Deep hind paw incision model
Fanglin Lu
Abstract
The deep hind paw incision model is established to evaluate postoperative pain.
Based on TJ Brennan's rat model of incisional pain (1996), several modifications are made.
This protocol outlines the procedures from a to data anesthesia to consciousness recovery.
Steps
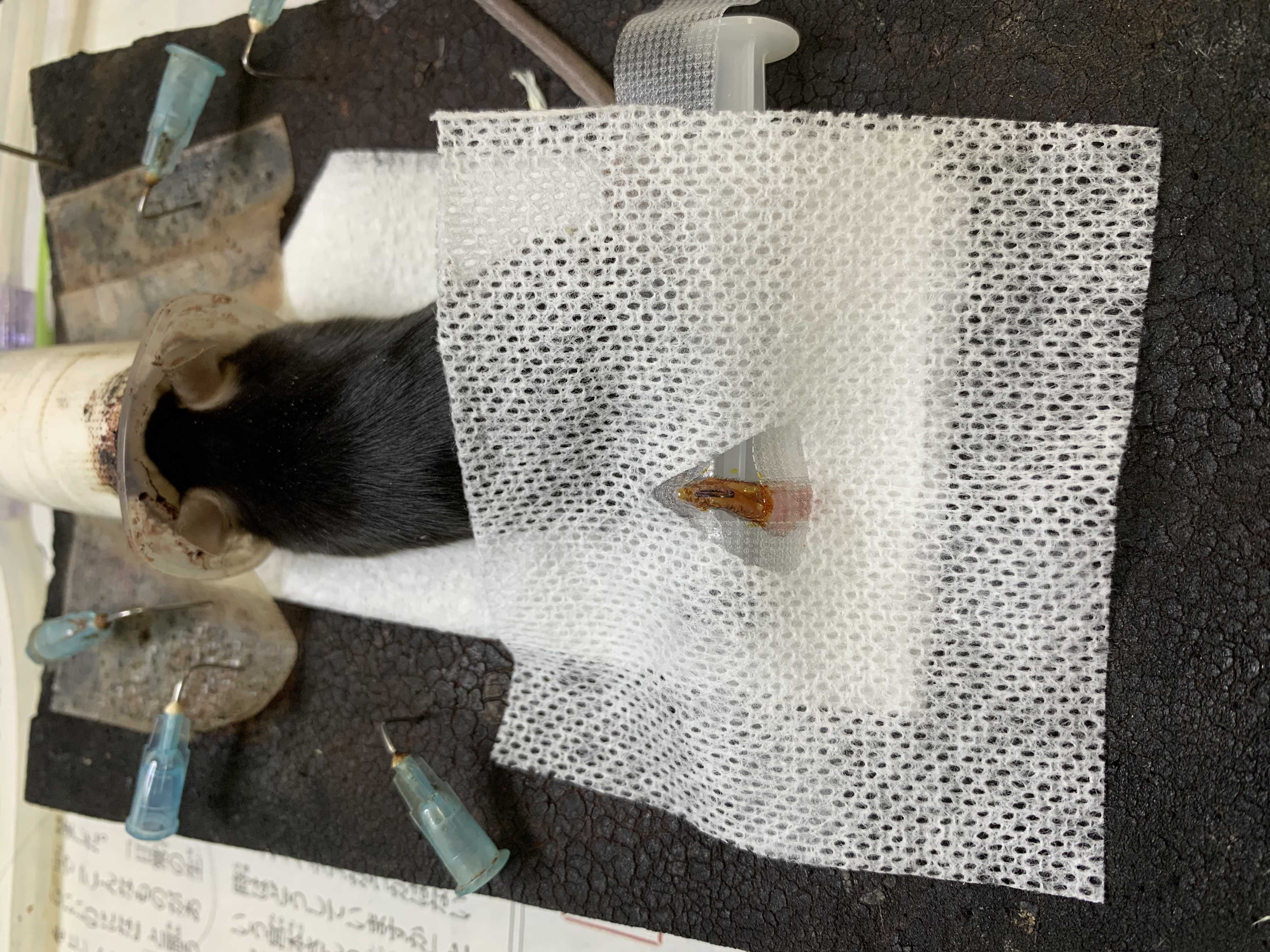
Anesthesia and disinfection
The mouse placed in a prone position under sevoflurane anesthesia (4 volume% in 1 L/min oxygen) delivered via a nose cone. Sevoflurane inhalation is used, as it is safe, non-invasive, rapid, and easy to control. Adequate anesthetic depth is ascertained by loss of response to tail clamp.
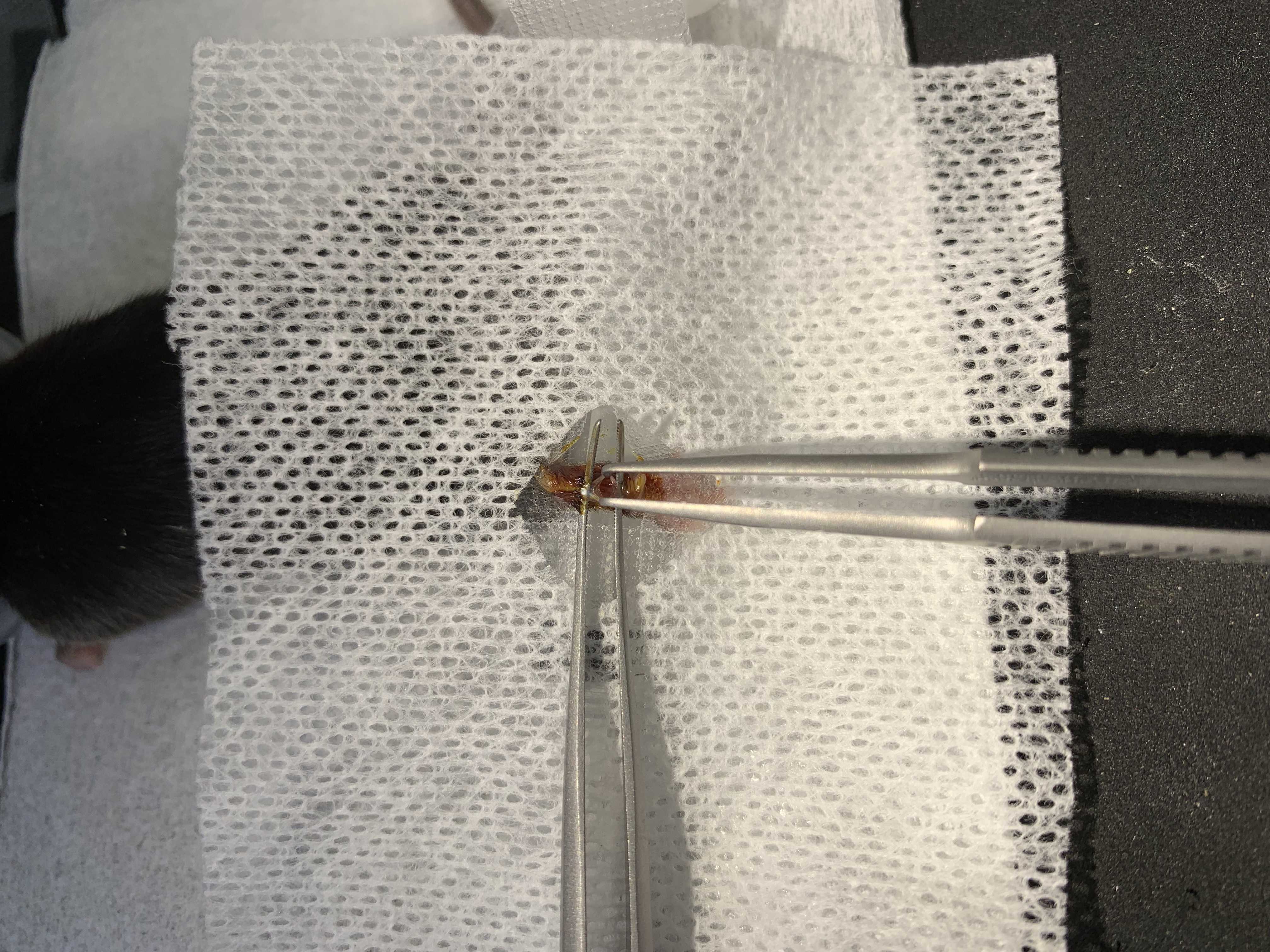
Keep the ipsilateral paw in plantar-flexion position. Disinfection with 10% povidone–iodine solution. Place a drape.
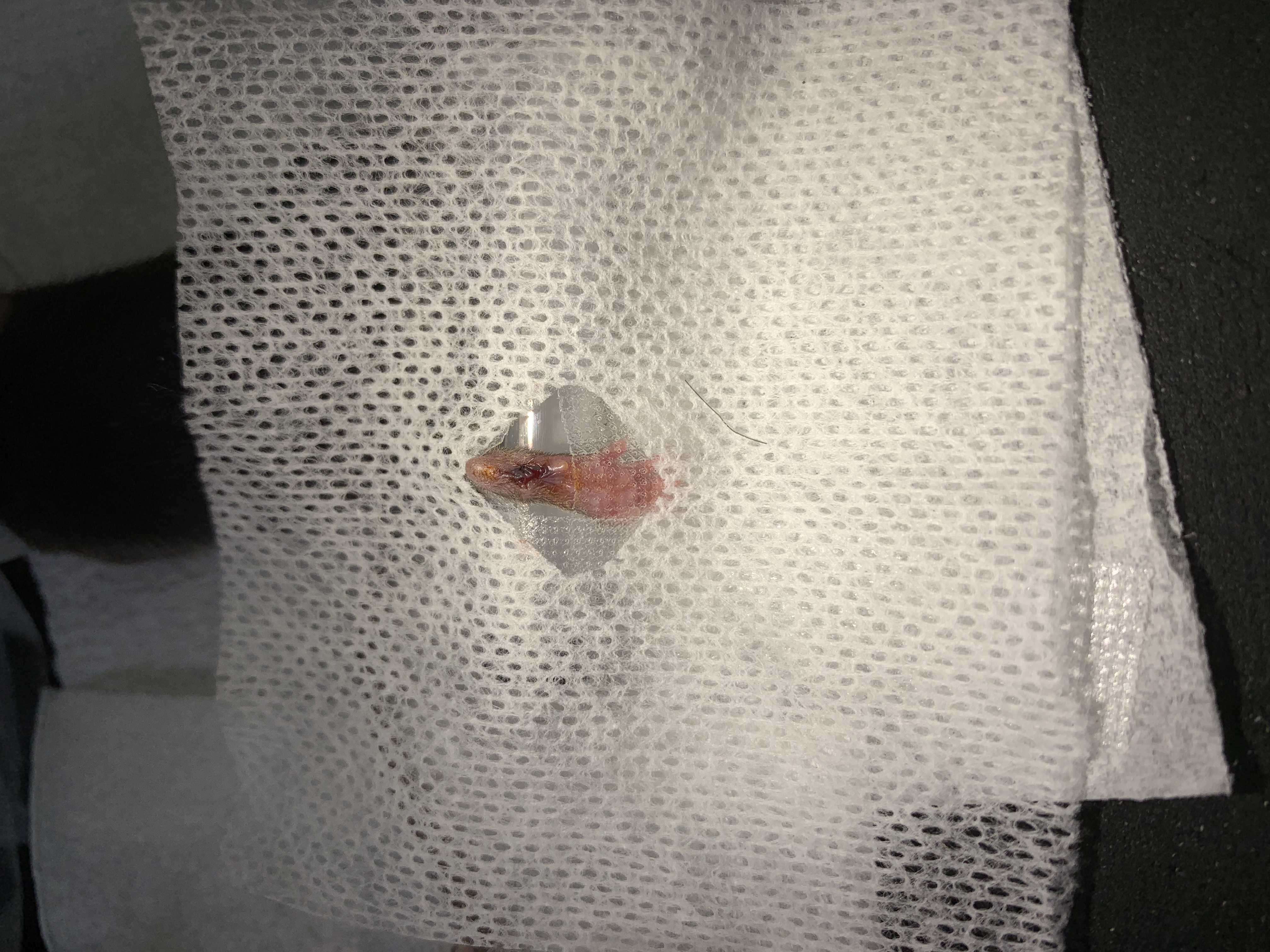
Deep hind paw incision
Place the mouse in a recovery cage. Once the mouse is fully recovered as it regains the righting reflex and ability to stand, return it to its home cage. Respiratory patterns and reactions to surgical stimulation are continuously monitored during the entire surgical procedure.
Sham surgery
The sham surgery comprises anesthesia, antiseptic preparation, and application of topical antibiotics without skin and muscle incision and elevation.