Lignin Reductive Catalytic Fractionation (RCF) Monomers Analysis by Gas Chromatography Flame Ionization Detection (GC-FID)
Gregg T. Beckham, Hannah M. Alt, David G. Brandner, Kelsey J. Ramirez
Abstract
A gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (GC-FID) method was developed to quantify reductive catalytic fractionation (RCF) monomers.
Before start
All solvents, analytes, and chemicals used in this protocol are listed in the 'Materials' section. They are excluded from in-line referencing to keep steps clear and concise.
Steps
Internal Standard Preparation
This analysis uses 1,3,5-tri-tert-butylbenzene (TTB) as an internal standard. Prepare adequate volume to allow for addition of 1µL of TTB per 100 µL of sample or standard volume.
Create a 10,000 µg/mL internal standard working solution by weight of TTB using methanol as the diluent.
Preparation of Standards
By weight, create individual 20,000 µg/mL stock solutions of all monomers (listed in Materials section) and use methanol as the diluent.
Combine the stock solutions to create a 1000 µg/mL mixed standard working solution in methanol.
For example, to prepare a 10 mL mixed standard working solution of woody RCF analytes (distinguished in Materials section), add 500 µL of each of the 20,000 µg/mL stock solutions (14 analytes) and add 3000 µL methanol.
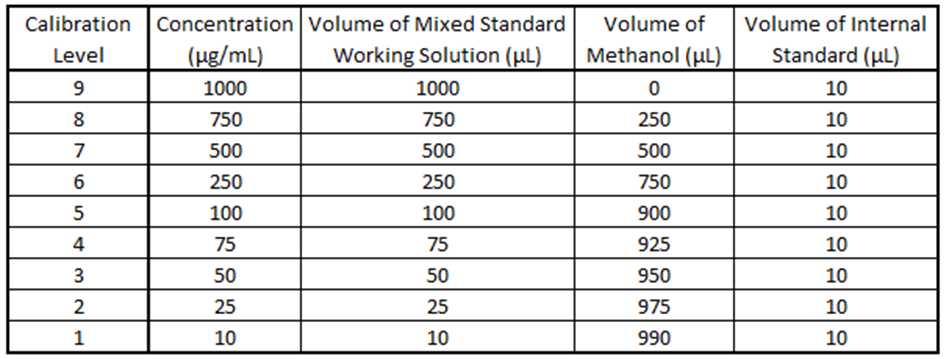
Using the mixed standard working solution at 1000 µg/mL, create a calibration curve from 10 µg/mL to 1000 µg/mL with a minimum of five calibration points using methanol as the diluent.
Add 1 µL of 10,000 µg/mL TTB internal standard working solution per every 100 µL of calibration standard.
Example: 10 µL into 1000 µL or 5 µL into 500 µL
Sample Preparation
Oil Samples:
- Weigh approximately 5-10 mg of oil into a GC vial and record weight.
- Add a known volume of methanol to each vial containing sample (for example 1 mL).
- Add 1 µL of 10,000 µg/mL TTB for every 100 µL of methanol added to the sample vial. Example: 10 µL into 1000 µL or 5 µL into 500 µL
Liquid Samples:
- Aliquot a known volume of sample into a GC vial (for example 1 mL)
- Add 1 µL of 10,000 µg/mL TTB for every 100 µL of methanol added to the sample vial. Example: 10 µL into 1000 µL or 5 µL into 500 µL
GC-FID Analysis
Analyze samples using an 8890 Agilent Gas Chromatograph (GC) or equivalent equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) per the method parameters below:
Method Parameters
Split/Splitless Inlet Parameters:
Inlet Temperature: 280 °C
Injection Volume: 1 µL
Split Ratio: 2:1
Inlet Liner: split, single taper, glass wool, deactivated (see Materials)
Syringe: P/N 5181-8809
Wash Solvent: Methanol
Column:
HP5-MS (see Materials)
Carrier Gas: Helium
Flow Rate: 1 mL/min (constant flow)
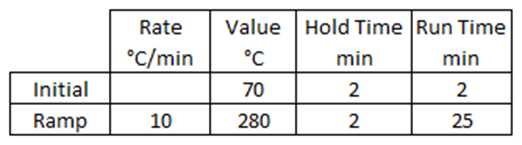
Oven Parameters:
Maximum Oven Temperature: 280 °C
Detector Parameters:
Detector: FID
Detector Temperature: 300 °C
Air Flow: 400 mL/min
H2 Fuel Flow: 40 mL/min
Makeup Flow: 10 mL/min
Analytical Quality Control
Several strategies are utilized when performing this analysis to ensure instrument stability and reproducibility.
Calibration Curves
All compounds must have a correlation coefficient (r2) of 0.995 or greater using a linear calibration fit.
Calibration Verification Standards (CVS)
A calibration verification standard (CVS) is a standard from the calibration curve that is re-analyzed every 20 or fewer samples to ensure instrument drift remains within the determined acceptance criteria. Acceptable CVS recoveries for this analysis are within 15% of the expected amount. Acceptance criteria may differ between instruments and should be determined experimentally.