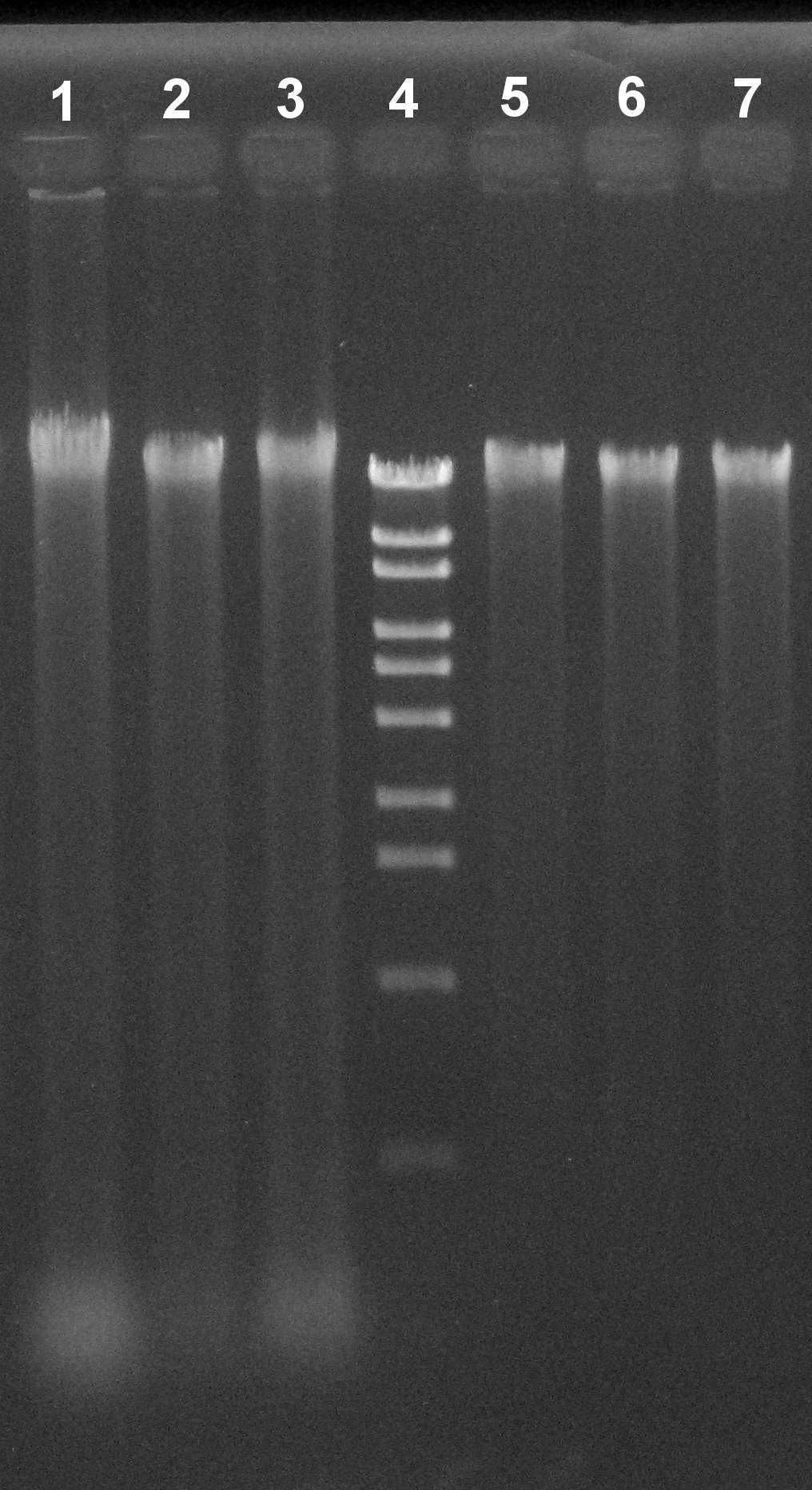
CTAB-based DNA extraction for citrus
Shingo Goto
Abstract
CTAB-based protocols are used for genomic DNA extraction from many kinds of plant species. However, the protocols can’t necessarily completely remove contamination of polysaccharide and RNA in extracted genomic DNA solution. Especially, citrus leaves generally contain high polysaccharide. This protocol is a simple and efficient method for extracting genomic DNA for citrus without contamination of polysaccharide and RNA.
Steps
Buffer preparation
2×CTAB solution: 2% (w/v) CTAB, 100mMTris-HCl pH8.0, 1.4M NaCl, 20mM EDTA pH8.0 [1]* High-salt precipitation solution: 1.2M NaCl , 0.8M Sodium citrate [2]
- 10 mg/ml RNase (Nippon gene)
- Chloroform
- Isopropanol
- 70% Ethanol
- TE buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0 Reference
- Allen GC, Flores-Vergara MA, Krasynanski S et al. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nat Protoc 2006;1:2320–5.
- Chomczynski P, Mackey K. Modification of the TRI Reagent procedure for isolation of RNA from polysaccharide- and proteoglycan-rich sources. Biotechniques 1995;19:492–5.
Homogenization and cell lysis
Preheat 2×CTAB solution to 60°C in water bath. Add 2% (v/v) of 2-Mercaptoethanol to the 2×CTAB solution just before use.
Homogenize 100mg of fresh leaf in liquid Nitrogen. Add 800µL of 2×CTAB solution and completely suspend homogenized leaf. Transfer the suspended solution to 2 ml tube.
Add4µL of 10mg/mL RNase, mix by inversion, and incubate at 37°C for 0h 15m 0s (In order to prevent RNase contamination in laboratory, RNase treatment is conducted before denaturing proteins by chloroform).
Incubate at 56°C for 0h 30m 0s inverting the tube once every 0h 10m 0s.
Chloroform extraction
Add 300µL of Chloroform and mix gently with tube rotator for 0h 15m 0s.
13000rpm,25°C
Transfer supernatant carefully to new 2 ml tube.
Repeat step 6 and 7
Precipitation and wash of DNA pellet
Transfer 600µL of supernatant to new 1.5 ml tube, add 300µL of High-salt precipitation solution, and mix by inversion.
Add 300µL of Isopropanol and mix by inversion.
15000rpm,25°C
Discard and remove supernatant (DNA pellet is often transparent).
Add 1000µL of 70% ethanol and mix by inversion 10 times to wash salts.
15000rpm,25°C
Completely remove supernatant and dry up DNA pellet in air.
Dissolve pallet in 100µL of TE buffer.