DNA / RNA isolation from whole blood with universal mini column kit for molecular analysis
Sudhir Bhatia, Gudrun Baersch
Disclaimer
Genekam Biotechnology AG
Duissernstrasse 65a
47058 Duisburg
Germany
Abstract
Whole blood is a simple source of DNA/RNA, however while there are several isolation methods in the literature, they are not capable of isolating pure enough nucleic acid to perform molecular analyses such as PCR. One possible explanation is that a variety of inhibitory substances in blood, such as hemoglobulin, are not eliminated or inactivated during the isolation process. Even in some situations, the mini column becomes plugged with blood, making isolation impossible. This is also true for a variety of commercial kits on the market. As a result, additional steps are required to remove these inhibitor components, which lead to the development of special cumbersome methods or commercial kits designed specifically for blood. We developed a universal mini column DNA/RNA isolation method that can separate DNA/RNA from whole blood without pretreatment or clotting of the small column. The EDTA blood samples or fresh blood samples should be used in this protocol , hence heparin blood samples cannot be used as heparin is known to inhibit the PCR. The extracted nucleic acid is used for performing various molecular assays on biomarkers, viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites such as Plasmodium species. This kit is also useful for detecting blood pathogens such as Plasmodium (a malaria parasite), Babesia, Anaplasma, and more. This approach can also be applied to buccal swabs, nasal swabs, tissue, plasma (serum), lymph nodes, and circulating cells. The user does not need to have multiple kits to perform nucleic acid isolation, which saves money and time.
Before start
-Read the protocol before start.
-Check the contents of the kit.
-Make the heat block on and adjust the temperature as given in the protocol.
-Elution buffer should be pre warmed.
- Only use EDTA blood samples.
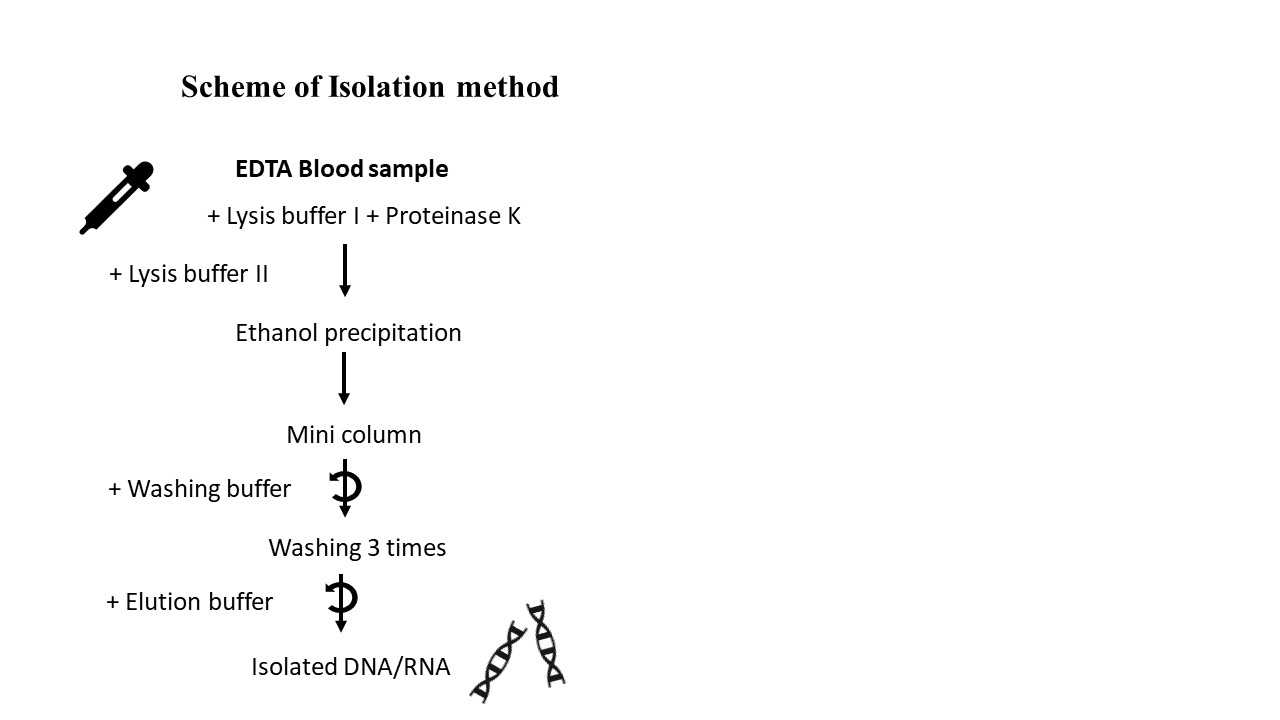
Steps
Add 300µl of Tube A and 15µl of Tube K to the 50µl whole blood sample in the tube.
Use EDTA whole blood sample and avoid heparin whole blood sample as heparin is known to inhibit PCR reaction.
Note: If user has problem, the blood can be diluted with equal volume of PBS to be used as input. Sometimes, one has to use double volume of PBS with blood as input.
Incubate at 56°C for 20-30 minutes. Add to this 400µl of Tube G. Incubate at 70°C for 5 minutes.
Add to this 400µl of molecular ethanol and shake with the vortexer.
Take a mini column in one collection tube and add 600µl of above made solution to this mini column.
Centrifuge this for one minute at 11000rpm. Discard the filtrated fluid.
Add the rest of your remaining fluid in this mini column and repeat the step 5 for centrifuge. Discard the filtrated fluid.
Now add 500µl of Tube B to mini column. Repeat the step 5 for centrifugation and discard the filtrated fluid.
Add 500µl of Tube C to mini column. Repeat the step 5 for centrifugation and discard the filtrated fluid.
Add 200µl of Tube C to mini column. Repeat centrifugation for 3 min at 13000rpm and discard the filtrated fluid.
Centrifuge the mini column for 1 min at 13000rpm to dry the matrix. Discard the used collection tube.
Now put the mini column (filter part) in a new 1.5 ml collection tube.
Add 100µl of Tube E (pre-warmed to 70°C) to the mini column.
Now keep this at room temperature for two minutes.
Centrifuge this at 13000rpm for one minute.
Now the user has fluid in the collection tube. This is isolated Nucleic acid. This can be used to perform different assays. The Nucleid acid should be stored at -20°C for long-term use