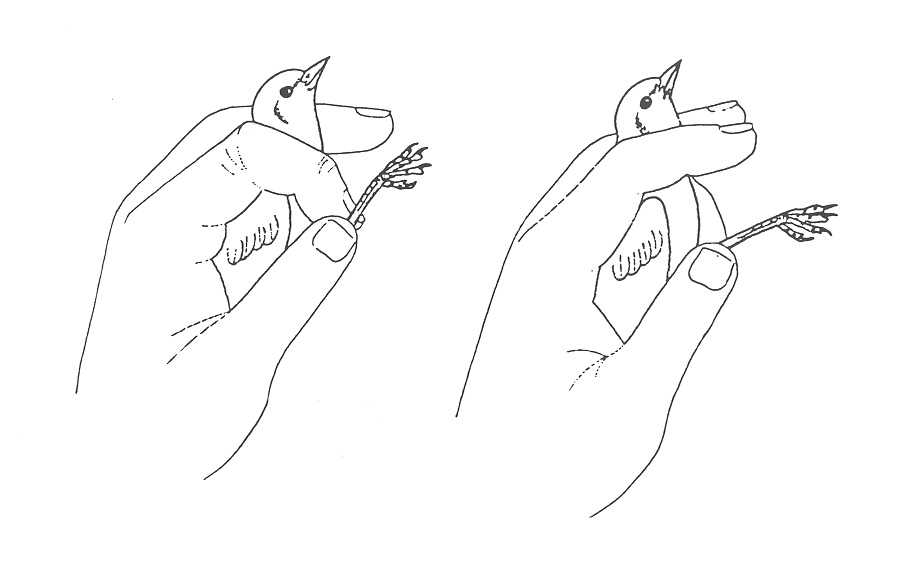
The image shows the position of the bander and the correct way to hold the bird's tarsal joint (from Lowe 1989, Pyle 2001)
Record the time that the animal is placed inside a cloth-bag (IN BAG TIME)
ANIMAL TRIAGE
Once removed, place bird inside a clean cotton bag and tie-up the opening of the bag to prevent escape. Follow these guidelines to determine priority of processing:
- Reproductive females have a noticeable incubation patch, if this patch is observed, prioritize it over all remaining birds so that it may return to the nest to continue incubating the eggs.
- a delicate species (like a hummingbird or other small birds < 10g) .
Release immediately if you have a
- small bird with an obvious brood patch and showing strong signs of net or capture stress, such as paralysis or intense panting.
- reproductive bird that has spent a long time in the net for any reason.
Bring the bags containing the birds to the processing tent and hang them on a dedicated string placed in the shade, using clothespins.
An animal is either processed straight away or left on a line and processed in order of net extraction. The waiting line must be in a dry place that is not exposed to wind.
Birds waiting in bags must be checked for signs of movement/life every 10 minutes. If any animal appears unwell the team leader must be notified immediately.
In the even of a low ambient temperature, place a hot water bag/bottle near to the bird, never in direct contact.
PROCESSING
PICTURE OF PROCESSING SHEET
A picture of the animal sheet showing the ANIMAL NUMBER, should be taken before beginning PROCESSING. This will serve as a place marker on the camera for sorting images later
WEIGH BIRD + BAG
The bag containing the bird is removed from the line and weighed with a pesola scale.
BAG REMOVAL
Open the bag where the bird is kept and identify the head of the animal, then:
- Insert hand and position animal so that the head will be facing away from hand.
- Place neck between index and medium fingers, and hold wings closed around the body between the thumb on one side and the ring finger on the other side. The dorsum of the bird should be resting in the palm of the non-dominant hand. T he dominant hand is free to manuever tools for sampling .
- Remove and pass the empty cloth bag to an assistant to record the BAG WEIGHT. Do NOT discard bag yet

MARKING, MEASUREMENT & PICTURES
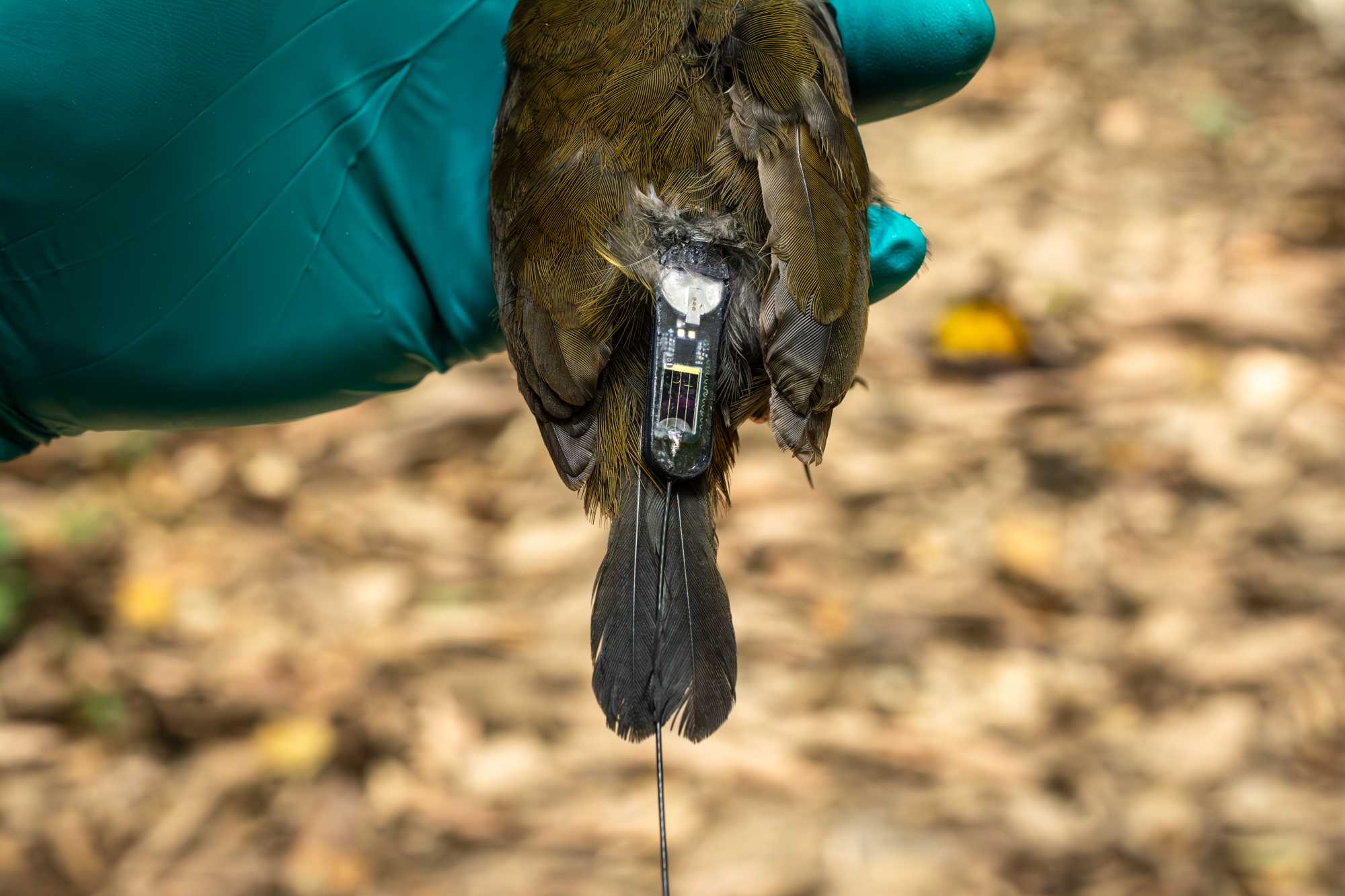
PLACING INDIVIDUAL ID TAGS: CTT LIFE TAGS
- For a subset of captures, CTT light-weight life-tags will be placed on birds that meet weight specifications. Birds of sizes similar to manakins and lower will not be tagged. Birds that will be tagged will include passernies such as woodcreepers, motmots, or foliage-gleaners.
- Tags will weigh 3-5g, obey the 5% body weight criterion, and be attached by either leg loops (stretch magic string, 0.7mm), or 3D printed harnesses (CTT provides these, sizes 1-20) (see video).

MORPHOMETRICS
Measure all body parts indicated in the PROCESSING FORM using a caliper and a ruler as explained in the BIRD MEASURING PROTOCOL.
PHOTOGRAPHS
Hold the bird while a research assistant takes the pictures listed in the PROCESSING SHEET.
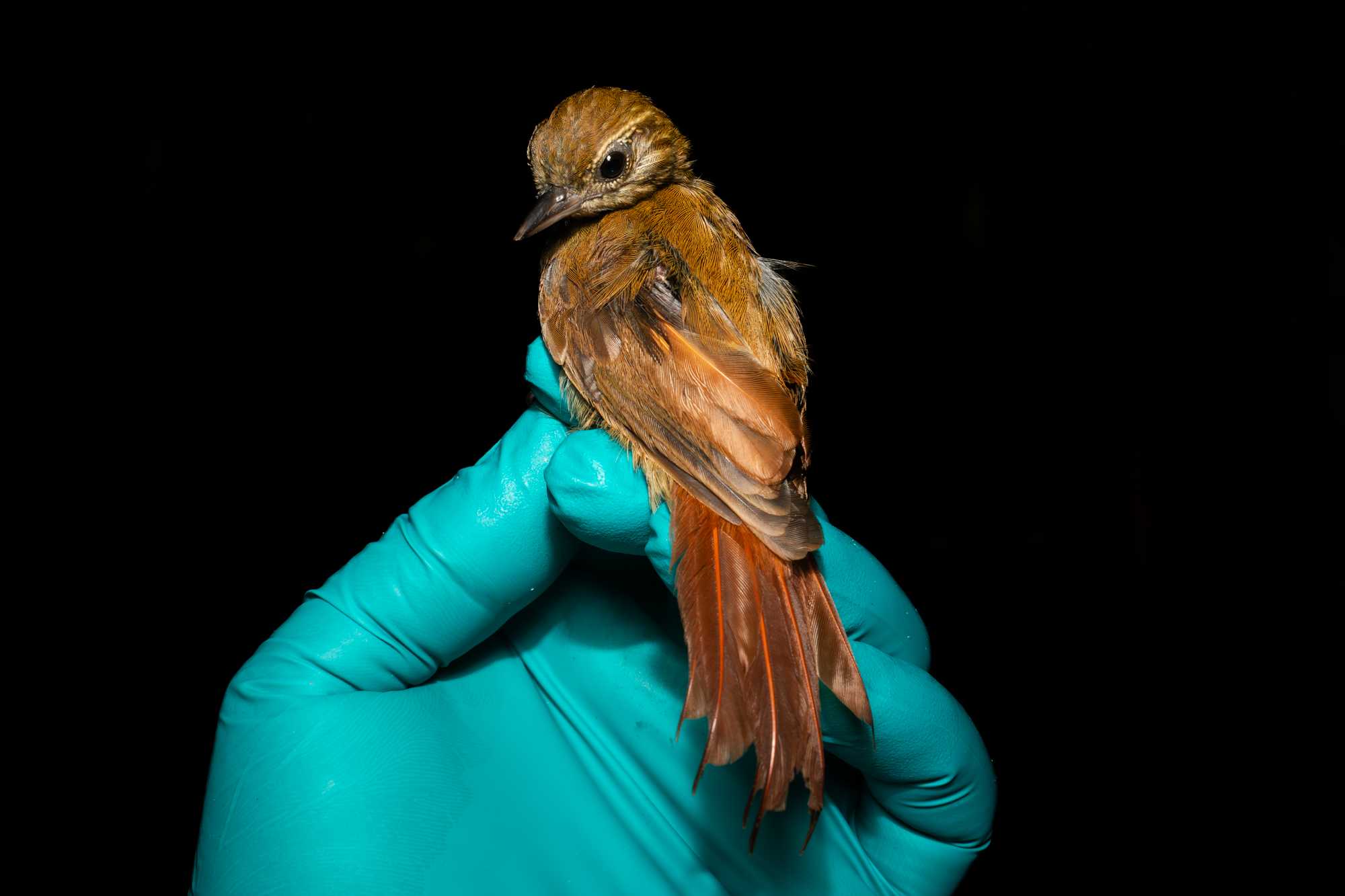


If the bird has a ring, read the identification code aloud so it is recorded
SAMPLING
FECES
Check for FECES inside the holding bag and always collect feces opportunistically during the PROCESSING phase. Use clean forceps or a sterile swab to transfer feces into a designated pre-labelled tube or plastic zip-lock bag.
FEATHER-DNA
Use forceps to gently pull one feather from the tail, and place it inside a plastic bag labelled as ”Feather-DNA” with a number code. If the bird is molting, sample the oldest feathers since they follow a symmetrical molting pattern and altering that symmetry could cause some harm to the bird.
FEATHER-MERC
With the help of a forceps, pluck some plumage from the breast of the animal and place it in a “Feather-merc” sample bag.
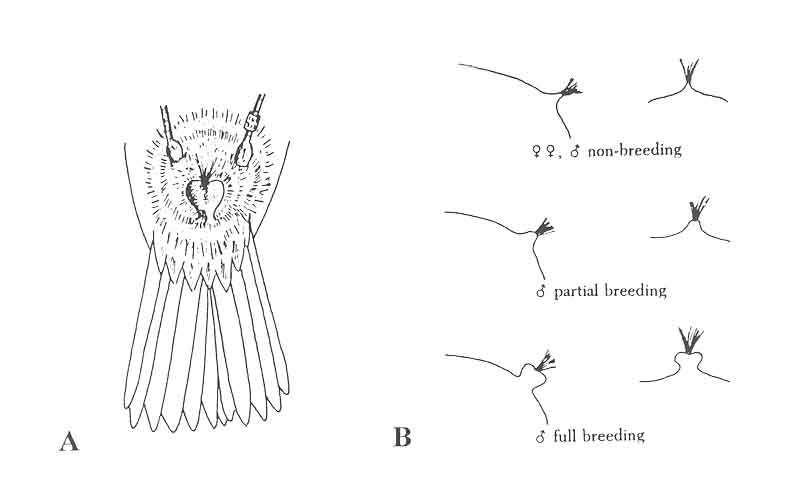
SPERM
Beforehand, verify if the bird is in a reproductive stage as observed from the size and shape of the cloacal protuberance.
To collect sperm samples, males are held in a modification of the standard banding grip, which exposes the cloaca while controlling leg and tail movements, then:
- The cloacal protuberance is massaged gently with fingertips from both hands until the cloaca everts.
- Typically, continued massaging produces a semen sample within a few seconds, and does not visibly stress the male.
- Males that do not quickly produce semen samples generally fail to produce samples at all, so it is unnecessary to continue cloacal massage for longer than approximately 1 minute.
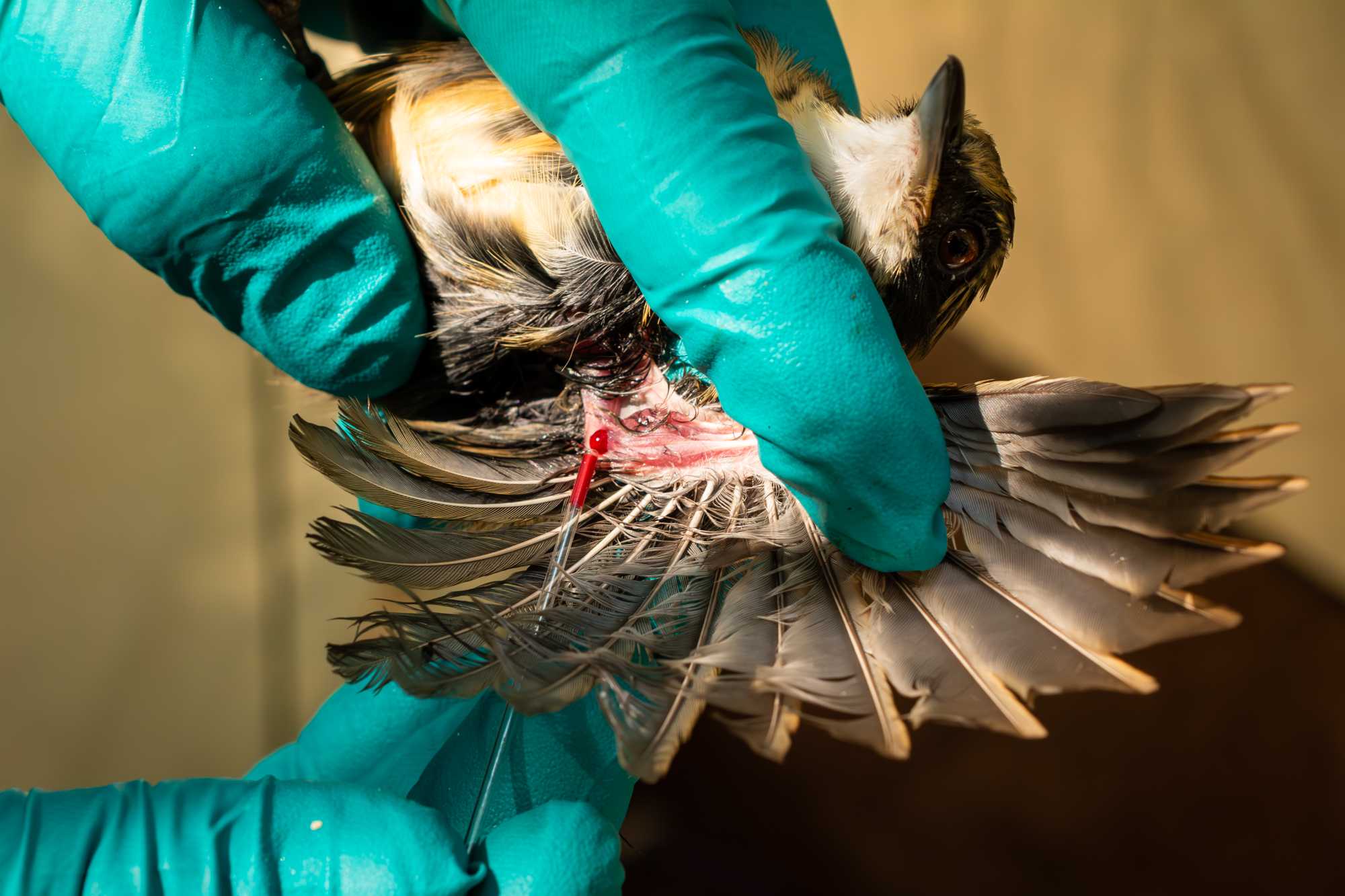
BLOOD
- Bird is manually restrained using the non-dominant hand and its wing extended until its fore and upper arm forms a 90° angle, exposing the ulnar brachial vein.
- The venipuncture site is cleaned with an antiseptic wipe.
- A 25g needle is used to puncture the brachial vein that is visible just underneath the skin as it passes over the medial surface of the elbow.
- Touch the blood drop that forms with the tip of a microhaematocrit capillary tube, fill it ¾ and seal it with clay on both sides .
- A second capillary tube of blood is collected and transfered into a 1.7 mL tube with lysis buffer.
- Small drops of blood are use to create 2 blood smears.
- (OPTIONAL) A drop of blood may be used for glucose and ketone reading.
- Use a cotton ball to put pressure on the venipuncture site and fold back the wing to hold it in place.
- Reopen the wing and check that the venipuncture site is no longer bleeding (1 - 2 minutes). Keep light pressure until bleeding stops.
ECTOPARASITE
Collect any ectoparasites that you might see, if necessary, cut some barbs where the ectoparasites might be hiding in between, and place them inside a 1.7 mL tube containing minimum of 70% ETOH.
Check the following locations:
- base of the wing feathers and the rachis and wattles
- the body by blowing and raising the feathers
- for mites, regions such as the cloaca or furcula
- for hummingbirds, the base of the beak and below the chin

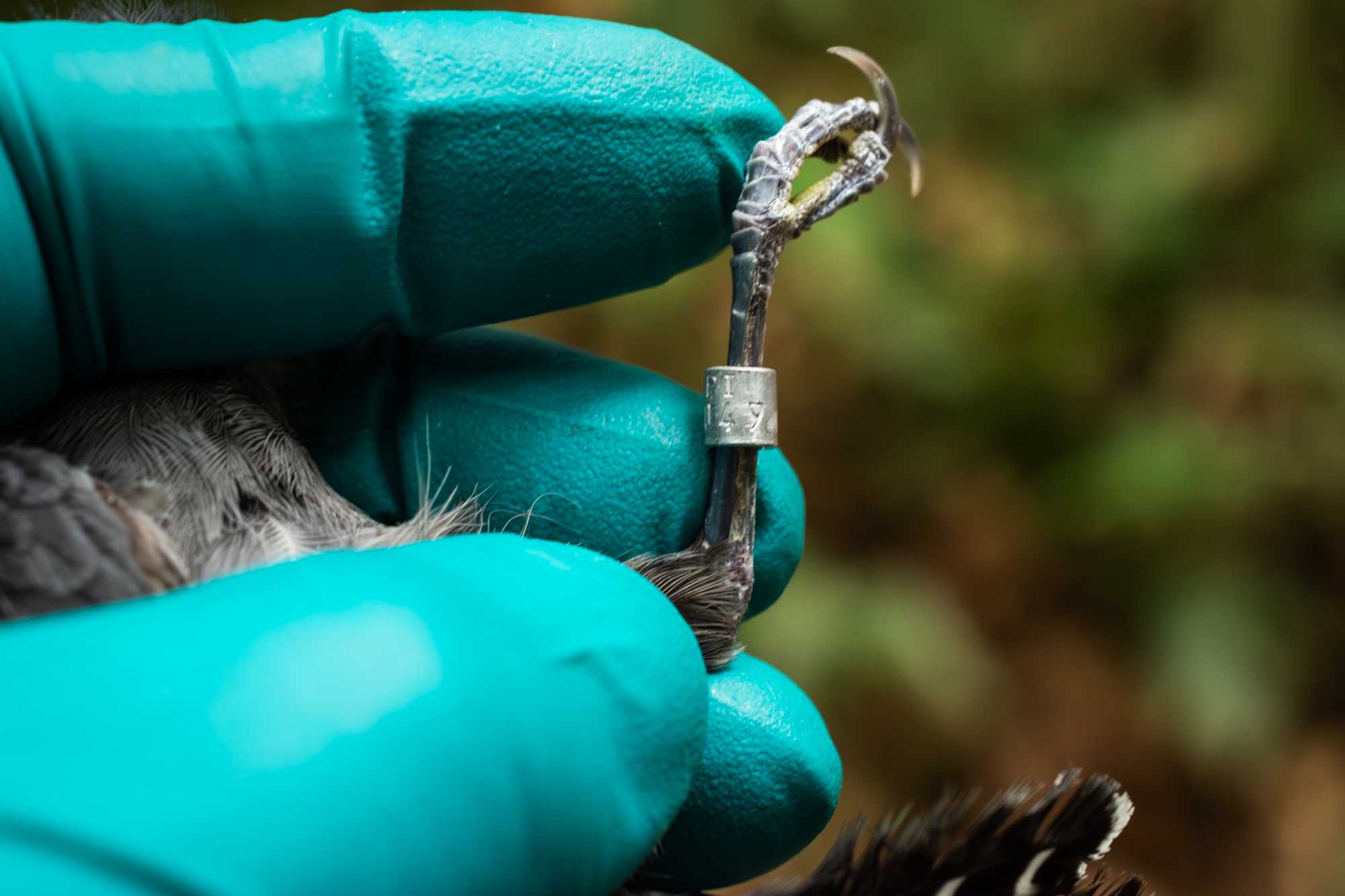
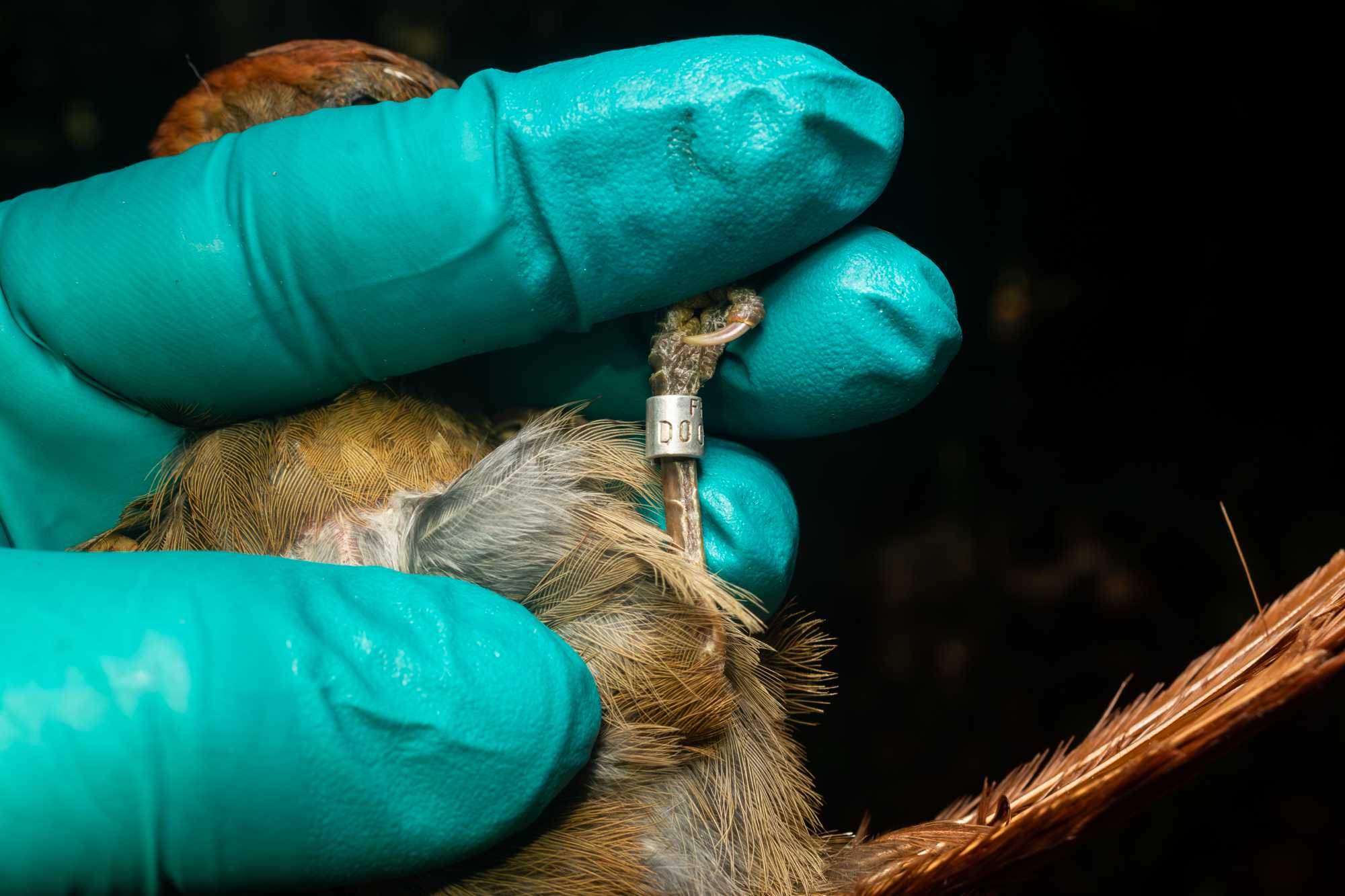
PLACING INDIVIDUAL ID TAGS: BIRD BANDS
- Measure the width of the tarsus with the aid of a caliper, or pre-cut sizing guide tool, and select the corresponding size ring using the size chart
- Use pliers to open the pre-cut ring and place on the bird’s tarsus.
- Close the ring on the bird's tarsus with the appropriately sized banding plier.
- Read aloud the BAND CODE so that it is recorded

RELEASE & REPEAT
RELEASE
Bring animal outside the tent away from nets -> place in hand --> hold bird close to ground-level -> open hand flat and allow bird to fly off. Do NOT shake, toss, or jostle the animal in any way, allow the bird to fly off on its own. The release can be recorded with a video
The RELEASE TIME should be reported on the animal’s processing sheet, along with any other notable observations from release.
CLEANING
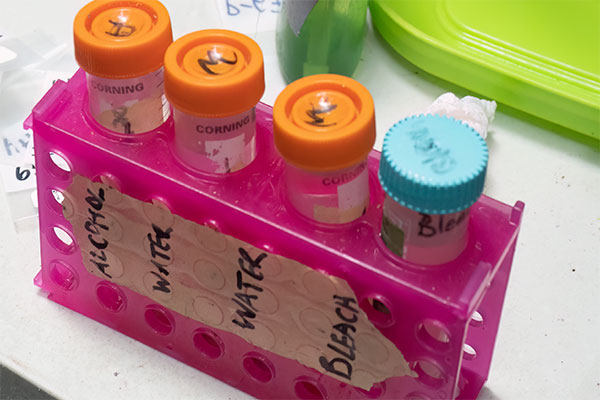
Clean the surfaces that have been in contact with the animal or its secretions by:
- Spraying 10% bleach and then alcohol;
- Disinfect all the tools used during the processing with the sterilization solutions, accordingly protocol: leave submerged in 10% bleach for 5 minutes -> 1st rinse in distilled water -> 2nd rinse in distilled water -> submerge in 70% ethanol
- Dry all tools and surfaces with with clean paper towels or sterile cotton.

Repeat the processing protocol with the next bird, following the order of the discovery.
END SESSION
FIELD WRAP UP
Once all animals have been released the team should:
- End the Voice Recorder after stating the following: full date, location, number of birds processed, names of each team member.
- Securely close the nets. If nets accidentally open during the day or later in the night it will lead to animal injury or death
- Record "NET CLOSE" time
- Clean and pack materials used for processing
- Check, arrange and pack samples
- Return to base camp
FIX BLOOD SMEARS
- Arrange slides face-up on a clean surface and confirm that sample code is clearly visible, if not, trace over to make clear
- Identify a coplin jar with methanol that has no expired
- Open the jar and place smears inside (pairs can be placed back-to-back, MAKE SURE THAT SMEAR IS FACING OUTWARD). Quickly close jar again to prevent the methanol from oxidizing.
- Leave the smears in solution for 5 minutes
- Wearing a pair of gloves, remove each slide and place in an open slide box to dry overnight. Make sure to close the coplin har as quickly as possible to preserve to the methanol
Retrieve the recording from the voice recorder. Name the file using the following convention "YYYY-MM-DD_BIRDsession
Group all the files from point 15.6 to 17.10 into a unique folder named by the date of the capture followed by the capture number.
Check that the laboratory team has all information they need for long-term sample storage
Re-supply and pack materials for the next capture session
SAMPLE SORTING
Organize all samples according to the sample storage protocol.
Unless otherwise indicated by the PI, all other samples should be stored in the freezer until sample intake procedure the next day. NOTE, serum samples must be spun and extracted to a serum storage tube the same night and stored frozen.
BREAK for shower and lunch
Wash all the animal bags used during the capture with detergent and a disinfectant product, such as quaternary ammonium based solutions.
Check any information on the processing sheet, and listen to the voice recording to fill in missing information on the data sheet with a differently colored ink pen (usually red).
Upload the information gathered on the PROCESSING FORMS to ODK. Once submitted, check that the laboratory team has all information they need for long-term sample storage
<img src="https://static.yanyin.tech/literature_test/protocol_io_true/protocols.io.6qpvr4zwpgmk/j87qbx73p1_update.png" alt="First page of the ODK "BirdCapture" form as it appears on the tablet." loading="lazy" title="First page of the ODK "BirdCapture" form as it appears on the tablet."/>
Write a detailed narrative report of the capture session.
Gather pictures and videos from and sort them into designated folders on the project hard drive
Scan the processing sheets and convert them into PDF files, named by the serial bat capture number.

