Bioinformatics manual for population epigenomics combining whole-genome and target genome sequencing
Odile Rogier, Isabelle Lesur Kupin, Mamadou Dia Sow, Christophe Boury, Alexandre Duplan, Abel Garnier, Abdeljalil Senhaji rachik, Peter Civan, Josquin Daron, Alain Delaunay, Ludovic Duvaux, Vanina Benoit, Erwan Guichoux, Gregoire Le Provost, Edmond Sanou, Christophe Ambroise, Christophe Plomion, Jérôme Salse, Vincent Segura, Jorg Tost, Stéphane Maury
DNA Methylation
Epigenetics
Epigenomics
Methylome
Natural population
Oak
Poplar
Transposon Insertion Polymorphism
SeqCapBis
WGS
WGBS
Abstract
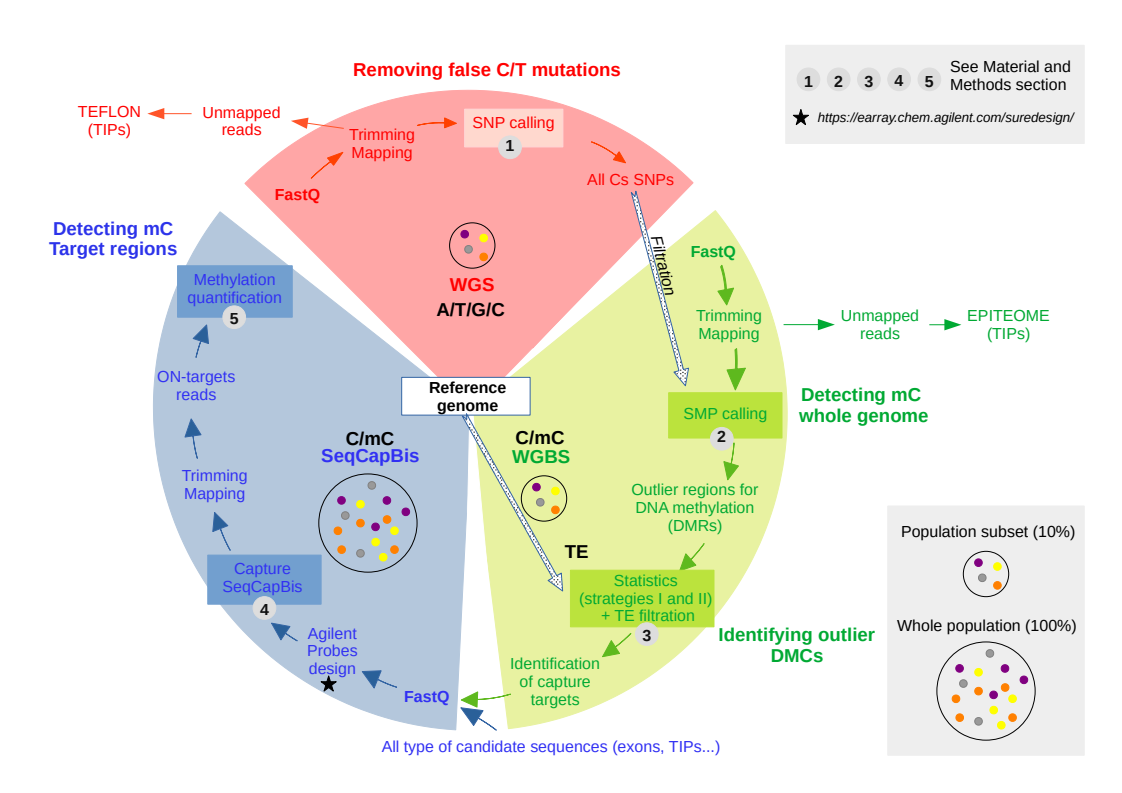
We developed a strategy and a workflow for quantifying epigenetic diversity in natural populations combining whole genome and targeted capture sequencing for DNA methylation.
We first identified regions of highly variable DNA methylation in a representative subset of genotypes representative of the biological diversity in the population by WGBS. We then analysed the variations of DNA methylation in these targeted regions at the population level by Sequencing Capture Bisulphite (SeqCapBis).
Steps
Whole Genome Sequencing - Removing false C/T mutations
A preliminary Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) step was considered for filtering purposes, to prevent C/T Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP) being interpreted as bisulfite conversions of unmethylated sites (i.e. false-positive calls). However, this C/T SNPs identification step is not required to study epigenetics levels along genomes.
Trimming
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| Trimmomatic | NAME |
| http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic | REPOSITORY |
| https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 | DEVELOPER |
| http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic | LINK |
| Version 0.39 | VERSION |
Publication: Bolger et al., 2014
Version: 0.38
Github: https://github.com/usadellab/Trimmomatic
java -Xmx4G -jar trimmomatic.jar PE -threads 12 file_R1.fastq.gz file_R2.fastq.gz
file_trimmed_1.fastq.gz file_unpaired_1.fastq.gz file_trimmed_2.fastq.gz
file_unpaired_2.fastq.gz ILLUMINACLIP:TruSeq3-PE.fa:2:30:10 LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15 MINLEN:35
Mapping
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BWA | NAME |
| Unix | OS_NAME |
| http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/ | REPOSITORY |
| Li, H., Durbin, R. | DEVELOPER |
| https://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997 | LINK |
| 0.7.12- r1039 | VERSION |
Publication: Li H, 2013
Version: 0.7.17
Publication: Tuskan GA et al., 2006.
bwa mem genome.fa file_trimmed_1.fastq.gz file_trimmed_2.fastq.gz -t 12 -M > file.sam
Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea Q. petraea
Oak genome: Quercus robur Haplome V2.3
Publication: Plomion C et al., 2018
Mapping conversion, sorting & statistics
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| SAMtools | NAME |
| https://github.com/samtools/ | REPOSITORY |
| Li et al. | DEVELOPER |
| http://www.htslib.org/ | LINK |
| 1.3.1 | VERSION |
Publication: Danecek et al., 2021
Version: 1.8
Github: https://github.com/samtools/samtools
samtools view -Sb file_trimmed.sam > file_trimmed.bam
samtools sort file_trimmed.bam -o file_trimmed_sorted.bam
samtools flagstat file_trimmed_sorted.bam > file_flagstats.txt
samtools stats file_trimmed_sorted.bam > file_stats.txt
Variant calling
Adjustment for Q. petraea : Digital normalization Q. petraea : Digital normalization
Computational limitations associated with GATK and FreeBayes due to the very deep sequencing in oak (100X on average) necessitated a reduction of the complexity of each dataset. To reduce redundancy within the WGS dataset, we randomly downsampled sequencing reads over genome regions that are over-covered.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| KHMER | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://khmer.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ | REPOSITORY |
| Titus Brown | DEVELOPER |
Publication: Crusoe et al., 2015
Version: 2.1.2
Github: https://github.com/dib-lab/khmer
Parameters: Python-3.6.3
interleave-reads.py file_R1.fastq file_R2.fastq -o file_interleave_R1_R2.fastq
``` _Step2: Digital normalization_
Parameters: Python-3.6.3; -k 20 --> kmer size = 20bp; -C 30 --> maximal coverage; -N 4 -x 4e9 --> 16Gb
normalize-by-median.py -k 20 -C 30 -N 4 -x 4e9 file_interleave_R1_R2.fastq -o file_normalize_by_median_R1_R2.fastq
Parameters: Python-3.6.3
extract-paired-reads.py file_normalize_by_median_R1_R2.fastq -f --output-paired file_diginorm_paired --output-single file_diginorm_single
Duplicates removing
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| picardtools | NAME |
Publication: “Picard Toolkit.” 2019. Broad Institute, GitHub Repository. https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/; Broad Institute
Version: 2.18.2
Github: https://github.com/broadinstitute/picard
java -Xmx16g -jar picard.jar MarkDuplicates I=file_trimmed_sorted.bam O=file_trimmed_sorted_rmdup.bam CREATE_INDEX=true REMOVE_DUPLICATES=true M=file_output.metrics
Variant Caller 1: GATK (Genome Analysis ToolKit)
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| GATK | NAME |
| https://github.com/broadinstitute/gatk | LINK |
| 4.1.7 | VERSION |
Publication: McKenna et al., 2010
Version: 4.0.11.1
Github: https://github.com/broadinstitute/gatk
Poplar genome: Populus trichocarpa v3.1
## HaplotypeCaller
gatk --java-options "-Xmx16G" HaplotypeCaller -R genome.fa -I file_trimmed_sorted_rmdup.bam -ERC GVCF -O file_trimmed_sorted_rmdup.g.vcf
## GenomicsDBImport
gatk --java-options "-Xmx96G -Xms96G" GenomicsDBImport -V file1_trimmed_sorted_rmdup.g.vcf -V file2_trimmed_sorted_rmdup.g.vcf --genomicsdb-workspace-path my_database -L list_Chr+scaff.list --batch-size 50 -ip 500
## GenotypeGVCFs
gatk GenotypeGVCFs -R genome.fa -V gendb://my_database -new-qual true -O all_trimmed_sorted_rmdup_gVCF_GATK.snps.indels.vcf
GATK adjustments for Q. petraea Q. petraea
Version: GATK 3.8
Oak reference genome: Quercus robur Haplome V2.3
Parameters: java 1.8.0_72 ; HaplotypeCaller; GenotypeGVCFs
#HaplotypeCaller
GATK -R haplome_v2.3.fa -T HaplotypeCaller -nct 20 -I sample1_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample2_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample3_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample4_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I
sample5_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample6_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample7_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample8_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample9_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam -I sample9_trimmed_vs_haploV23.bam
--emitRefConfidence GVCF -o gatk_nct20_slurm_1node-c20_snps.vcf
#GenotypeGVCFs
GATK -T GenotypeGVCFs -R haplome_v2.3.fa --variant sample1.vcf --variant sample2.vcf --variant sample3.vcf --variant sample4.
vcf --variant sample5.vcf --variant sample6.vcf --variant sample7.vcf --variant sample8.vcf --variant sample9.vcf --variant sample10.vcf -o gatk_all10samples_SNPs.vcf
Variant Caller 2: samtools / bcftools
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| SAMtools | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://github.com/samtools/samtools | REPOSITORY |
| Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute | DEVELOPER |
| http://www.htslib.org/download/ | LINK |
| 1.8 | VERSION |
Publication: Danecek et al., 2021
Version: 1.8
Github: https://github.com/samtools/samtools
Poplar genome: Populus trichocarpa v3.1
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| bcftools | NAME |
| https://github.com/samtools/bcftools | REPOSITORY |
| https://github.com/samtools/bcftools | LINK |
| 1.12 | VERSION |
Publication: Li H, 2011
Version: 1.8
Github: https://github.com/samtools/bcftools
samtools mpileup -uf genome.fa mapping_file_sort_without_duplicate.bam | bcftools call -mv -Oz > file_bcftools_noduplicate.vcf.gz
bcftools adjustments for Q. petraea Q. petraea
Oak genome : Q. robur haplome V2.3
bcftools version: 1.6
Download: https://sourceforge.net/projects/samtools/files/samtools/1.6/
Variant Caller 3: FreeBayes
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| freebayes | NAME |
| https://github.com/freebayes/freebayes | REPOSITORY |
| Garrison and Marth | DEVELOPER |
Publication: Garrison and Marth, 2012
Version: 1.2.0-2
Github: https://github.com/freebayes/freebayes
Oak genome : Q. robur haplome V2.3
freebayes -f genome.fa all_samples.bam > freebayes_all_samples.vcf
SNP filtering
For poplar, we considered only biallelic intra-nigra SNPs with quality threshold ≥ 30.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| VCFtools | NAME |
| https://vcftools.github.io/man_latest.html | REPOSITORY |
| Adam Auton, Petr Danecek, Anthony Marcketta | DEVELOPER |
Publication: Danecek et al., 2011
Version: 0.1.15
Github: https://vcftools.github.io/man_latest.html
vcftools --vcf all_tool.snps.indels.vcf --out all_filtered_tool.vcf --remove-indels --max-alleles 2 --min-alleles 2 --minQ 30--recode --recode-INFO-all
```For oak, we considered bi-allelic SNPs, depth >= 20, maf >= 30% and <= 70%
SNP identification
Only SNPs identified by at least 2 callers were selected to obtain the final set of SNPs.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| bcftools | NAME |
| https://github.com/samtools/bcftools | REPOSITORY |
| https://github.com/samtools/bcftools | LINK |
| 1.12 | VERSION |
Publication: Danecek P, et al. 2021
Version: 1.8
Github: https://github.com/samtools/bcftools
bcftools index sample1_diginorm_gatk3.8_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz
bcftools index sample1_diginorm_FreeBayes_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz
bcftools index sample1_samtools_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz
bcftools isec -n +3 sample1_diginorm_gatk3.8_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz sample1_diginorm_FreeBayes_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz sample1_samtools_depth20_maf30.vcf.gz -O v -o common_SNPs_sample1_GATK_FreeBayes_samtools_depth20_maf30_bcftools.txt
Selection of C/T SNP
SMPs colocalizing with a C/T SNP (see the WGS and SNP detection section of the manuscript) will be removed at step #7 "SMPs filtering".
Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing - Detecting mC whole genome and Identifying outlier DMCs
Galaxy pipeline
SMPs were identified with the GALAXY (The Galaxy Community, 2022) pipeline (Dugé de Bernonville et al., 2022; Sow et al., 2023).
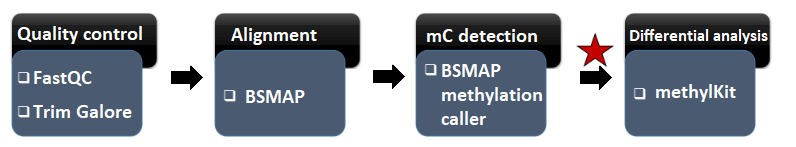
Trimming
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| TrimGalore | NAME |
| https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore | REPOSITORY |
| Felix Krueger | DEVELOPER |
| https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ | LINK |
Publication: Krueger F et al., 2023. FelixKrueger/TrimGalore: v0.4.3.1
Version: v0.4.3.1
Github: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore
Parameters: --paired read1.fastq read2.fastq --clip_R1 10 --clip_R2 30
Mapping
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BSMAP | NAME |
| https://github.com/genome-vendor/bsmap/ | REPOSITORY |
Publication: Xi Y and Li W, 2009
Version: v1.0.0Github: https://github.com/genome-vendor/bsmap/
Parameters: default options
Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea Q. petraea
Oak genome: Quercus robur Haplome V2.3
Methylation calling (SMP)
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BSMAP methylation caller | NAME |
| Greg Zynda | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz | LINK |
| 1.0.0 | VERSION |
Publication: Xi Y and Li W, 2009
Version: v1.0.0Github: https://github.com/genome-vendor/bsmap/
methratio.py --ref ref_genome.fa --zero-meth TRUE --trim-fillin 2 --combine-CpG --min-depth 8 --context all bsmap_sample*.sam
``` **Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea** _Q. petraea_
Oak genome: _Quercus robur_ Haplome V2.3
SMP filtering
Each methylation context (CpG, CHG, CHH) was considered separately.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| methylKit | NAME |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | REPOSITORY |
| Alexander Blume | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | LINK |
| 0.99.2 | VERSION |
Publication: Akalin et al., 2012
Version: Methylkit R package v0.99.2
Github: https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases
Site: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/methylKit.html
Parameters: R (v3.5.1), library(methylKit)
meth.CpG <- unite(CpG, destrand = TRUE, min.per.group = 7L)
meth.CHG <- unite(CHG, destrand = FALSE, min.per.group = 7L)
meth.CHH <- unite(CHH, destrand = FALSE, min.per.group = 7L)
``` **Step2:** Positions corresponding to C/T SNPs were removed.
SNPdat <- read.delim("SNP_file.txt", header = F)
#with SNP_file.txt:
ScaffoldID position allele1 allele2
SNPdat
for (i in 1:19) { cov <- getData(meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov)[,colnames(meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov) == paste0("coverage", i)] cov_filt <- sort(c(which(cov < 7), which(is.na(cov)))) meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov[cov_filt, colnames(meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov) == paste0("numCs", i)] <- NA meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov[cov_filt, colnames(meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtCov) == paste0("numTs", i)] <- NA rm(cov, cov_filt) }
Identification of target regions for the SeqCapBis design
We first grouped SMPs into 1kb sliding windows of 250bp for each methylation context. Following the calculation of the methylation levels in each window, the outlier DMRs were identified using two strategies (see 8.2 and 8.3) with homemade scripts (given as examples). Finally, target sequences correspond to outlier DMRs identified by the two strategies.
Grouping SMPs in windows and DMRs identification
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| methylKit | NAME |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | REPOSITORY |
| Alexander Blume | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | LINK |
| 0.99.2 | VERSION |
Publication: Akalin et al., 2012
Version: 1.18.0
Github: https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases
Site: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/methylKit.html
Parameters: MethylKit package
meth.CpG.window <-tileMethylCounts(meth.CpG.filtind.filtSNP.filtTE.filtCov.filtNA,win.size = 1000, step.size = 250)
meth.CHG.window <-tileMethylCounts(meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtTE.filtCov.filtNA,win.size = 1000, step.size = 250)
meth.CHH.window <-tileMethylCounts(meth.CHH.filtind.filtSNP.filtTE.filtCov.filtNA,win.size = 1000, step.size = 250)
```<Note title="Citation" type="info" >Akalin A, Kormaksson M, Li S, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Figueroa ME, Melnick A, Mason CE 2012 methylKit: a comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r87">https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r87</a></Note>
Strategy I: STANDARD DEVIATION OF THE MEANS
Calculate average C-methylation by averaging the methylation level across all (pre-filtered) cytosines in each window for each individual. Then calculate standard deviation of this average across individuals.
#Identification of windows to remove
percmeth.CpG.window.sd <- rowSds(percmeth.CpG.window, na.rm = TRUE)
sum(percmeth.CpG.window.sd == 0)
# Removal of windows showing the less variable levels of methylation
percmeth.CpG.window <-percmeth.CpG.window[which(percmeth.CpG.window.sd != 0), ] dim(percmeth.CpG.window)
#Identification of the windows associated with the most variable methylation levels
percmeth.CpG.window.sd <- rowSds(percmeth.CpG.window, na.rm = TRUE)
layout(matrix(c(rep(1, 2), 2), nrow = 1))
hist(percmeth.CpG.window.sd, col = "grey", main = "")
bp <- boxplot(percmeth.CpG.window.sd, col = "grey")
length(bp$out)
bp$stats
Strategy II: MEAN OF THE STANDARD DEVIATIONS
For each (pre-filtered) cytosine, calculate the standard deviation of methylation across individuals. Then calculate the mean standard deviation from all cytosines in a window.
dag_window_size=1000
dag_step=250
load("meth.CHG.filtind.filtSNP.filtTE.filtCov.filtNA.Rdata")
y<-x[,c("chr","start","end","strand")]
for (i in 1:length(colnames(x)[colnames(x) %like% "coverage"])){ # To recover the C/coverage values
j=5+3*(i-1)
print(paste0(j," ",j+1))
y[,paste0("in",i)]<-x[,j+1]/x[,j]
}
yy<-x[,c("chr","start","end","strand")]
rm(x)
z<-rowSds(as.matrix(y[,5:ncol(y)]),na.rm=TRUE) # Calculate row standard deviations
yy$STDEV<-z
rm(z)
y<-yy
rm(yy)
# Do last adaptations and launch
dag_window=dag_window_size/dag_step
colnames(y)<-c("CHR","START","END","STRAND","STDEV")
y$MEAN<-(y$START+y$END)/2
y$CHR<-gsub("Chr0","Chr",y$CHR,perl=TRUE)
y$WINDOW<-floor(y$MEAN/dag_step)+1
stdev_counts = data.table(
CHR = character(),
WIN = numeric(),
POS = numeric(),
STDEV = numeric()
)
count=0
for (i in unique(y[y$CHR %like% "Chr" | y$CHR %like% "scaffold",]$CHR)){
window_size=dag_window_size
step=dag_step
#i<-paste0("Chr",i)
z<-y[y$CHR==i,]
min=0
max=max(z$WINDOW)
#print(paste(i,min,max,min(z$MEAN),max(z$MEAN)))
count=count+1
print(paste(i,min,max,min(z$MEAN),max(z$MEAN),count,length(unique(y[y$CHR %like% "Chr" | y$CHR %like% "scaffold",]$CHR))))
zz<-data.frame(matrix(ncol=2,nrow=max*step))
colnames(zz)<-c("MEAN","STDEV")
zz$MEAN<-rownames(zz)
zz[zz$MEAN %in% z$MEAN,]$STDEV<-z[z$MEAN %in% zz$MEAN,]$STDEV
# Sliding window
total <- nrow(zz)
if (max(z$MEAN)<window_size){ # Adapted to avoid problems with scaffolds smaller than window_size
spots <- 1
}
else {
spots <- seq(from=1, to=(total-window_size), by=step)
}
if (spots[length(spots)]<=total-window_size){spots<-c(spots,(spots[length(spots)]+step))} # Adapted to recover the last bits inside smaller window
result <- vector(length = length(spots))
for(j in 1:length(spots)){
if (j%%50000==0){print(paste(j,length(spots)))}
if ((spots[j]+window_size)>=total){window_size=(total-spots[j])} # Adapted to recover the last bits inside last smaller window
result[j] <- mean(zz[spots[j]:(spots[j]+window_size-1),"STDEV"],na.rm=TRUE)
}
stdev_counts<-rbind(stdev_counts,data.frame(CHR=i,WIN=1:length(spots),POS=spots,STDEV=result))
}
x<-stdev_counts
write.table(x,file=paste0(save_file_name))
Outlier threshold
The threshold for DMRs is defined as (Q3+1.5*(Q3-Q1)) where Q1 and Q3 are the first and third quartiles (i.e. the threshold is not defined by a percentile, but instead depends on the length of the boxplot box)
*** Strategy I**
Parameters: Python 3.7
#$Id$
###run with python get_threshold_over_all_windows_calc1.py OUTPUT_FILE_from_calc1_get_mean_and_stdv_for_each_window.py > threshold_calc1.txt
import os
import re
import string
import sys
import glob
import numpy
file1 = sys.argv[1]
file1_stream = open(file1)
list_of_means = []
for line1 in file1_stream.readlines():
if (line1.count('start') == 0):
line1 = line1.replace('\n','')
splitted_line1 = line1.split('\t')
scaffold = splitted_line1[0]
start = splitted_line1[1]
end = splitted_line1[2]
mean = splitted_line1[13]
mean = float(mean)
list_of_means.append(mean)
list_of_means.sort()
nbre_de_means = len(list_of_means)
##XXX corresponds to the first half of the dataset
##YYY corresponds to the second half of the dataset
Q1 = numpy.median(list_of_means[:XXX])
Q3 = numpy.median(list_of_means[YYY:])
##for CHH context, hreshold = (Q3 + 3*(Q3- Q1))
threshold = (Q3 + 1.5*(Q3- Q1))
threshold = round(threshold,5)
print 'threshold = ',threshold
``` *** Strategy II**
Parameters: Python 3.7
#
###run with python get_threshold_stdv_over_all_windows_calc2.py OUTPUT_FILE_from_get_stdv_between_individuals_for_each_window_calc2.py > threshold_calc2.txt
import os import re import string import sys import glob import numpy
file1 = sys.argv[1] file1_stream = open(file1) list_of_stdv = []
for line1 in file1_stream.readlines(): if (line1.count('start') == 0): line1 = line1.replace('\n','') splitted_line1 = line1.split('\t') scaffold = splitted_line1[0] start = splitted_line1[1] end = splitted_line1[2]
stdv = splitted_line1[4]
stdv = float(stdv)
list_of_stdv.append(stdv)
list_of_stdv.sort() nbre_de_stdv = len(list_of_stdv) ##XXX corresponds to the first half of the dataset ##YYY corresponds to the second half of the dataset Q1 = numpy.median(list_of_stdv[:XXX]) Q3 = numpy.median(list_of_stdv[YYY:])
##for CHH context, hreshold = (Q3 + 3*(Q3- Q1)) threshold = (Q3 + 1.5*(Q3- Q1)) threshold = round(threshold,5)
print 'threshold = ',threshold
Identification of capture targets
Target sequences correspond to outlier DMRs identified by the two strategies. This is a two-steps strategy where the 3 contexts are first merged and, then, sequence redundancy between the three methylation contexts is removed.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| bedtools | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://ubuntu.pkgs.org/20.04/ubuntu-universe-amd64/bedtools_2.27.1+dfsg-4ubuntu1_amd64.deb.html | LINK |
| 2.27.1 | VERSION |
Publication: Quinlan AR and Hall IM, 2010
Version: 2.27.1
Github: https://github.com/arq5x/bedtools2
Parameters: intersect, merge
SeqCapBis - Detecting mC Target regions
Agilent Probes design and sequencing
A set of 120 bp probes was selected to capture 18 Mb of each genome (Agilent, https://earray.chem.agilent.com/suredesign/)..) The targeted regions corresponded to the regions identified as differentially methylated between populations. Custom targeted genome bisulfite sequencing was performed with SureSelect XT Methyl-Seq Target Enrichment (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
For poplar, in total, 17.84 Mb of sequence corresponding to the 25,434 DMRs was covered by 339,658 probes. Regarding oak, a set of 140,249 probes (120 bp) was designed by Agilent to cover 16.15 Mb DMRs.
Trimming
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| TrimGalore | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore/releases | LINK |
| 0.6.5 | VERSION |
Publication: Krueger F et al., 2023. FelixKrueger/TrimGalore: v0.6.5
Version: 0.6.5
Github: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore
trim_galore input_R1.fastq.gz input_R2.fastq.gz --paired ADAPTER1 -a2 ADAPTER2 -o output_directory --gzip -j {threads}
Quality control
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| FastQC | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Simon Andrews | DEVELOPER |
| https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ | LINK |
| 0.11.9 | VERSION |
Publication: Andrews, S. (2010). FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data [Online]. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
Version: 0.11.9
Github: https://github.com/s-andrews/FastQC
fastqc trimmed_reads.fq.gz -o fastQC_output_directory -t {threads}
Mapping
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BsmapZ | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz | LINK |
| 1.1.3 | VERSION |
Publications:
- Xi Y, Li W, 2009
* Zynda G. 2018. BSMAPz. https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz Version: 1.1.3Citation
Xi Y, Li W 2009 BSMAP: whole genome bisulfite sequence MAPping program. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-232
Github: https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz
Poplar genome: Populus trichocarpa v4.1
bsmapz -a fileR1.fq.gz -b fileR2.fq.gz -o {output.out} -d mapped_file.bam -d ref_genome.fa -p threads
``` **Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea** _Q. petraea_
Oak genome: _Quercus robur_ Haplome V2.3
Duplicate Removing
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| samtools | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://sourceforge.net/projects/samtools/files/samtools/1.11/ | LINK |
| 1.11 | VERSION |
Publication: Danecek et al., 2021
Version: 1.11
Github: https://github.com/samtools/samtools
Parameters: stat, fixmate, sort, markdup
Poplar genome: Populus trichocarpa v4.1
samtools stats sample_bsmapz_sorted.bam -r ref_genome.fa -@ {threads} > sample.statics
samtools fixmate -@ {threads} -O BAM -m sample_bsmapz_sorted.bam sample_fixmate.bam
samtools sort -@ {threads} -O BAM sample_fixmate.bam -o sample_fixmate_sort.bam
samtools markdup -r ref_genome.fa -@ {threads} -s -f sample.statics sample_fixmate_sort.bam sample_fixmate_sort_temp.bam
``` **Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea** _Q. petraea_
Oak genome: _Quercus robur_ Haplome V2.3
Detection of methylated cytosines (mC)
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BsmapZ | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz | LINK |
| 1.1.3 | VERSION |
Publications:
- Xi Y and Li W, 2009.
* Zynda G. 2018. BSMAPz. https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz Version: 1.1.3Citation
Xi Y, Li W 2009 BSMAP: whole genome bisulfite sequence MAPping program. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-232
Github: https://github.com/zyndagj/BSMAPz
Poplar genome: Populus trichocarpa v4.1
Parameters: methratio.py, python 2.7, samtools 1.11, pysam 0.16.0.1
python methratio.py sample.dedup.bam -o meth_sample.txt -d ref_genome.fa -N {threads} -I
``` **Mapping adjustments for Q. petraea** _Q. petraea_
Oak genome: _Quercus robur_ Haplome V2.3
10X sequencing filtering
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| methylKit | NAME |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | REPOSITORY |
| Alexander Blume | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | LINK |
| 0.99.2 | VERSION |
Publication: Akalin A et al, 2012.
Version: 1.18.0
Parameters: MethylKit package
Github: https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases
Site: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/methylKit.html
SeqCapBis_CHG = methRead(location = path_to_the_files, sample.id = sample.ids, assembly = "quercus", mincov = 10, context = "CHG", treatment = rep(0,10))
Splitting context
We set up a homemade bash script (splitting.sh) to obtain methylation files for each sample in the three contexts (CG, CHG and CHH).
#!/bin/bash
# Splitting context:
usage()
{
cat << EOF
usage: $0 <options>
splitting context.
OPTION:
-h show this Help message.
-o Output.
-i Input.
EOF
}
# Get options
while getopts "ho:i:" OPTION
do
case $OPTION in
h) usage; exit 1;;
o) output=$OPTARG;;
i) input=$OPTARG;;
?) usage; exit;;
esac
done
# Check that all options were passed
if [[ -z $output ]] || [[ -z $input ]]
then
printf "\n=========================\n ERROR: missing options\n=========================\n\n"
usage
exit 1
fi
#in_file = snakemake.input["isoforms"]
#out_file = snakemake.output["plot"]
# Fail on the first error
set -e
######################
file=$(echo $output|rev|cut -d "/" -f 1 |rev)
path=$(echo $output|rev|cut -d "/" -f 2- |rev)
for context in "CHH" "CG" "CHG"; do
awk "NR<=1 || \$4~/$context/" $input > $path/$context-$file ;
done
Methylation quantification
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| methylKit | NAME |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | REPOSITORY |
| Alexander Blume | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases | LINK |
| 0.99.2 | VERSION |
Publication: Akalin A et al, 2012.
Version: 1.18.0
Parameters: MethylKit package
Github: https://github.com/al2na/methylKit/releases
Site: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/methylKit.html
# Read methylation using methylkit function methRead
myobj <- methRead(location = files, sample.id = sample_id, assembly = "populus tricharpa v3.1", mincov = 1, context = context,treatment = rep(0, length(files)), pipeline = list(fraction=TRUE, chr.col=1, start.col=2, end.col=2, coverage.col=6, strand.col=3, freqC.col=5 ))
# Concatenate all samples tables into one unique table
finalFrame <- mergeMethylkitOutput(myobj)
#Write the final table as a csv2 file
write.csv2(finalFrame,file = table,)
# head(myobj)
# plots for statistcs and coverage simple :
pdf(file = XXX)
getMethylationStats(myobj[[1]],plot=TRUE,both.strands=FALSE)
getCoverageStats(myobj[[1]],plot=TRUE,both.strands=FALSE)
dev.off()
Transposon insertion polymorphisms (TIPs)
Trimming
Eliminate unwanted or irrelevant parts of the read. Data trimming may include removing low quality bases or adapters used during sequencing.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| TrimGalore | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Felix Krueger | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore/releases/ | LINK |
| 0.6.5 | VERSION |
#Trim the paired sequences
trim_galore -q 30 --paired -o paired_1.fastq paired_2.fastq
Detection of TIPs on whole genome sequencing (WGS) data with TEFLoN
Mapping
Alignment of DNA sequences to a reference genome.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BWA | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Heng Li | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/lh3/bwa/releases/ | LINK |
| 0.7.17 | VERSION |
#Index Genome
bwa index genome_ref.fa
#Align
bwa mem -Y genome_ref.fa paired_trimmed_1.fastq paired_trimmed_2.fastq > whole.sam
Extracting unmapped reads
Search for TIPs from reads not aligning with the reference genome. It is interesting to choose non-mapped sequences, because we hypothesize that the insertion of a transposable element is one of the reasons which prevented the alignment of certain reads to their reference genome.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| samtools | NAME |
| https://github.com/samtools/samtools | REPOSITORY |
| https://github.com/samtools/samtools | LINK |
| 1.12 | VERSION |
#From SAM2BAM
samtools view -S -b whole.sam -o whole.bam
#Extract Unmapped reads
#An unmapped read whose mate is mapped.
samtools view -u -f 4 -F264 whole.bam > tmps1.bam
#Both reads of the pair are unmapped
samtools view -u -f 12 -F 256 whole.bam > tmps2.bam
#merge
samtools merge unmapped.bam tmps1.bam tmps2.bam
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| BamToFastq | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Maxime U Garcia | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/nf-core/bamtofastq/releases/ | LINK |
| 1.3.5 | VERSION |
#Extract the reads in FASTQ format (paired)
bamToFastq -bam unmapped.bam -fq1 unmapped_reads1.fastq -fq2 unmapped_reads2.fastq
TIPs detection
Search for TIPs from reads not aligning with the reference genome. It is interesting to choose non-mapped sequences, because we hypothesize that the insertion of a transposable element is one of the reasons which prevented the alignment of certain reads to their reference genome.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| TEFLoN | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Jeffrey Adrion | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/jradrion/TEFLoN | LINK |
| 0.4 | VERSION |
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| RepeatMasker | NAME |
| Linux | OS_NAME |
| Robert Hubley | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/rmhubley/RepeatMasker | LINK |
| 4.1.2 | VERSION |
WD="path/to/working/_directory"
PREFIX="prefix_you_want"
##For each samples
python teflon_prep_custom.py -wd ${WD}reference -g genome_ref -l path/to/TE_LIBRARY -p ${PREFIX}
bwa index ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_MP/${PREFIX}.mappingRef.fa
bwa mem -Y ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_MP/${PREFIX}.mappingRef.fa ${READS1} ${READS2} > ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.sam
samtools view -Sb ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.sam | samtools sort -o ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.sorted.bam
samtools index ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.sorted.bam
#Run Teflon
#For each samples
python teflon.v0.4.py -wd ${WD} -d ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_TF/ -s path/to/samples -i unique_ID -l1 family -l2 class
#Teflon collapse
##Only once
python teflon_collapse.py -wd ${WD} -d ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_TF/ -s path/to/samples -n1 minimum_reads_to_support_TE_in_one_sample -n2 minimum_reads_to_support_TE_in_all_samples
#Teflon Count
#For each samples
python teflon_count.py -wd ${WD} -d ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_TF/ -s path/to/samples -i unique_ID
#Teflon genotype
##Only once
python teflon_genotype.py -wd ${WD} -d ${WD}reference/${PREFIX}.prep_TF/ -s path/to/samples -dt pooled
Detection of TIPs on whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) data with epiTEome
Mapping and extracting unmapped reads
Alignment of DNA sequences to a reference genome. Search for TIPs from reads not aligning with the reference genome. We choose non-mapped sequences, because we hypothesize that the insertion of a transposable element is one of the reasons which prevented the alignment of certain reads to their reference genome.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| Bismark | NAME |
| Felix Krueger | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/FelixKrueger/Bismark/ | LINK |
| 0.19.0 | VERSION |
bismark_genome_preparation --verbose genome_ref.fa
bismark --genome genome_ref.fa paired_trimmed_1.fastq paired_trimmed_2.fastq --un
TIPs detection
Search for TIPs from reads not aligning with the reference genome. It is interesting to choose non-mapped sequences, because we hypothesize that the insertion of a transposable element is one of the reasons which prevented the alignment of certain reads to their reference genome.
Software
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| epiTEome | NAME |
| Josquin Daron | DEVELOPER |
| https://github.com/jdaron/epiTEome | LINK |
| 1.0 | VERSION |
idxEpiTEome.pl -l 100 -gff genome_ref.gff -t /path/to/TE_LIBRARY -fasta genome_ref.fa
epiTEome.pl -gff genome_ref.gff -ref genome_ref.epiTEome.masked.fasta -un unmapped_reads.fastq -t /path/to/TE_LIBRARY

