Coomassie Purity Stain of Recombinant Antibodies
Addgene The Nonprofit Plasmid Repository
Disclaimer
We have listed the specific equipment, reagents, and methods that we use in our lab at Addgene. Equipment and reagents from other vendors should produce similar outcomes when using these protocols. However, please be aware that your protocol may need to be adjusted to accommodate slight differences between products. Addgene does not endorse or recommend specific products or equipment. Inclusion of this information is solely for transparency intended to support reproducibility in science.
Abstract
This protocol describes how to determine the purity and concentration of recombinant antibodies using ready-to-use bio-safe Coomassie G-250 stain (Addgene uses SimplyBlue SafeStain) and ImageJ software. The sample is separated by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis alongside serial dilutions of a standard antibody of known concentration. After staining with Coomassie blue, protein band intensities are measured using ImageJ software and a standard curve is generated. The ratio of the antibody protein content to the total protein content of the sample is determined.
Before start
See the Materials section for preparation of necessary reagents.
- Warm the hot plate to
100°C - Thaw IgG standard and prestained protein ladder on ice.
Steps
SDS-PAGE
Add 5µL of 4X sample buffer to each sample.
Add 2µL10X reducing agent to each sample.
Spin the sample briefly in the microcentrifuge.
Heat the samples for 0h 10m 0s at 100°C in a heat block.
Spin the sample briefly in the microcentrifuge.
Remove the gel from the plastic wrapper and rinse with deionized water.
Gently remove the white sticker on the bottom of the gel.
Place the gel in the electrophoresis chamber and secure it.
Carefully remove the comb from the gel.
Rinse each well with 200µL 1X MOPS running buffer.
Fill the chamber with 1X MOPS running buffer.
Make sure that the chamber is sealed.
Load 5µL of the prestained protein ladder to the appropriate well.
Load 20µL of each recombinant antibody sample to the appropriate well.
Cover the electrophoresis chamber and attach to a power supply.
Run the gel at 150 V for 1h 0m 0s.
Turn off the power supply and unplug the electrophoresis chamber.
Remove the gel from the chamber.
Use the metal spatula to gently break the gel cast open.
Use a razor blade to cut the top of the wells and bottom part of the gel where dye is visible.
Staining the Gel
Place the gel in a plastic tray with 100mL of deionized water.
Rinse gel with deionized water for 0h 5m 0s with gentle agitation on a rocking platform.
Pour off the water in the sink.
Add 20mL of SimplyBlue SafeStain and incubate for 1h 0m 0s with gentle agitation on a rocking platform.
Pour off the SimplyBlue SafeStain in the sink.
Add 100mL of deionized water and incubate for 1h 0m 0s with gentle agitation on a rocking platform.
Pour off the water in the sink.
Add 100mL of deionized water and incubate for 1h 0m 0s with gentle agitation on a rocking platform.
Pour off the water in the sink.
Take a brightfield image of the gel with an appropriate imaging system.
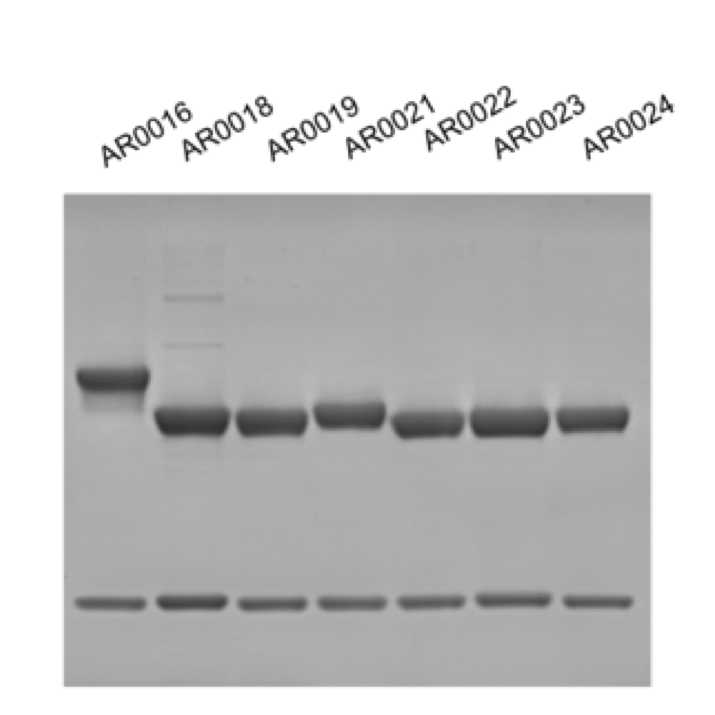
Image Analysis
Use ImageJ or a similar photo software to determine the relative intensity of the protein bands to the overall lane.
Import the gel image into ImageJ.
- Select File .
- Select Open .
- Choose the location of the file to open.
Change the image type to 8-bit .
- Select Image .
- Select Type .
- Choose 8-bit .
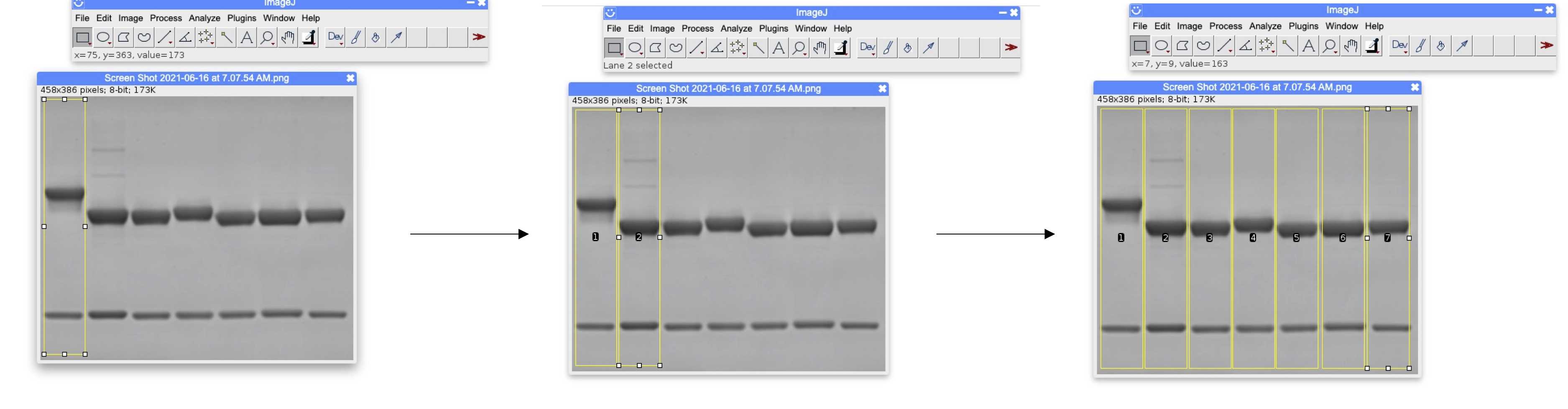
Determine each lane of the gel as follows:
- Using the box tool, draw a box around the entire first gel lane (as in Figure 2).
- Select Analyze .
- Select Gels .
- Select Select First Lane .
- Drag the box to the next lane.
- Select Analyze .
- Select Gels .
- Select Select Next Lane .
- Repeat for all lanes.
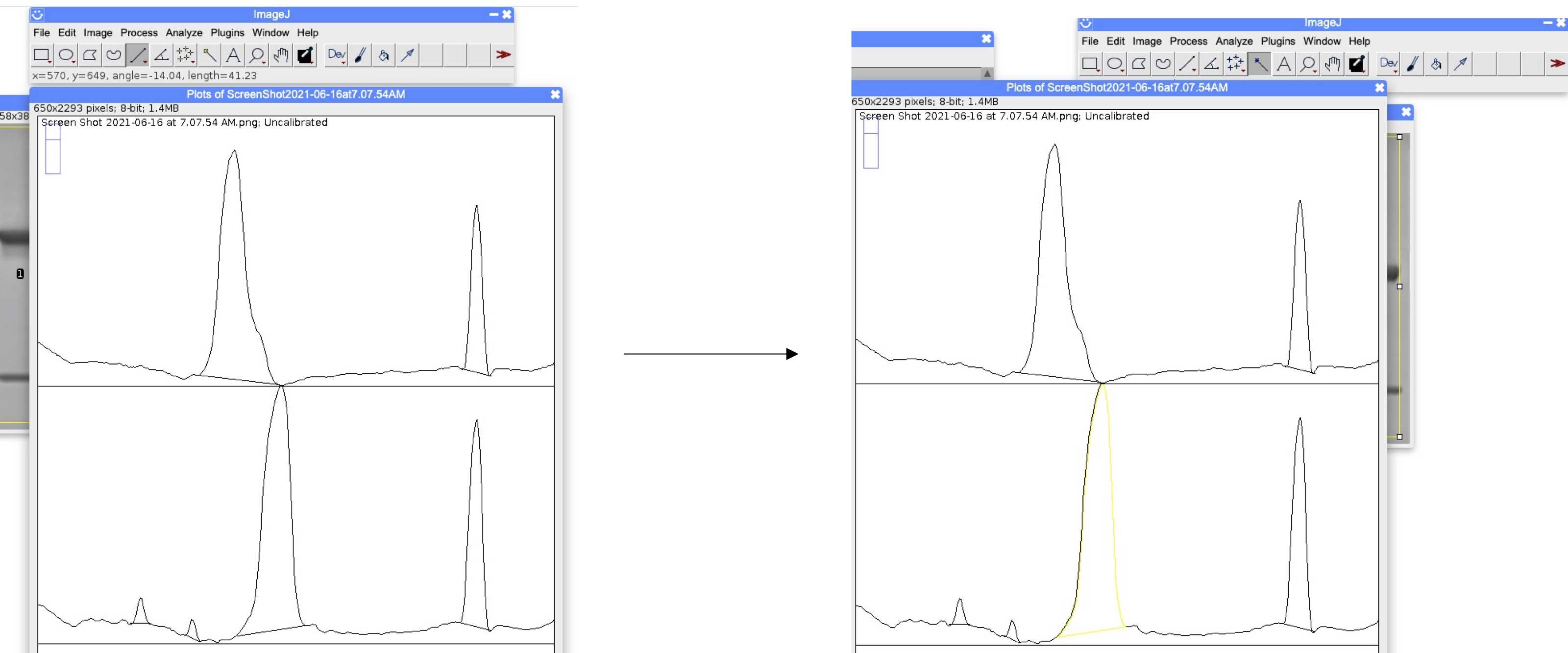
Plot the area under the curves for the protein bands as follows:
- Select Analyze .
- Select Gels .
- Select Plot Lanes .
Use the line tool to connect the bottom of each peak.
Select the wand tool.
Fill in each peak by selecting the center of the peak.
Export results as a csv file.
- In the results table, select File and Save As .
Determine the percent purity of the samples.
% purity = (Area of HC + Area of LC) / (Sum of the Area of lane bands) x 100
Example for AR0018 (lane 2 in Figure 1):
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Peak 1 (contaminant) | Peak 2 (contaminant) | Peak 3 (HC) | Peak 4 (LC) | Total Area | HC + LC Area | % Purity |
| AR0018 | 310.142 | 207.971 | 11469.296 | 4655.113 | 16642.522 | 16124.409 | 96.88681199 |
Plot the mg/mL versus the HC + LC Area for the IgG standards in Microsoft Excel.
Add a linear trendline for the standards.
Microsoft Excel can calculate this for you as follows:
- Select the graph.
- Select the Chart Design tab.
- Select the Add Chart Element drop down menu and select Trendline , Linear .
Determine the linear equation and the R2of the trendline on Microsoft Excel as follows:
- Select the graph.
- Select the Chart Design tab.
- Select the Add Chart Element drop down menu and select More Trendline Options .
- Select Display Equation on chart.
- Select Display R-squared on chart.
Note
The R2of the trendline should be between 0.95 - 1.
Use the equation of the trendline to determine the concentration of your samples based on your sample’s HC + LC area.
Example calculation:
If the sample HC + LC Area is 18179.442 and the linear equation of the standard curve is y = 14725x + 3748.4, then substitute 18179.442 for y and solve for x.
18179.442 = 14725x + 3748.4
x = 0.980
The concentration of the sample is 0.980 mg/mL