Manual extraction of High Molecular Weight DNA from single mosquitoes using the Qiagen MagAttract HMW DNA kit
Mara Lawniczak, Fiona Teltscher, Harriet Johnson
Abstract
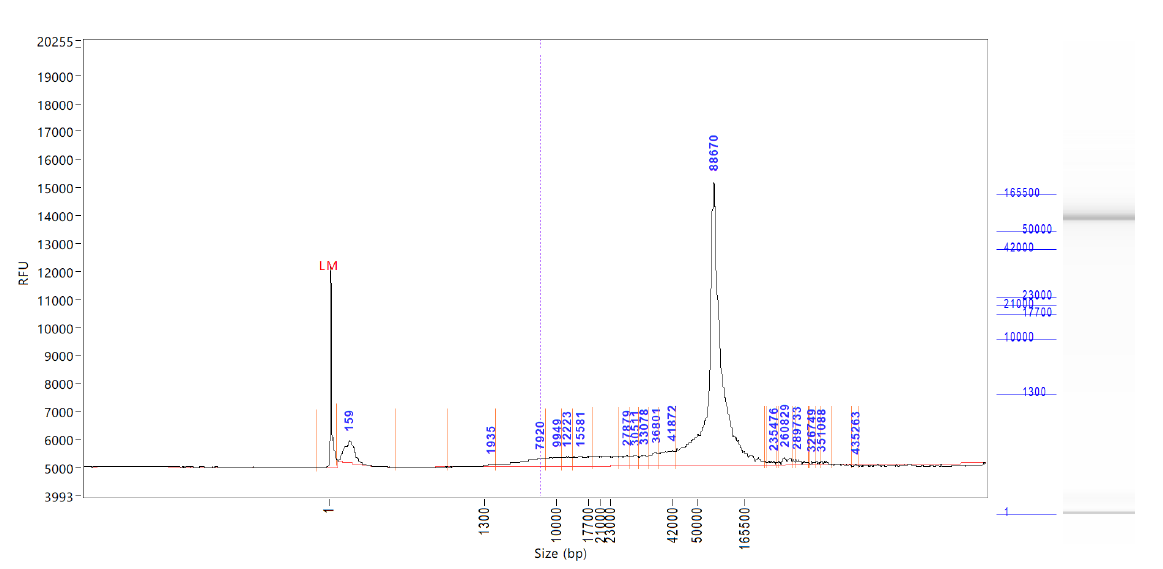
This is a protocol for the manual extraction of high molecular weight (HMW) DNA from insects. It uses the Qiagen MagAttract kit and factors in modifications described in the ChromiumTMGenome Reagent Kits User Guide pages 6-8 (https://support.10xgenomics.com/genome-exome/library-prep/doc/user-guide-chromium-genome-reagent-kit-v2-chemistry). It includes further modifications that benefited two particular needs. First, most reagents are halved per extraction (apart from beads) due to small specimen size (2 mg is a typical weight of an Anopheles mosquito, which is far less than the 25 mg of tissue the MagAttract kit can support). Second, due to this small specimen size, we need to maximize DNA yield, so we also perform a second elution to release more DNA.
DNA resulting from this protocol can be further sheared and cleaned for successful PacBio HiFi sequencing. In our experience, a single fresh Anopheles gambiae mosquito weighing 2-3 mg yields about 600-800 ng of DNA (quantified using qubit HS DNA kit) using this protocol. Following shearing using G-tubes or the MegaRuptor and SPRI based clean up, we typically retain about 200 ng of sheared DNA, which is just about sufficient to reach 25x coverage PacBio HiFi of a 250 Mb genome. The quality and quantity of DNA is best when starting with a snap frozen from living specimen. However, we have also successfully extracted HMW DNA using this protocol from ethanol and DESS preserved specimens held at room temperature for as long as a week, as long as the specimen was punctured or gently squished to ensure rapid penetration of the preservative. See: Squishing insects for preservation of HMW DNA in the field https://www.protocols.io/view/squishing-insects-for-preservation-of-hmw-dna-in-t-cyp3xvqn
We normally perform up to 8 DNA extractions in parallel (this will also depend on which magnetic rack is being used). Please add a comment to let the wider community know if it has worked or not on your species.
NB -- an automated version of this protocol that works on the Kingfisher Apex is also available here on protocols.io
Before start
Ensure all surfaces have been cleaned with 70-80% Ethanol (and ideally bleach before that). Have cleaning wipes for forceps. All kit components, buffers, and RNase A stock solution can be stored at room temperature (15–25°C) for up to 1 year. The box should be labelled with received date. Mix Buffer AL thoroughly by shaking before use. Buffers MW1 and PE are supplied as a concentrate. Before using for the first time, be sure to add the appropriate amount of ethanol (96–100%) as indicated on the bottle. Many components of the kit are also available from Qiagen separately.
Steps
Procedure
Prepare an open insulated box of dry ice to store sample tubes on whilst working through steps 2-4.
Make mastermix of reagents for lysis.
100µL 10µL 2µL 75µL For each sample, add 187µL of the mastermix from step 2 into a new 1.5 mL DNA LoBind tube.
Carefully remove the Sample from the sample tube using clean forceps. If the Sample has been stored in a preservation liquid, lightly make contact on a clean piece of tissue to remove surface liquid from the sample. Submerge the Sample into the mastermix in a tube (see step 3) with clean forceps. Insert a sterile pestle in the tube and smash, smear, squash, twist, grind the tissue against the wall of the tube for 0h 1m 0s. There should be no recognisable body parts visible following pestle smashing, only flakes. Place the sample in a tube rack on the bench. Clean forceps with 100% ethanol.

Repeat step 4 for the remaining samples.
Briefly spin all samples in a minicentrifuge or similar to collect solution at bottom before next step.
Incubate the sample at 25°C for 2h 0m 0s.
Briefly spin samples to collect solution at the bottom of the tube.
Vortex the 0h 1m 0s and add 15µL to each sample.
Add 140µL0h 1m 0s for the beads to bind. Doing multiple samples will often take more time than this.
Remove the Sample from the magnetic rack. Add 350µL
Centrifuge the tube briefly and place on a DynaMagTM-2 Magnetic Rack for 0h 1m 0s to allow bead capture.
Remove and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the bead pellet.
Repeat steps 13-15 for a total of 2 washes.
Remove the sample from the magnetic rack. Add 350µL
Centrifuge the tube briefly and place on a DynaMagTM-2 Magnetic Rack for 0h 1m 0s to allow bead capture.
Remove and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the bead pellet.
Repeat steps 17 and 18 for a total of 2 washes but do not remove supernatant immediately, proceed to step 21.
If you have more than four tubes, split them into groups of four or fewer. Perform steps 22-24 (water wash) on the first group of samples, whilst the remaining samples wait in
Remove and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the bead pellet. With a P20 pipette remove any remaining supernatant. Leave the sample on the magnetic rack for the next step. Do not pipette water directly onto the beads.

Carefully add 350µL0h 0m 15s add water to the second sample, after 0h 0m 30s add to the third sample, after 0h 0m 45s add to the fourth sample. At 0h 1m 0s remove and discard the water from the first sample, at 0h 1m 15s remove and discard water from the second sample, at 0h 1m 30s the third, and 0h 1m 45s the fourth. This will enable multiple samples to be incubated for exactly 0h 1m 0s.
Repeat step 23 for a total of 2 washes.
Remove the samples from the magnetic rack. Add 100µL 25°C and 1400rpm shaking for 0h 3m 0s.
During this 0h 3m 0s incubation perform steps 22-25 on the second group of samples if present.
Centrifuge each tube briefly and place them on a magnetic rack for 0h 1m 0s to allow bead capture.
Using a wide-orifice pipette tip, carefully transfer the supernatant containing purified gDNA to a new labelled 1.5 mL LoBind microcentrifuge tube or barcoded (e.g. FluidX) tube.
Second elution: remove the samples from the magnetic rack. Add 100µL 25°C and 1400rpm shaking for 0h 3m 0s.
Using a wide-orifice pipette tip, carefully transfer the supernatant containing purified gDNA to the same 1.5 ml LoBind microcentrifuge tube or Fluidx tube with a final volume of 200µL.