Crystallization of Zika virus NS3 helicase
Peter Marples, Lizbé Koekemoer, Andre Schutzer de Godoy
crystallisation
XChem
ASAP
AViDD
CMD
Diamond Light Source
i04-1
Research complex at Harwell
Zika NS3
NS3
Disclaimer
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Acknowledgements:
Diamond Light Source Ltd, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot OX11 0QX, UK
Sao Carlos Institute of Physics, University of Sao Paulo, Av. Joao Dagnone, 1100 - Jardim Santa Angelina, Sao Carlos, 13563-120, Brazil
Research Complex at Harwell, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot OX11 0FA, UK
Oxford Lab Technologies crystal shifter https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798320014114
Abstract
The crystallization protocol and buffer conditions used to obtain Zika NS3 helicase crystals suitable for XChem fragment screening. The Zika virus (ZIKV), discovered in Africa in 1947, swiftly spread across continents, causing significant concern due to its recent association with microcephaly in newborns and Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults. Despite a decrease in prevalence, the potential for a resurgence remains, necessitating urgent therapeutic interventions. Like other flaviviruses, ZIKV presents promising drug targets within its replication machinery, notably the NS3 helicase (NS3Hel) protein, which plays critical roles in viral replication. However, a lack of structural information impedes the development of specific inhibitors targeting NS3Hel. This protocol was used to grow Zika NS3 crystals that were applied high-throughput crystallographic fragment screening on ZIKV NS3 Helicase.
Steps
Equipment needed
Formulatrix Rock Imager (or incubator of choice)
Equipment
| Value | Label |
|---|---|
| Mosquito HV | NAME |
| High Volume 16-Channel Robotic Liquid Handler | TYPE |
| SPT LabTech | BRAND |
| 3097-01057 | SKU |
P100 8 multi-channel pipette
Crystallization experiment
Prepare seed stock: seed stock:
Diamond XChem Seeding Protocol1: 100 dilution Sample seeds
Protein and buffer requirements:
43.2µL``5mg/mL Sample
4.8mL
4.8mL seeds, dilution 1:100
Crystallisation screen composition:
0.12Molarity (M) NPS Mix
0.1Molarity (M) MES 6.5
33% Prcipitant Mix 4
Stock solutions used:
1Molarity (M) NPS Mix (consisting of 0.3 M Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate, 0.3 M Ammonium sulphate, and 0.3 M Sodium nitrate from Molecular Dimensions)
1Molarity (M) MES (Molecular Dimensions)
Precipitant Mix 4 (11% MPD, 11% PEG 1,000, and 11% PEG 3,350 from Sigma Aldrich)
Dispense 50µL into SwissCI 3 lens plate reservoir wells using a 100 µl multi-channel pipette.
Dispense 150``5mg/mL Sample to each lens using the SPT mosquito.
Dispense 100 to each lens using the SPT mosquito.
Dispense 50 to each lens using the SPT mosquito.
Drop ratio: 3:2:1 ratio (150 nL Sample : 100 nL reservoir solution: 50 nL seeds)
Final drop volume: 300 nl
Incubate at 20°C for 24h 0m 0s in Formulatrix Rock Imager.
Imaging Schedule : The first images are taken after 12 h and the imaging schedule follows a Fibonacci sequence of days for further collections.
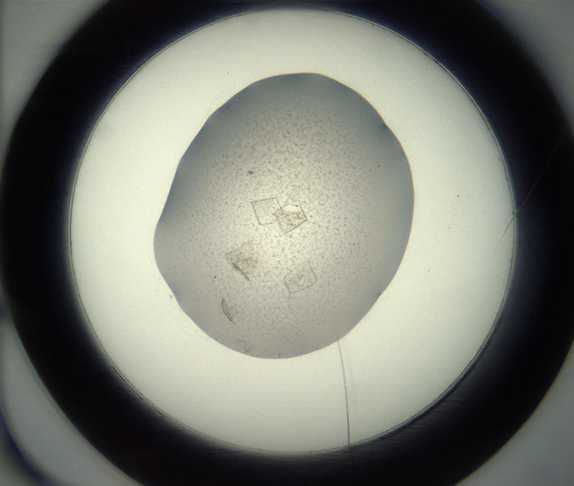
Data collection at Synchrotron
Diamond Light Source
Unattended Data Collection (UDC)
Data Collection Temperature: 100K
Detector: DECTRIS EIGER2 X 9M
Beamline: I04-1
Wavelength: 0.9212 Å
Resolution (Å): 1.62
Beam Size (μm): 60 X 50
Number of images: 3600
Oscillation: 0.10°
Exposure (s): 0.0020
Transmission (%): 100
Flux (ph/s): 3.80e+12

