Short HPLC gradient method for 20-Hydroxyecdysone (20E) quantification in malaria vectors
Oswald Yedjinnavenan Djihinto, Luc S. Djogbenou, Luisa Nardini, Armorel Van Eyk, Lizette L. Koekemoer
Abstract
Ecdysteroids are arthropod steroid hormones that are primarily involved in insect moulting. In arthropod vectors, especially in mosquitoes, ecdysteroids of interest include mainly ecdysone (E) and 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E). These two compounds are involved in several important biological processes. Targeting these compounds and their regulatory pathways could lead to the characterisation of novel genetic tools towards implementing new malaria control strategies. To date, there are two main methods for quantifying E and 20E. These methods include an enzymatic method (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)) and a chromatographic method (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)). However, for ecdysteroids quantification, the HPLC methods available in literature go from 30 minutes to one hour. Here, we developed a short HPLC gradient method for 20-hydroxyecdysone quantification in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae . This method was developed specifically when sample material is limited as well as to save time and cost.
Before start
The HPLC system pump should be purged prior to usage to remove air bubbles. * The autosampler (if available) should be flushed to clean the injection system.
- The column should be equilibrated with the mobile phases (starting conditions) for at least 30 min prior to initiating analyses.
Steps
Instrument
Analytical HPLC separations were performed on the Flexar LC system (Perkin Elmer) with a UV/Vis Detector and a Phenomenex Kinetex RP C18–5 µm column (4.6 x 150 mm).
The detection wavelength was set at 254 nm.
The flow rate was 1 ml/minute.
The mobile phase included gradient elution with Methanol:Acetonitrile (85-15) and 0.5% acetic acid-Water for 16 minutes (See the chromatographic conditions).
The injection volume was 1 µL.
Chromatographic conditions
Column: Phenomenex, Kinetex® 5 µm C18, 100 Å, 150 x 4.6 mm
Column temp: 20°C
Mobile phase A: 85:15:Methanol:acetonitrile (v:v)
Mobile phase B: 0.5% acetic acid: 95% HPLC grade water (v:v)
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Detector: UV at 254 nm
Injection volume: 1 µL
Run time: 16 min
Gradient profile: (ramps are linear)
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| % Mobile phases | |||
| Time (min) | Flow (ml/min) | A (MeOH-ACN) | B H2O – 0.5% acetic acid |
| 0.5 | 1 | 10 | 90 |
| 10 | 1 | 70 | 30 |
| 6 | 1 | 10 | 90 |
Mobile phase preparation
Mobile phase A: 85:15 Methanol:acetonitrile (v:v)
Mobile phase B: 0.5% acetic acid: water (v:v)
Preparation of mobile phase A
Mobile phase A was prepared by mixing methanol and acetonitrile to have a ratio of 85:15.
For example, to prepare 1L , combine 850mL of methanol, 150mL of acetonitrile and mix well.
Preparation of mobile phase B
Mobile phase B was prepared by adding glacial acetic acid to water at a ratio of 0.5% glacial acetic acid.
For example, to prepare 1L , combine 5mL of glacial acetic acid and 995mL of MilliQ water and mix.
Standard samples preparation
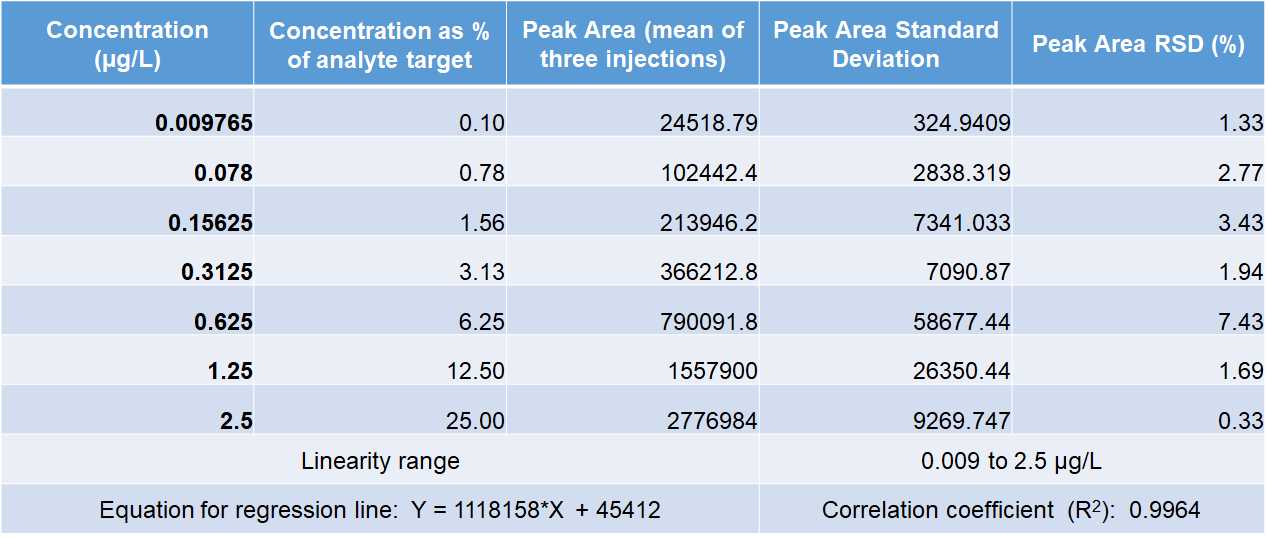
The standard samples used were prepared from the 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) stock solution at (5 µg/L).
All samples were prepared in methanol to a final volume of 500 µL.
Make three injections for each standard sample.
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (µg/L) | Final volume (µL) | Volume of 20E solution (5 µg/L) in µL | Volume of methanol to be added (µL) |
| 2.5 | 500 | 250 | 250 |
| 1.25 | 500 | 250 | 250 |
| 0.625 | 500 | 250 | 250 |
| 0.3125 | 500 | 250 | 250 |
| 0.156 | 500 | 250 | 250 |
| 0.078 | 500 | 7.8 | 492.2 |
| 0.0097 | 500 | 0.97 | 499.03 |
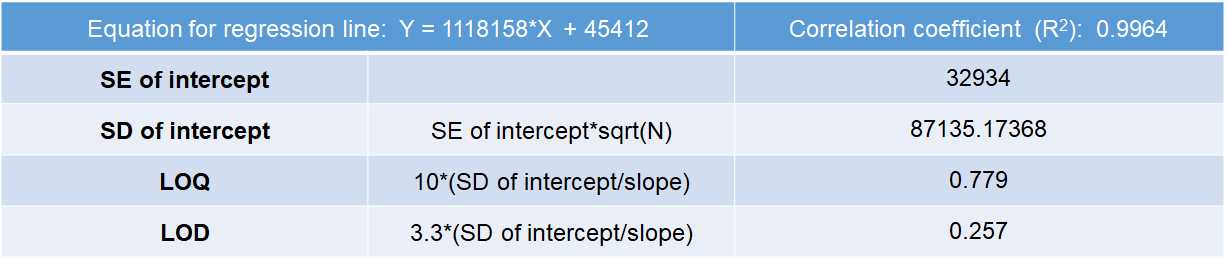
Linearity, Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
Total ecdysteroid extraction and 20E quantification
20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) was detected in total ecdysteroid extract from only female mosquitoes.
Here, female mosquitoes of Anopheles gambiae (COGS strain) were used.
Total ecdysteroid was extracted using methanol according to the method described by McKinney et al., 2017.
- Vortex and centrifuge for 5 min at 13000xg
- Transfer the supernatant to another tube
- Homogenize the remaining pellet in 500 µL of methanol 95% and centrifuge
- Poole the supernatant with the first one.
- Dry the pooled supernatants in a vacuum centrifuge
- Resuspend the dried sample in 500 µL of methanol 100% and filter the solution before injection.
HPLC analysis of the extracts
Inject the sample using the same method as with the standard samples.