Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry to assess dopamine release in ex vivo mouse brain slices
Stephanie J Cragg, Katherine Brimblecombe
Abstract
This protocol is to assess whether a drug changes the dopamine concentration released following a single pulse (1p) electrical stimulation.
Before start
Prior to drug application, you first need to determine a stable baseline. The variance permitted in the baseline will depend upon the effect size of your drug of interest. We recommend you first perform a pilot experiment to determine the approximate effect size and then determine a cut-off for any change in dopamine release over time, allowing you to pre-determine an exclusion criteria based on your control (pre-drug) data.
If your cut-off is too stringent, you might use more animal tissue than is necessary (not in accordance with the 3Rs ), but also you may be sub-selecting a populations of release-sites that may not reflect the properties of the striatum you hope to generalise to. Setting a cut-off too permissive may result in a larger decay component due to time and may either over-estimate or underestimate your drug effect.
Consider designing your experiment with a time-matched control. Having a pre-determined exclusion criteria will prevent you from erroneously excluding data that does not match your hypothesis and ensures your findings are more reproducible.
Steps
Preparation of ex vivo mouse brain slices
Prepare HEPES buffer solution (see Materials ), chill and oxygenate.
Prepare vibratome settings: 300 μm slices, 0.44 mm/s speed, Δ1.45 mm vibration. Chill plate and buffer tray in freezer, rinse razor blade in acetone.
Kill mouse by cervical dislocation, confirm death by exsanguination.
Decapitate mouse and take ear-clip for post-hoc genotyping where required (put in 2.5 ml Eppendorf).
Remove brain.
Block brain with razor blade to remove olfactory bulb and brain posterior to ~-1.055 mm bregma.
Add small amount of cyanoacrylate glue to magnetic chuck, smooth with pipette tip.
Transfer brain containing striatum to glue using filter paper to pick up block, and dampening fliter paper to reomve paper.
This step is optional.
Save posterior brain block by transferring to Eppendorf containing 4 % PFA to allow fixation of midbrain (SNc and VTA) containing dopaminergic neurons. Tissue block can be sectioned once fixed to 40 µm sections and used for IHC.
Section striatum to 300 μm-thick coronal slices.
Move slices to slice saver chamber at room temperature >1 hr.
Optional: If comparing drug vs vehicle control from tissue taken from same mouse
Set up needle bubbler (carbogen inlet connected to needle (26G) that rests above glass vial containing 10 mls aCSF).
Add required drug or vehicle to 10 mL of aCSF in the vial and clearly label vial.
Bisect slice and put each hemisphere into appropriate vial.
Allow slices to be incubated in drug or vehicle for typically 30 mins.
Setting-up rig
Prepare bicarbonate-buffered artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) solution (see Materials ).
Circulate dH2O through inflow pipes and recording chamber.
Transfer silver weight pins from isopropanol to recording chamber to rinse.
Circulate aCSF, ensuring no wicking up temp probe or reference Ag/AgCl2 pellet.
Heater on, light on, stim box on, computer on. Master8 and VOLTAMMETER* must stay off until in circuit.
Place coronal section in recording chamber and place silver pins on cortex to keep slice in place.
Insert the recording electrode ~100 µm into the tissue at 45o angle, connect it to voltammeter headstage, and switch on voltammeter.
Check waveform of electrode, and perform a quality control of the electrode.
Allow electrode to charge for >30 mins to gain capacitance to ensure stable baseline of DA detection before start of stimulation.
Determining evoked extracellular dopamine (DA) concentration
The below parameters were used to assess the effect of application of a drug (DHBE) on dopamine release evoked by single electrical pulses.
Stimulation: 200 µs, 0.6 mA
Temperature: 31-33ºC
Perfusion speed: >1.8 ml/min
Inter-stimulation interval: 2.5 min
Voltammeter sweep: -700V to 1300V to -700V, 800 V/s. Repeated at 8 Hz. Switches out of circuit between scans.
Default gain settings: faradaic gain: x20, full signal gain: ~3-10 mV/nA, to avoid saturation of amplifier.
Drugs: record in DHBE 1 µM throughout to exclude effect of co-activation of ACh release and nAChR activation. Wash on drug of interest added to this solution.
Check settings on axoscope and set file directory and filenames.
Make up drugs and ensure fully thawed.
Place stimulation electrode (bipolar concentric electrode) on surface of tissue. Surface location minimises damge.
Place recording electrode ~100 µm from recording electrode, 100 µm into the tissue.
Record dopamine (DA) release.
Before recording, “refresh” voltammeter. (Specific for acquisition and use of Millar Voltammeter)
Record >1s of baseline prior to then delivering 1p electrical stimulation.
Record for sufficient time to allow DA to return to baseline (in drug free condition ~3 s, in the presence of DAT inhibitors will need to record for longer).
Note approximate peak voltage at DA oxidation potential in a lab book to alllow investigator to follow the approximate outcome of experiments during progress.
Wait 2.5 mins.
Repeat steps 26 and 27 until >6 stable recordings in control condition.
Move inflow pipe to drug cylinder try to minimise bubbles.
As drug washes into the recording chamber, watch the oscilloscope in real time as drug washes on for indication of electroactive drugs.
Continue steps 26 and 27 until 12 recordings in drug condition.
If wash-off is required, move inflow pipe to control solutions and repeat data acquisition for approximately 20 stims.
After experiment has finished, remove electrodes and ensure voltammeter is switched off when out-of-circuit.
Remove slice.
Allow aCSF to run through rig before placing next slice for more experiments or before electrode calibration.
Calibration
Immediately before calibration make up 2 µM DA (see Materials ).
Allow aCSF to circulate at high speed (~4 ml/min).
Switch tube to aCSF, and repeat as for wash-on to record negative ox potential for wash off
Repeat 3x and average wash-on and wash-off for approx. electrode sensitivity.
Repeat calibration for each recording solution used (i.e. each drug you use) to check drugs are not affecting electrode sensitivity. This is especially important if changing divalent ion concentration.
Keep electrode until data has been analysed.
Place electrode directly in front of inflow tube.
Connect electrode to voltammeter and turn on voltammeter to allow the electrode to settle for >10 mins.
Switch trigger settings on axoscope to “immediate” to record without triggering stim electrode.
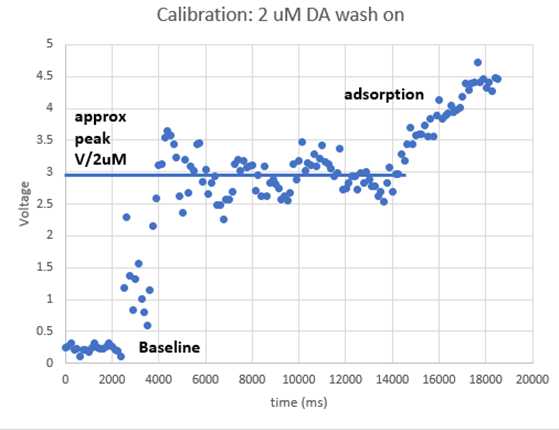
Rapidly switch inflow tube from aCSF to 2 µM DA solution. Minimise bubbles which interfere with the electrode
Watch bubbles to know when DA is washing on.
Start recording axoscope.
Refresh voltammeter immediately before DA washes on.
Watch oxidation peak rise with DA wash-on, for ~30 s.
At end of the day, wash through with dH20 and then air to ensure clean and dry. Use cotton bud with HCl to clean bath and check no salt build up around temperature probe or ref.
Rinse bubblers and bubble dry to ensure they do not backfill with liquid and become contaminated or grow mould.
Release pressure points from the peristaltic pump on inflow and outflow tubes to prolong the life of the tubing. Do not stretch tubing beyond where is necessary to hook on as they may break.