Morphological and molecular preservation through universal preparation of fresh-frozen tissue samples for multimodal imaging workflows
Andreas Dannhorn, Emine Kazanc, Lucy Flint, Fei Guo, Alfie Carter, Andrew R. Hall, Stewart A. Jones, George Poulogiannis, Simon T. Barry, Owen J. Sansom, Josephine Bunch, Zoltan Takats, Richard J. A. Goodwin
sample preparation
fresh-frozen tissue
multimodal imaging
morphological preservation
molecular degradation


























Extended
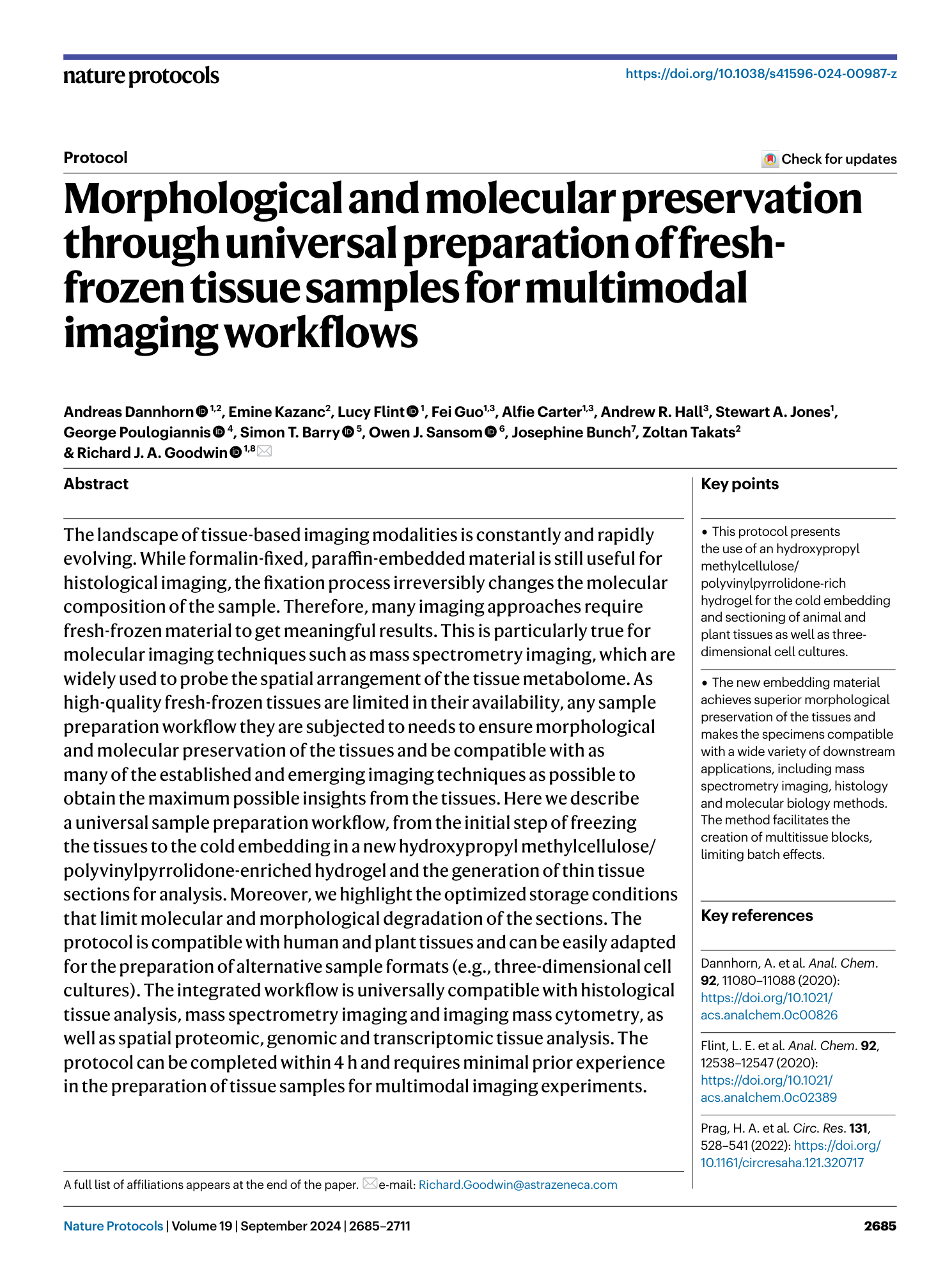
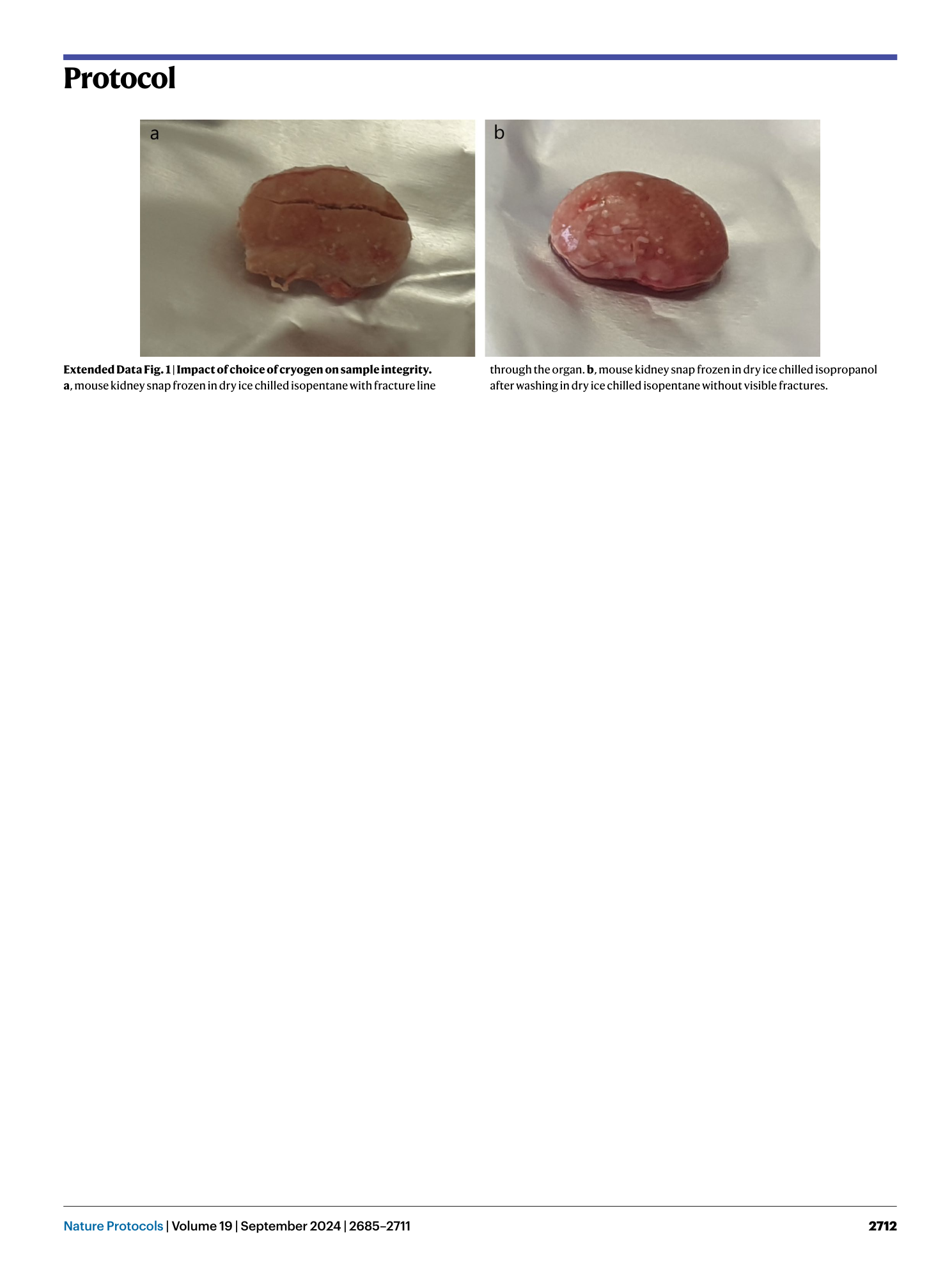
Extended Data Fig. 1 Impact of choice of cryogen on sample integrity.
a , mouse kidney snap frozen in dry ice chilled isopentane with fracture line through the organ. b , mouse kidney snap frozen in dry ice chilled isopropanol after washing in dry ice chilled isopentane without visible fractures.
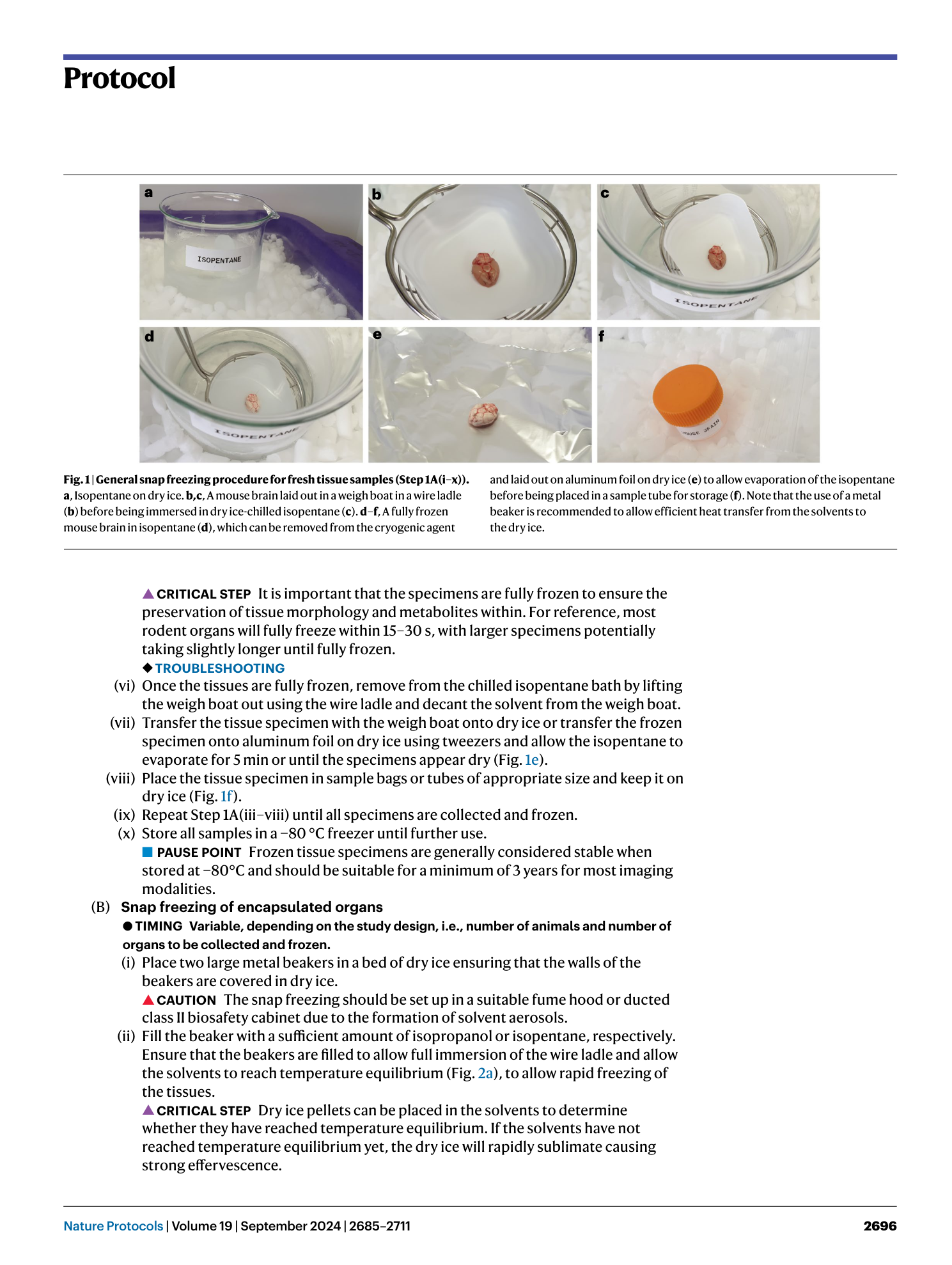
Extended Data Fig. 2 Troubleshooting of the freezing of the multi-tissue blocks.
a , Multi-tissue block that was fully frozen before being washed in the isopentane dry ice slurry. b , Multi-tissue block that was not fully frozen before being washed in the isopentane dry ice slurry and that fractured due to pressure building up during rapid freezing. The fracture line is indicated with ▲.
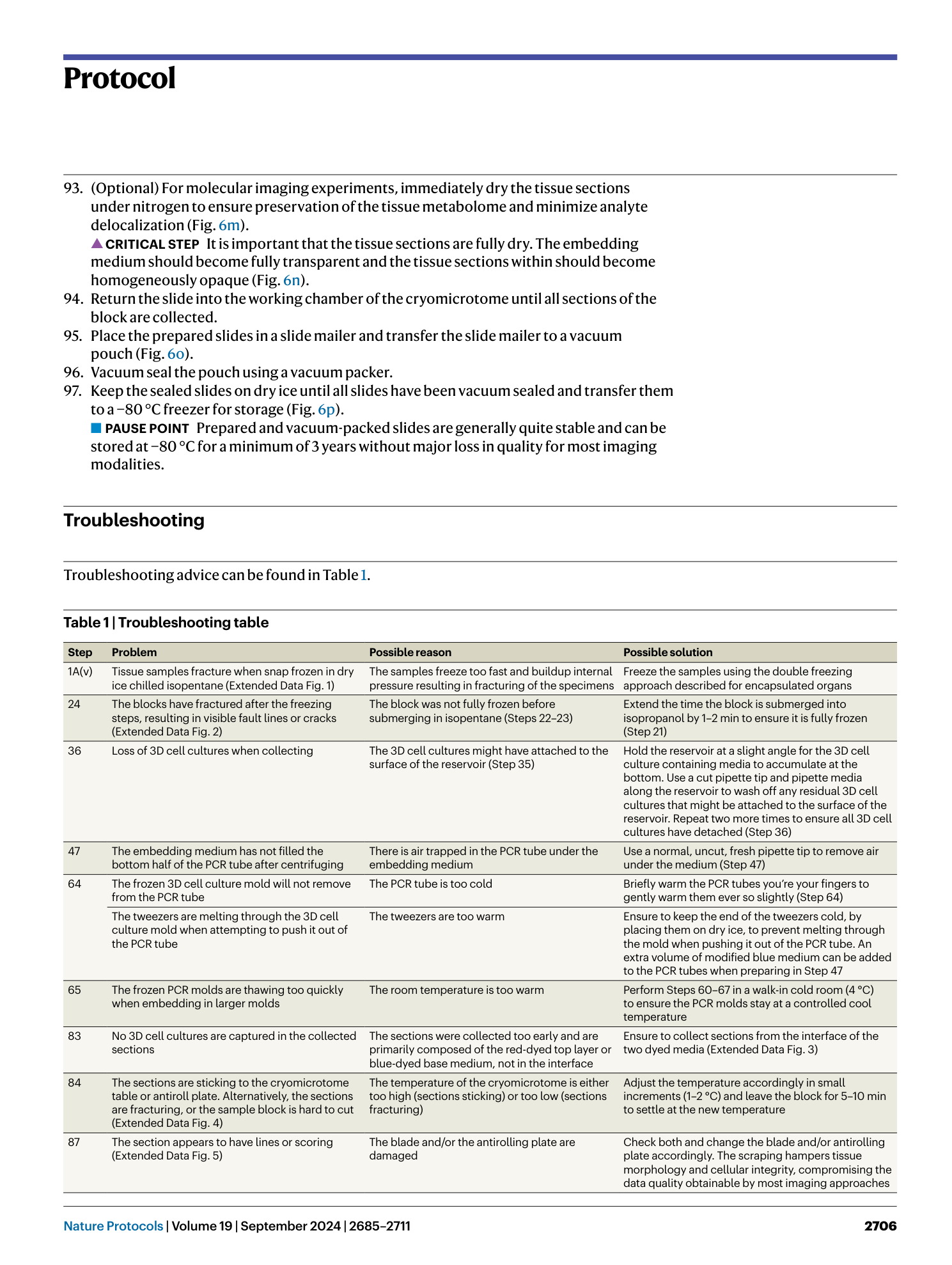
Extended Data Fig. 3 Identification of the sectioning level for 3D cell culture blocks.
a , Top layer of the red-dyed embedding medium. b , Interface layer between the two dyed embedding media in which the 3D cell cultures are positioned and sections of the tissues should be collected. c , tissue-free, blue-dyed base medium after exhaustion of the sample.
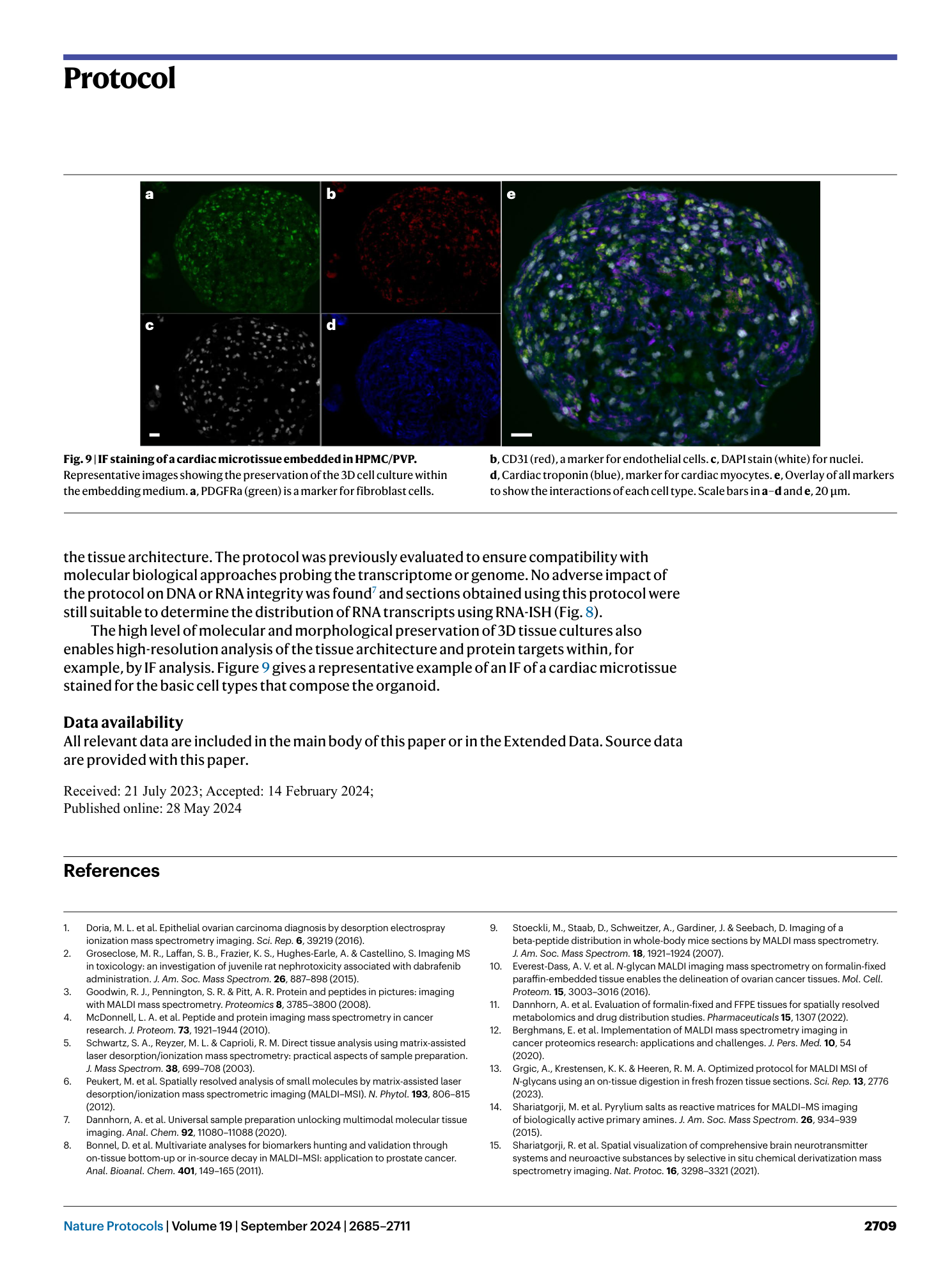
Extended Data Fig. 4 Troubleshooting of the sectioning temperature.
a , Section of a multi-tissue block collected at the appropriate temperature without visible fractures of the tissues or sticking to the surfaces of the cryomicrotome. b , Section collected at too low temperature with visible fracturing of the tissues within. c , Section of a multi-tissue block collected at too high temperature with visible damage to the embedding medium and tissue sections.
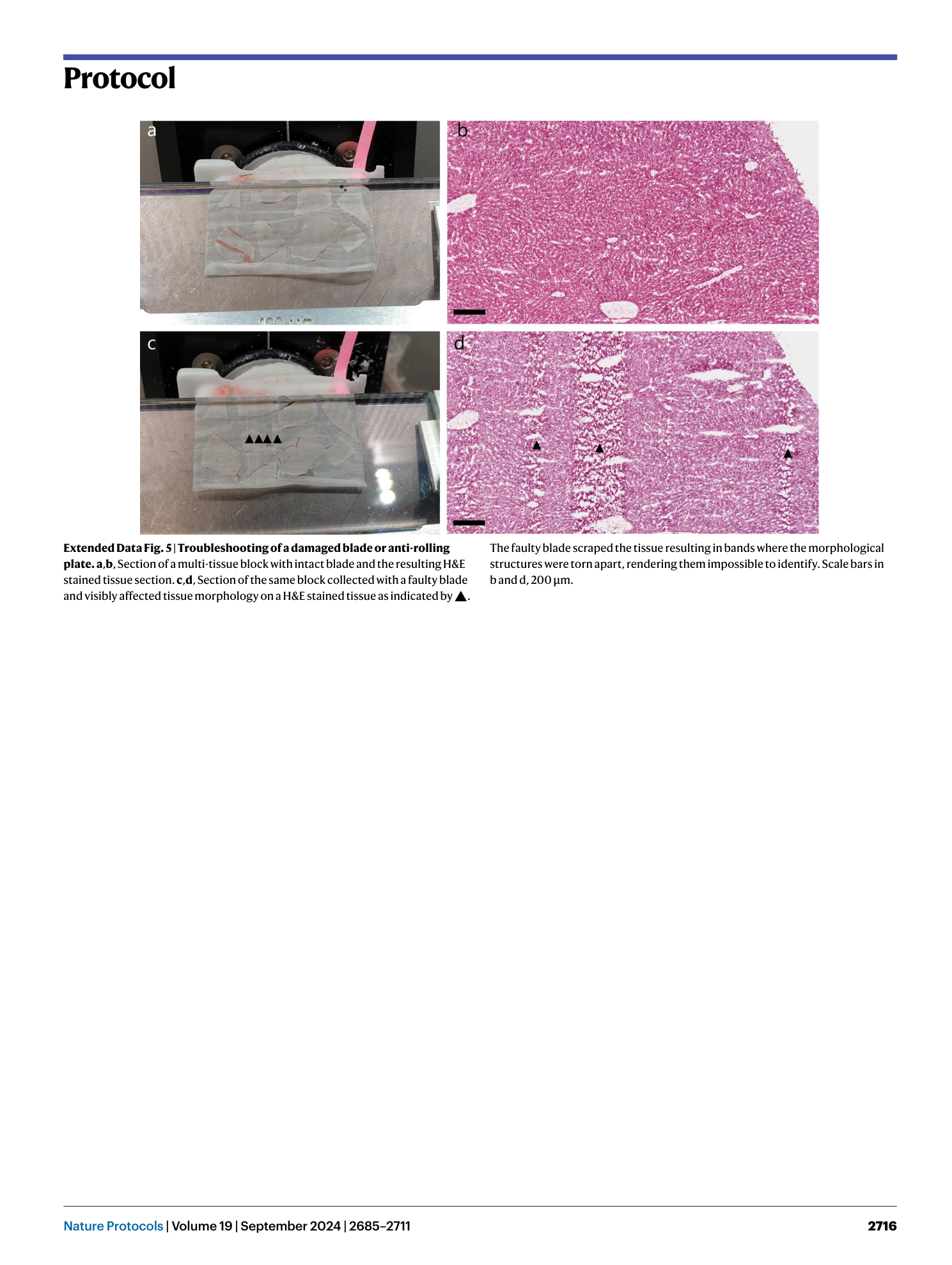
Extended Data Fig. 5 Troubleshooting of a damaged blade or anti-rolling plate.
a , b , Section of a multi-tissue block with intact blade and the resulting H&E stained tissue section. c , d , Section of the same block collected with a faulty blade and visibly affected tissue morphology on a H&E stained tissue as indicated by ▲. The faulty blade scraped the tissue resulting in bands where the morphological structures were torn apart, rendering them impossible to identify. Scale bars in b and d, 200 µm.

