Glucosylceramidase Beta (GBA) Genotyping
Huw Morris, Nigel Williams
Abstract
This protocol details the steps for GBA genotyping . This protocol has been adapted from the PRoBaND Clinical Consortium (incorporating methods described by Neuman et al., 2009 and Stone et al., 2000) and has been used for all publications for PRoBaND / Tracking Parkinson's describing clinical data and outcomes with respect to GBA status
Before start
Check that you have the correct forward and reverse primers and required materials, supplies and equipment.
Steps
Primer Sequences
Use the following primer sequences:
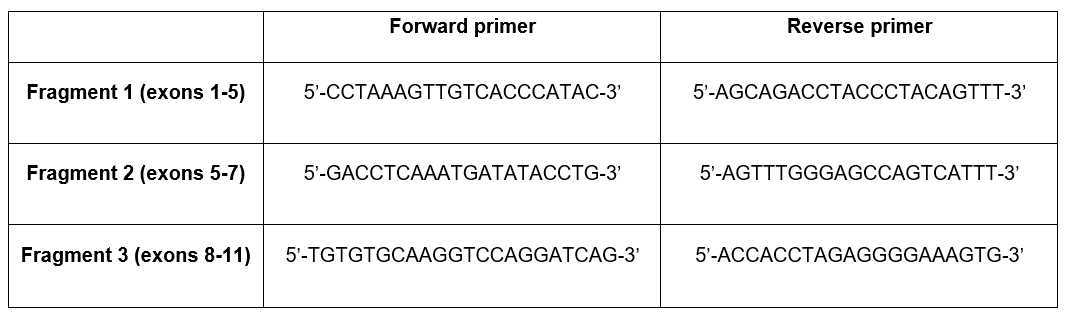
Amplification of the GBA gene
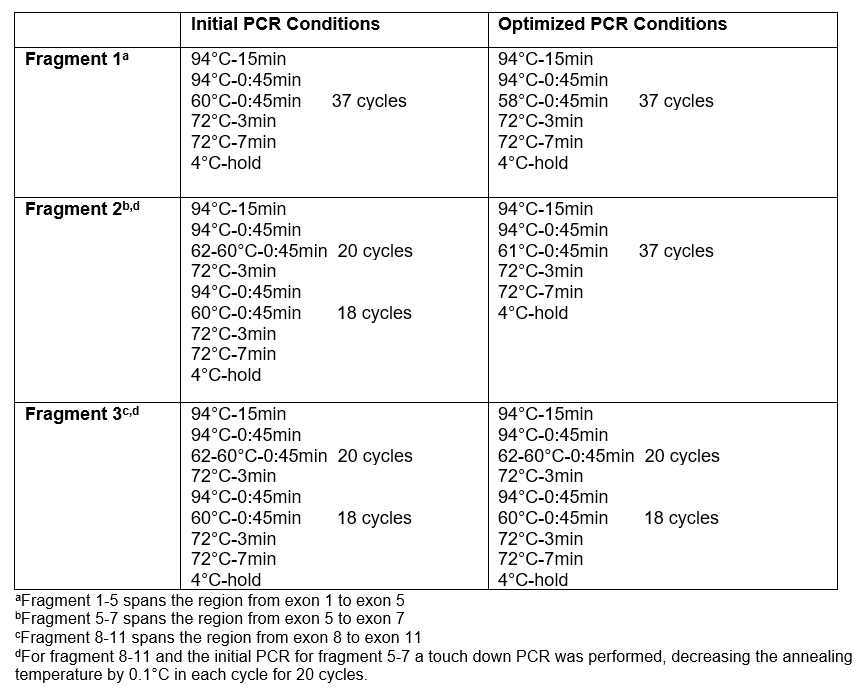
Three different PCR reactions are performed. Refer to Table 2 for a detailed description of the PCR conditions used for each fragment.
In order to avoid amplification of the pseudogene, primer sequences are designed to bind to DNA regions exclusively found within the GBA gene. As an internal control, calculate the size of the PCR products resulting from amplification of the pseudogene for these three fragments. Confirm they are an alternative size to those amplified from GBA .
Amplify three distinct fragments spanning all exonic and most intronic sequences of GBA .
PCR
Prepare the following reagents for the PCR in a total reaction volume of 15µL :
7.5µLfast start PCR master mix (Roche)1µLof 10 µM Forward primer4.5µLDeionised water1µLGenomic DNA template (50 ng/µl)
Run all PCR products on a 1% agarose gel with ethidium bromide and size check to rule out amplification of the GBA pseudogene (GBAP) .
If the initial primers failed or showed an incomplete read then and alternative set of primers can be used:
Table 3.
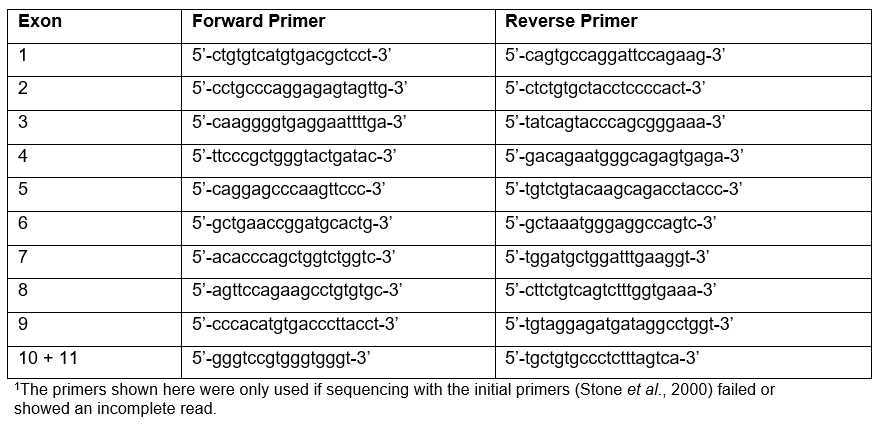
Perform cycle sequencing for each exon and the flanking intronic sequences using the Dye Terminator Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems) and run on an ABI 3700xl genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Sequence all amplicons both in the forward and the reverse direction.
Analyse sequence chromatograms using Sequencher software (Genecodes).
Analyse all exons and the flanking intronic regions when clean, complete sequence reads are obtained.