Autofluorescence Microscopy Data Acquisition
Elizabeth Neumann, Jamie Allen, Jeff Spraggins, Maya Brewer, Mark De Caestecker, Danielle Gutierrez, Angela R.S. Kruse, Katerina V Djambazova, Heath Patterson
Abstract
Scope:
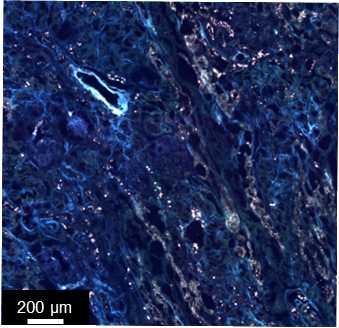
Obtain autofluorescence microscopy images of tissues.
Expected Outcome:
An RGB autofluorescence microscopy image of the tissue section that enables visualization of tissue morphology as well as registration and correlation of different imaging modalities on a pixel by pixel basis.
Steps
If sectioned tissue is frozen, return to room temperature (~20oC) within a vacuum desiccator (~30 min), otherwise proceed directly to step 2.
Place microscope slide within adapter and insert into the Zeiss AxioScan Z1 Slide Scanner. Be sure to orient the slide with the label facing downward in the adapter.
For registration with IMS, match the orientation of the slides within the Zeiss adapter and the Bruker two-slide holder.
Open Zeiss Zen software
Change the file storage location to the appropriate local folder
Select appropriate scan profile template (e.g. HuBMAP-preAF_10x-LED-latest.czspf)
Name each slide with the date, donor, and modality information
Perform a preview scan of each slide
Define the imaging region that includes the tissue using the Tissue Detection Wizard. This can be found using the gear icon on the right of the Scan Profile selection for each slide. Outline the imaging region area using the polygon, square, circle, or spline tool.
Press 'Start Scan' to begin image acquisition.
The method will automatically begin generating by a focus map of the imaging region using the following parameters:
Coarse focusing of the tissue is performed using the following parameters:
EGFP filter set (peak emission 509 nm) as focus reference channel
~4 ms exposure time
~50-90% LED light source
Software autofocus
Default quality
Full search
Coarse sampling
Z-positions from 3900um to 4300um using ~14.24 µm step size
Coarse focus is performed with ~8 support points.
Note that exposure times, light source energy, and number of support points may vary based upon tissue type, age of LED light source, and tissue section size and quality.
Fine focusing of the tissue is performed using the following parameters:
EGFP filter set (peak emission 509 nm) as focus reference channel
~4 ms exposure time
~50-90% LED light source
Software autofocus
Default quality
Full search
Medium sampling
Z-range of 30um using ~7.12 µm step size.
Fine focus is performed with ~6 support points.
Note that exposure times, light source energy, and number of support points may vary based upon tissue type, age of LED light source, and tissue section size and quality.
The method will acquire a tiled brightfield and autofluorescence image using the following channel parameters:
DAPI (blue, reference channel)
\~50-90% LED light source
\~20 ms exposure time
EGFP (ex. 450-490 nm; em. 500-550, green)
\~50-90% LED light source
\~60 ms exposure time
DsRed (ex. 538-562 nm; em. 570-640, red)
\~50-90% LED light source
\~250 ms exposure time
Resulting czi files can be visualized using Zen or QuPath softwares.
If desired, images can be exported via Zen software under the Processing tab using the Image Export method in formats including Tiff, PNG, and JPEG.