High-Yield Monocyte/Macrophage Differentiation from hiPSC
Lilia Rodriguez, Florence Petit, Janelle Drouin-Ouellet
Differentiation of iPSCs to Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells
Differentiation of HPC to monocytes
Differentiation of iPSC-derived monocytes into macrophages
Macrophage activation
ASAPCRN
Abstract
Here, a highly efficient method for differentiating monocytes/macrophages from hiPSC is described. The process utilizes commercially-available materials to derive CD34+ progenitor cells that are apically released from a hemogenic endothelium. Subsequently, the hemogenic endothelium gives rise to highly pure (>95%), CD34-CD14+ monocytes in 19-23 days and yields more monocytes by day 35 when compared to previous methods. These monocytes are further differentiated to macrophages after 7 days. The efficient workflow and increase in monocyte output boost feasibility for high throughput studies and enables clinical-scale iPSC-derived manufacturing processes.
Steps
Differentiation of iPSCs to Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPCs)
Start with large cultures of pluripotent stem cells around 50–70% confluence cultured on Matrigel hESC.
Coat 6-well plates with fresh Matrigel (1mg/plate) 1 h to 1h 0m 0s at 37°C.
Prepare iPSC maintenance medium (mTeSRplus) with 10micromolar (µM) Rock inhibitor (concentration depending on your line). Add 1.5mL of medium supplemented with rock inhibitor to each well of the Matrigel coated 6-well plate.
Prepare 96-well plate for counting cell clusters. Add 40µL DPBS to 3 empty wells of the 96-well plate.
Dissociate iPSC cultures with GCDR:
Remove iPSC medium and wash 1mL DPBS to remove dead cells.
Treat cells with 1mL GCDR to each well of a 6-well plate for 5-6 min.
Remove GCDR from the well.
Scrape the cells in 1mL mTeSRplus + Rock inhibitor and transfer to a 15 mL Falcon. Using a 5 ml pipette, gently pipette up and down 2-3 times in order to achieve clusters of ~ 50-100 cells.
Pipette 5µL of cell cluster mixture into each well of the 96-well plate (n = 3 wells) for counting.
Count all cell clusters of ~100 cells (100–200 μm diameter). Determine # of clusters per μL (total count of correct sized clusters in 3 wells/15 μL total cell cluster suspension).
Using cluster #/μL calculations, plate 20–40 clusters per well. The goal is to produce 10–20 surviving clusters of ~100 cells each per well the next day. Swirl plate in incubator to evenly distribute the clusters throughout the plate.
24 h after plating, count colonies and choose wells to begin with. Do not blindly start differentiations in all wells. Choose only wells with 10–20 undifferentiated iPSC clusters of ~100 cells each.
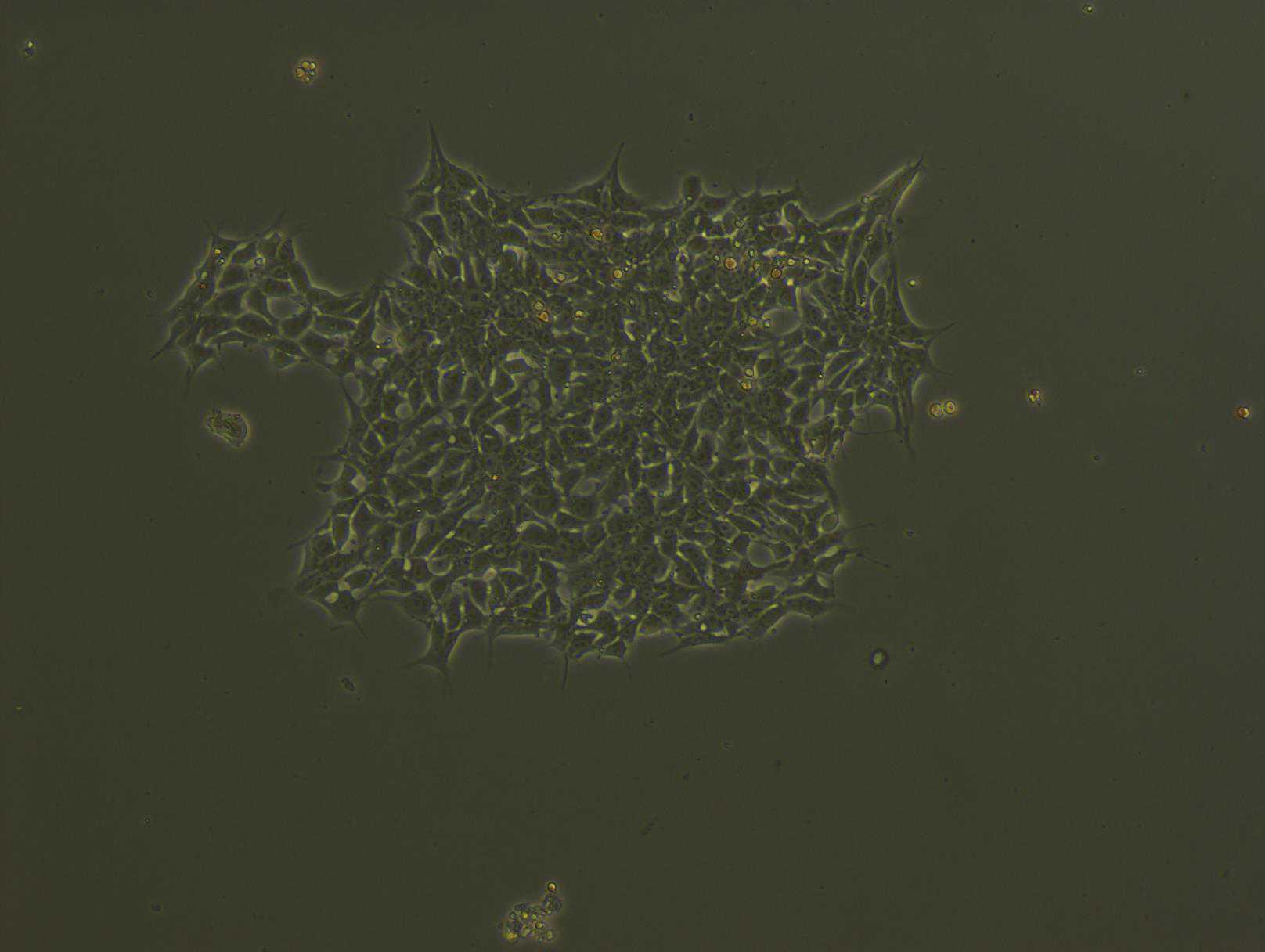
Prepare Medium A from StemDiff Hematopoietic kit by diluting Supplement A 1:200 in basal medium. You will need 3mL Medium A per well for the entire differentiation.
Remove mTeSRplus and add 2mL Medium A per well (Day 0).
48 h later, remove all medium A and add 2mL Medium B (1:200 dilution of supplement B into basal medium) per well (Day 4).
Repeat addition of 1mL medium B every 48 h three times (Day 6, 8, 10).
On Day 10, collect round, floating, phase-bright cells by agitating the plate gently and collecting all medium with a serological pipette.
Centrifuge 300x g. To continue collecting cells on day 12, replace 2mL supernatant (conditioned medium) per well (add to 1mL fresh medium).
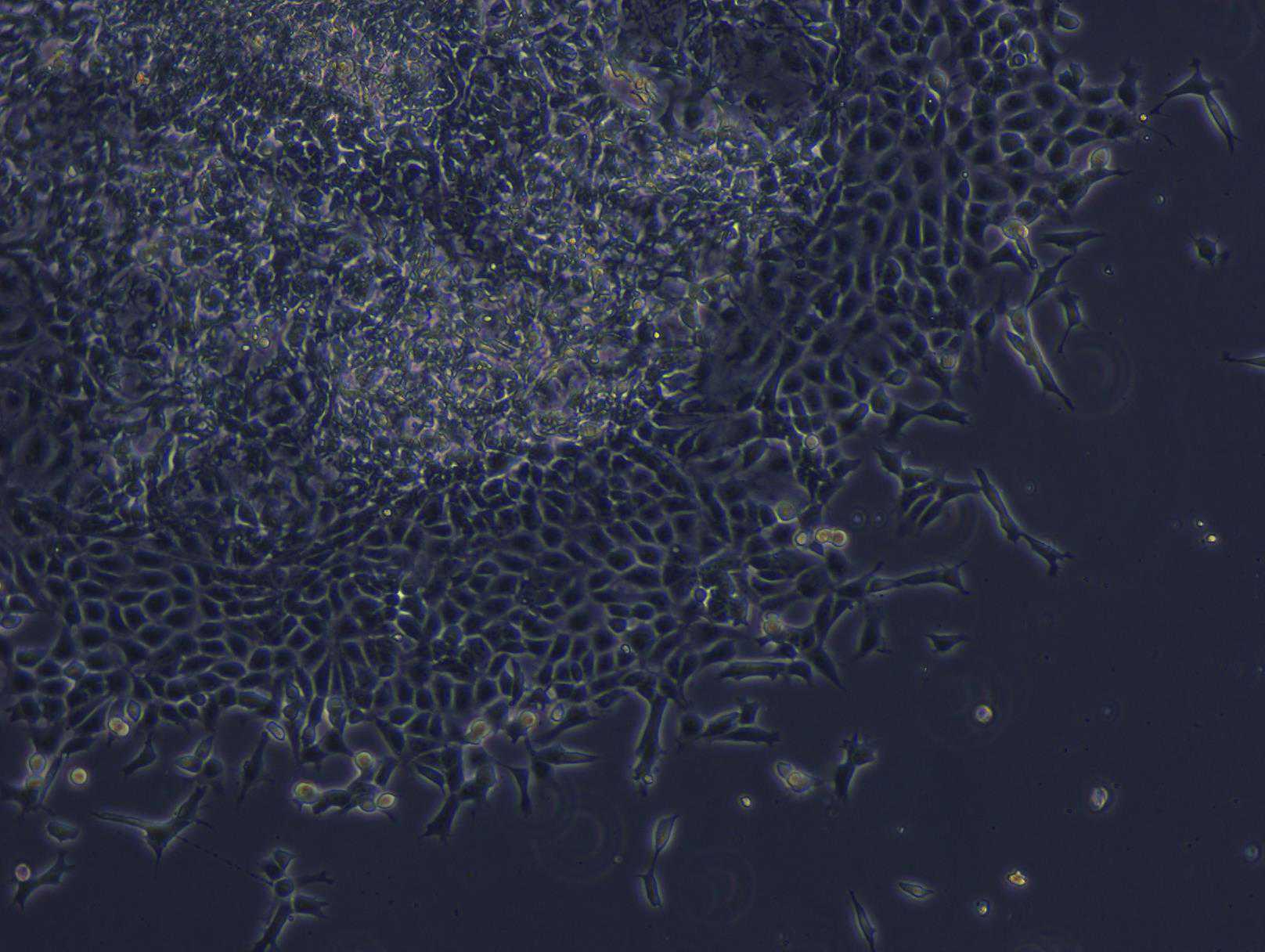
At this point cells may be analyzed for HPC markers by flow cytometry or ICC (cells should always be >95% CD43+).
Differentiation of HPC to monocytes
On Day 12, CD34+ cells are harvested from the plate leaving behind a hemogenic endothelium.
On Day 19 monocytes are harvested by gently rinsing monocytes off each well before passing through a 70 µm nylon filter and centrifuging at 300x g.
CD45+, CD14+, CD11b+ cells are checked by flow cytometry. We usually obtain >85% CD14+ cells.
The medium in each harvested well is immediately replaced with 2mL of fresh monocyte factory medium.
Differentiation of iPSC-derived monocytes into macrophages
Freshly harvested monocytes are plated at 2.5-3x105 per well of a 6-well plate ultra-low attachment plate in 2mL of macrophage differentiation media (MDM) Day 0 ( Day 19 from beginning ).
On Day 4, 1mL of media is removed and each well is supplemented with 2mL of MDM.
Between days 7 and 10 ( Day 26-29 ), monocyte-derived macrophages are gently dissociated from the plate using Cell Dissociation Buffer, enzyme-free, pelleted at 300x g, resuspended in fresh MDM medium, and plated for experiments. CD11b+, CD68+ cells are checked by flow cytometry.
Macrophage activation
iPSC-derived MDM are plated at 5x105 cells per well in a 6 well plate in 2mL of MDM medium without M-CSF.
Cells are left untreated or activated with 500ng/mL of LPS, 20ng/mL of rhIFNγ, or both LPS and rhIFNγ.
After 24 hours of activation, supernatants are harvested and assayed for human IL-6, TNF, and IL-1β via enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Table 1 . iPSC lines used.
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| Line | Reprogramming method | Cell source |
| KOLF | CRISPR Cas9 ARID2 | Fibroblast male 55-59 yrs |
| AIW002-02 | CytoTune™-iPS 2.0 Sendai Reprogramming Kit to generate iPS (non integrative system) | PBMC male 37 yrs |
| A18945 | episomal reprogramming to generate iPSc | Female CD34 + cord blood using a three-plasmid < 1 yr |