Quality control assessment for microbial genomes: GalaxyTrakr MicroRunQC workflow
Ruth Timme, Errol Strain, Maria Balkey, Tina Lusk Pfefer, Yesha Shrestha, Paul Morin
Disclaimer
Please note that this protocol is public domain, which supersedes the CC-BY license default used by protocols.io.
Abstract
PURPOSE: Step-by-step instructions for checking WGS sequence quality for bacterial pathogens. The MicroRunQC workflow, implemented in a custom Galaxy instance, will produce quality assessments for raw reads (Illumina paired-end fastq files) and draft de novo assemblies, along with reporting the sequence type for each isolate. This workflow will work on most microbial pathogens, so we advise laboratories to upload their entire MiSeq/NextSeq run through this workflow.
SCOPE: This protocol covers the following tasks:
-
set up an account in GalaxyTrakr
-
Create a new history/workspace
-
Upload data
-
Execute the MicroRunQC workflow
-
Interpret the results
Version updates:
V3: updated with Cronobacter thresholds
V4: MicroRunQC updated to V1.1 Includes updates to skeza and mlst methods, as well as adjusted assembly QC thresholds for E.coli. Added Enterobacter QC thresholds to threshold table.
Before start
Steps
Account set up
Create a GalaxyTrakr account here: https://account.galaxytrakr.org/Account/Register
Log into your GalaxyTrakr account: https://galaxytrakr.org
Create a new history
Create a new history.
We recommend creating a new history for each new MiSeq Run and including the flow-cell ID and date in the history name.
Save your MicroRunQC output here and any other relevant analyses, like serotyping, or AMR detection.
After all the analysis output from this run is saved to your internal data network or computer, older history's should be purged/deleted so as not to occupy the limited storage space in your account. In some cases it may be useful to save, for a limited time, multiple histories or to run analyses concurrently in multiple histories. In these cases you need to pay attention to your % usage bar (shows % used of allocated storage space) in the upper right corner of the GalaxyTrakr page. If you need additional space you can contact galaxytrakrsupport@fda.hhs.gov and request additional storage.
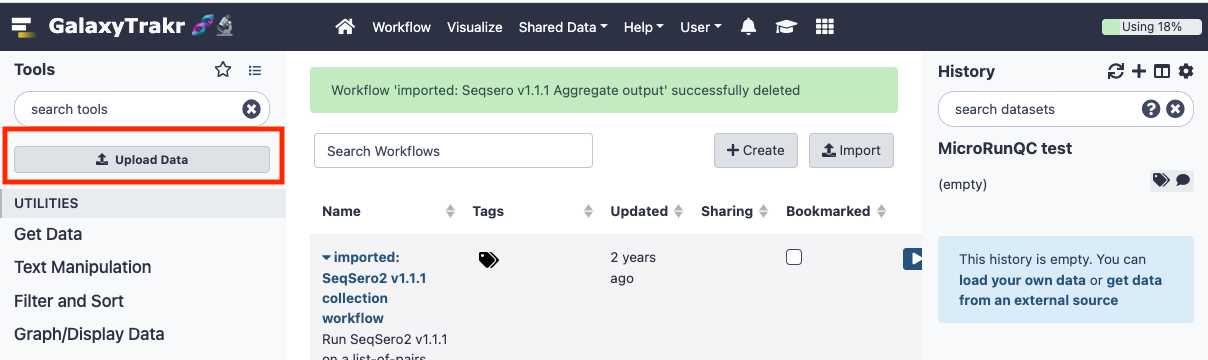
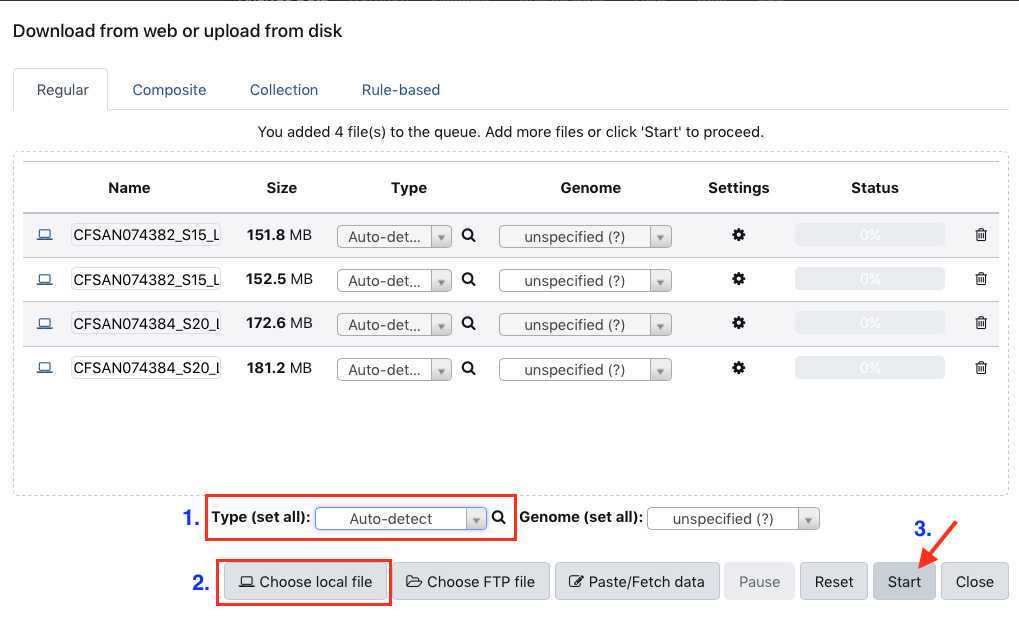
Upload data
This section will describe the process for uploading raw fastq files into your active History panel. After the files have been uploaded they will stay in your account until they are deleted.
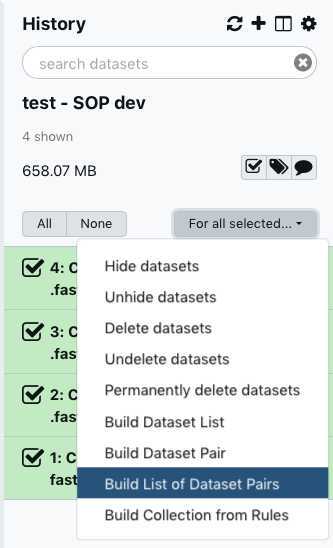
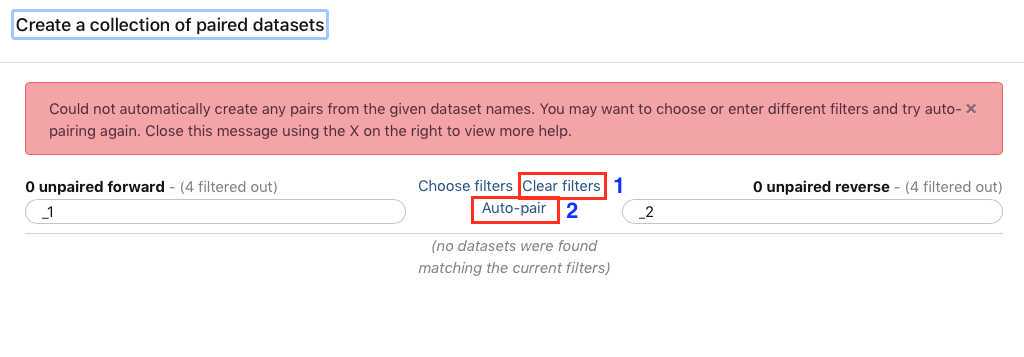
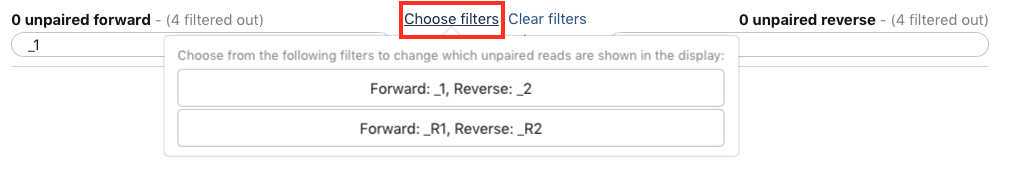
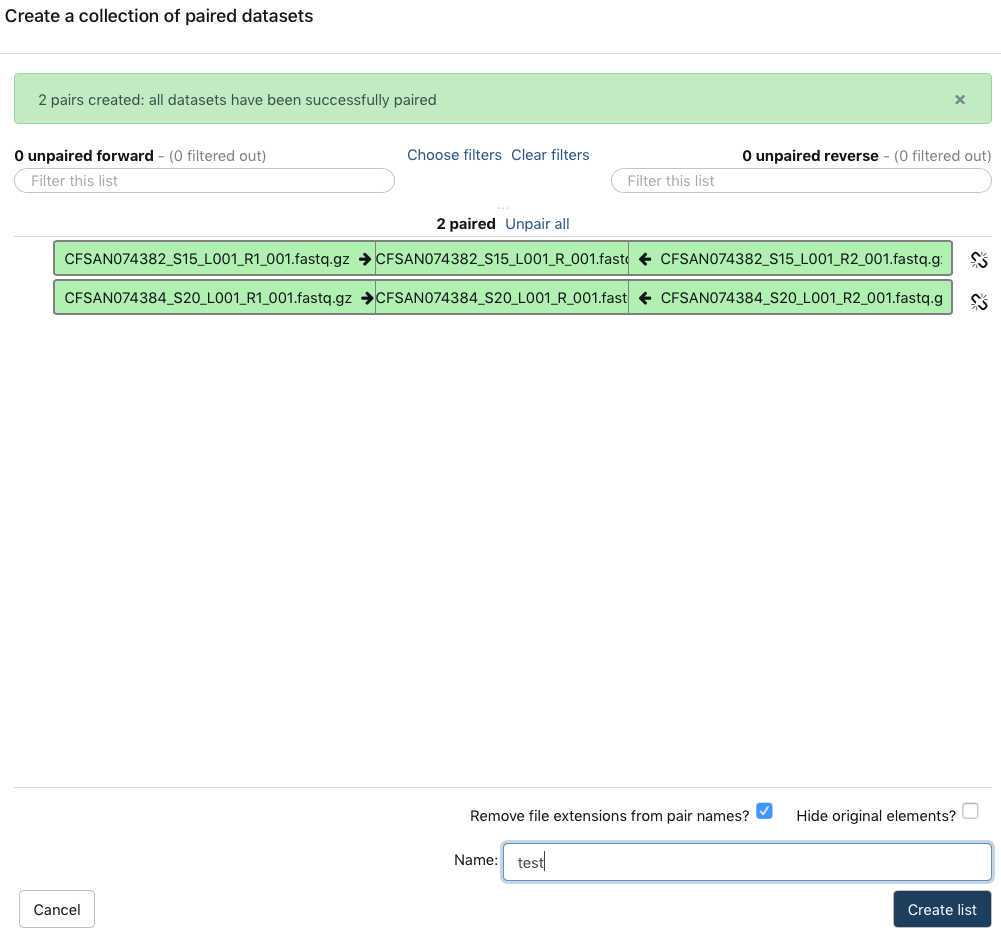
You have just upload a set of forward and reverse reads. For further analysis these files need to be paired properly so the platform knows which R1 and R2 files go with each sample/isolate. GalaxyTrakr does this by creating a List of Dataset Pairs.
Within your newly created History panel, click the "check box," then select all the files you just uploaded by clicking "All" or by individually selecting the ones you want to pair.
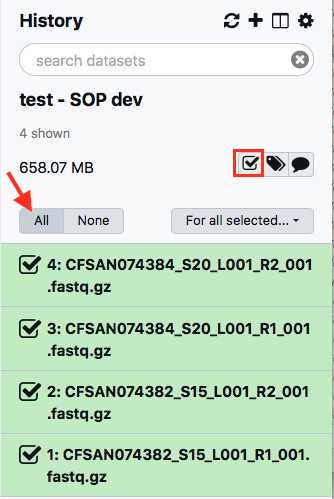
This paired dataset will now be available for analysis in your history panel. You can run multiple analyses on the same dataset in a history rather than upload the same sequence data to a new history to perform additional analyses. This will help you use your allocated storage space efficiently.
You can re-name this PairedList by clicking on the name.
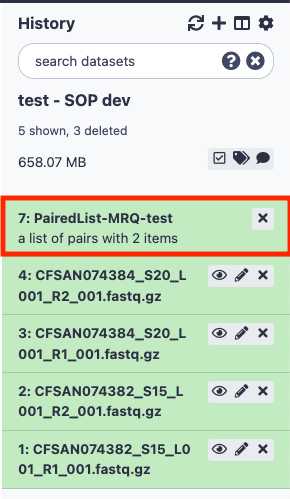
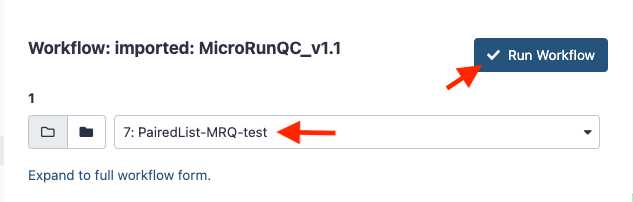
Run the MicroRunQC workflow
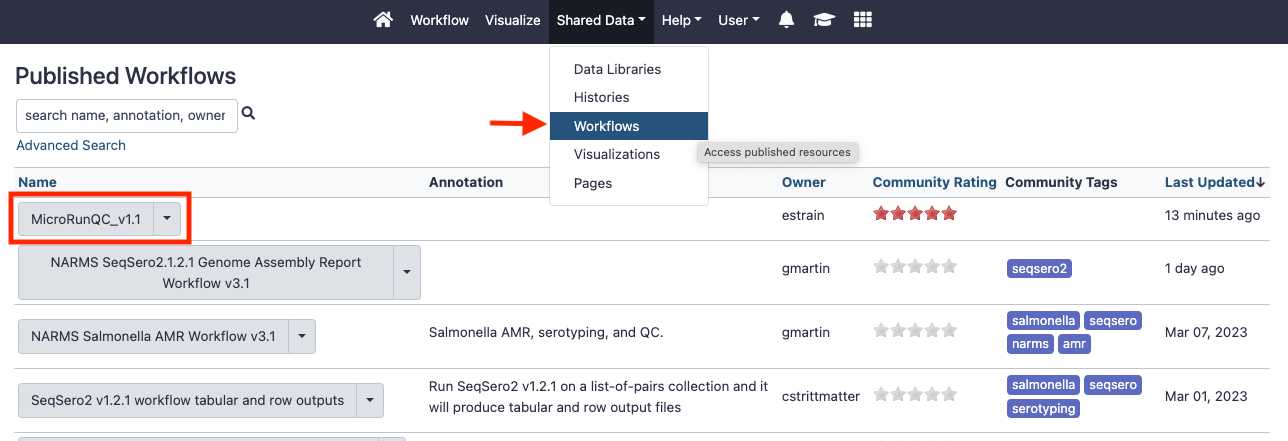
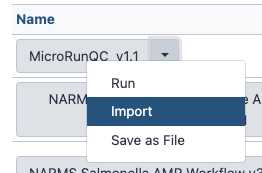
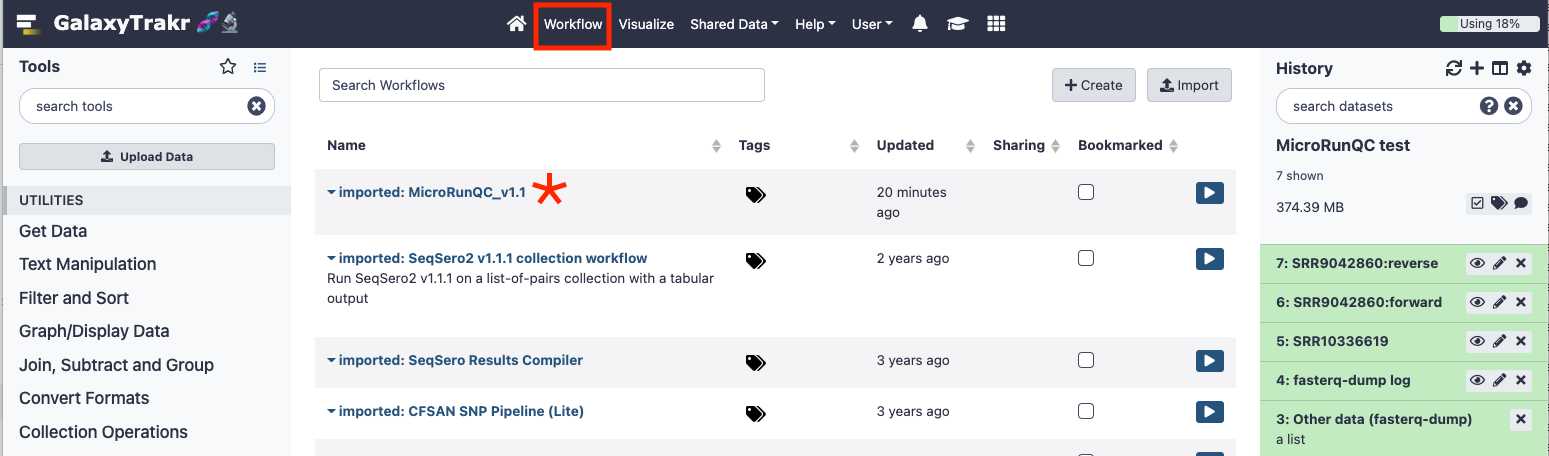
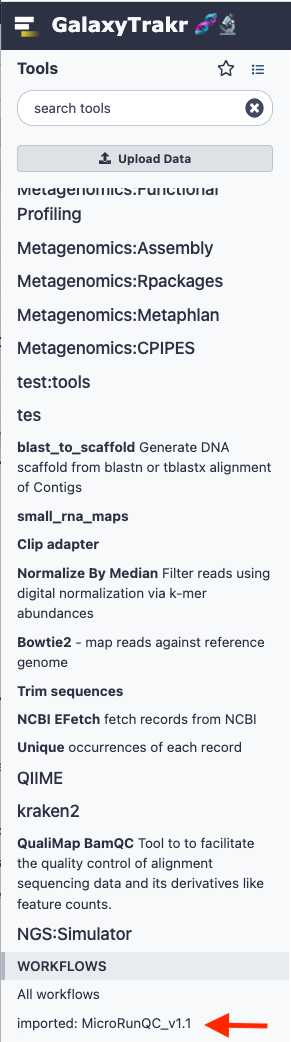
Add the MicroRunQC workflow to your own "workflows" panel. You only have to do this step once for each new workflow you need.
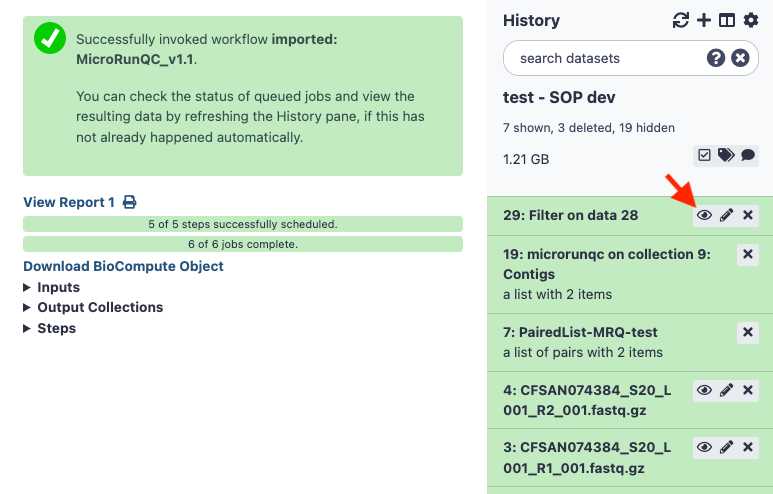
Interpret the results
Download and interpret the results:
The MicroRunQC output file includes the following columns:
Parameter | A | B | C | | --- | --- | --- | | Parameter | Input | Description | | Contigs | Assembly | Number of contigs in the de-novo SKESA assembly. Contigs smaller than 200 base-pairs (bp) are not counted. | | Length | Assembly | Total length of all contigs > 200bp. This should approximate the size of the genome for the target organism. | | EstCov | Assembly | Mean coverage for contigs in the SKESA assembly. | | N50 | Assembly | Sequence length of the shortest contig at 50% of the total genome length | | MedianInsert | Read | Distance between forward and reverse reads. Calculated by mapping reads to SKESA assembly using bwa. | | MeanLength_R1 | Read | Mean length of forward read | | MeanLength_R2 | Read | Mean length of reverse read | | MeanQ_R1 | Read | Mean Q-score of forward read | | MeanQ_R2 | Read | Mean Q-score of reverse read | | Scheme | Assembly | PubMLST scheme name (output from mlst application that scans contig files against traditional PubMLST typing schemes. | | ST | Assembly | Sequence Type | | Loci | Assembly | gene (allele number) – for example aroC(118) |
MicroRunQC output table headers. This table lists the summary metrics for sequence quality, number of contigs, and estimated genome size, along with other common metrics for reads (Median Insert Size and Mean Length) and assemblies (N50). Additionally, if the Multi-Locus Sequence Type (MLST) for the isolate is available from pubmlst, the workflow also reports Sequence Type (ST) and the associated alleles. Input Description Contigs Assembly Number of contigs in the de-novo SKESA assembly. Contigs smaller than 200 base-pairs (bp) are not counted. Length Assembly Total length of all contigs > 200bp. This should approximate the size of the genome for the target organism. EstCov Assembly Mean coverage for contigs in the SKESA assembly. N50 Assembly Sequence length of the shortest contig at 50% of the total genome length MedianInsert Read Distance between forward and reverse reads. Calculated by mapping reads to SKESA assembly using bwa. MeanLength_R1 Read Mean length of forward read MeanLength_R2 Read Mean length of reverse read MeanQ_R1 Read Mean Q-score of forward read MeanQ_R2 Read Mean Q-score of reverse read Scheme Assembly PubMLST (pubmlst.org) database scheme (e.g. senterica for Salmonella enterica) ST Assembly Sequence Type Loci Assembly gene (allele number) – for example aroC(118)
**This output should be saved either to your LIMS or to a spreadsheet linked to the sequencing run and samples.
Example output for 1 Salmonella and 5 Listeria isolates.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| Srain ID | Lab Confirmation |
| FDA1216271-C001-001 | Listeria mono |
| FDA817806-S073-001 | Listeria mono |
| FDA746634 | Listeria mono |
| FDA1213377-C001-002 | Listeria grayi |
| FDA933376-S060-005 | Listeria innocua |
| FDA1213835-C001-001 | Salmonella |
Lab confirmed IDs for 6 isolates
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File | Contigs | Length | EstCov | N50 | Median Insert | Mean Length_R1 | Mean Length_R2 | Mean Q_R1 | Mean Q_R2 | Scheme | ||||||||
| FDA1216271-C001-001 | 16 | 2911949 | 36.7 | 476210 | 321 | 148.4 | 148.4 | 36.4 | 34.6 | listeria_2 | 5 | abcZ(2) | bglA(1) | cat(11) | dapE(3) | dat(3) | ldh(1) | lhkA(7) |
| FDA817806-S073-001 | 20 | 3068354 | 179.6 | 525438 | 329 | 234.7 | 235.2 | 36.7 | 31.9 | listeria_2 | 321 | abcZ(5) | bglA(6) | cat(8) | dapE(62) | dat(6) | ldh(7) | lhkA(34) |
| FDA746634 | 30 | 3052888 | 41.4 | 293947 | 320 | 148.4 | 148.4 | 36.5 | 36 | listeria_2 | - | abcZ(2) | bglA(1) | cat(11) | dapE(3) | dat(3) | ldh(1) | lhkA(~7) |
| FDA1213377-C001-002 | 20 | 2672180 | 155.1 | 473181 | 270 | 147.3 | 147.3 | 37.2 | 36.1 | - | - | |||||||
| FDA933376-S060-005 | 9 | 2881869 | 213 | 1498790 | 303 | 232.1 | 232.2 | 37 | 36.2 | listeria_2 | 1489 | abcZ(250) | bglA(21) | cat(83) | dapE(298) | dat(20) | ldh(458) | lhkA(216) |
| FDA1213835-C001-001 | 37 | 4832365 | 34.4 | 294936 | 354 | 149 | 149 | 36.6 | 35.7 | senterica_achtman_2 | 214 | aroC(14) | dnaN(72) | hemD(21) | hisD(12) | purE(6) | sucA(19) | thrA(15) |
MicroRunQC example report showing mlst ST results for different Listeria species.
The listeria database includes multiple species, including Listeria monocytogenes and L. innocua . If users want to investigate which Listeria DB corresponds to the resulting ST types, they can query the Institut Pasteur mlst database:
Example : query Listeria ST type here: https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/cgi-bin/bigsdb/bigsdb.pl?db=pubmlst_listeria_seqdef&page=query
Quality control threshold guidelines for the GenomeTrakr surveillance network. These are also relevant for NARMS and VetLIRN contributors.
*MicroRunQC users should follow QC threshold guidelines established by their respective surveillance coordinating body(s).
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality metric | Salmonella | Listeria | E. coli | Shigella | Campylobacter | Vibrio para. | Cronobacter | Enterococcus faecium | Enterococcus faecalis |
| Average read quality Q score for R1 and R2 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 | >=30 |
| Average coverage | >=30X | >=20X | >=40X | >=40X | >=20X | >=40X | >=20X | >=50X | >=40X |
| De novo assembly: Seq. length (Mbp) | ~4.3-5.2 | ~2.7-3.2 | ~4.5-5.9 | ~4.0-5.0 | ~1.5-1.9 | ~4.8-5.5 | ~4-5 | ~2.5-3.5 | ~2.5-3.25 |
| De novo assembly: no. contigs | <=300 | <=300 | <=400 | <=550 | <=300 | <=300 | <=500 | <=350 | <=200 |