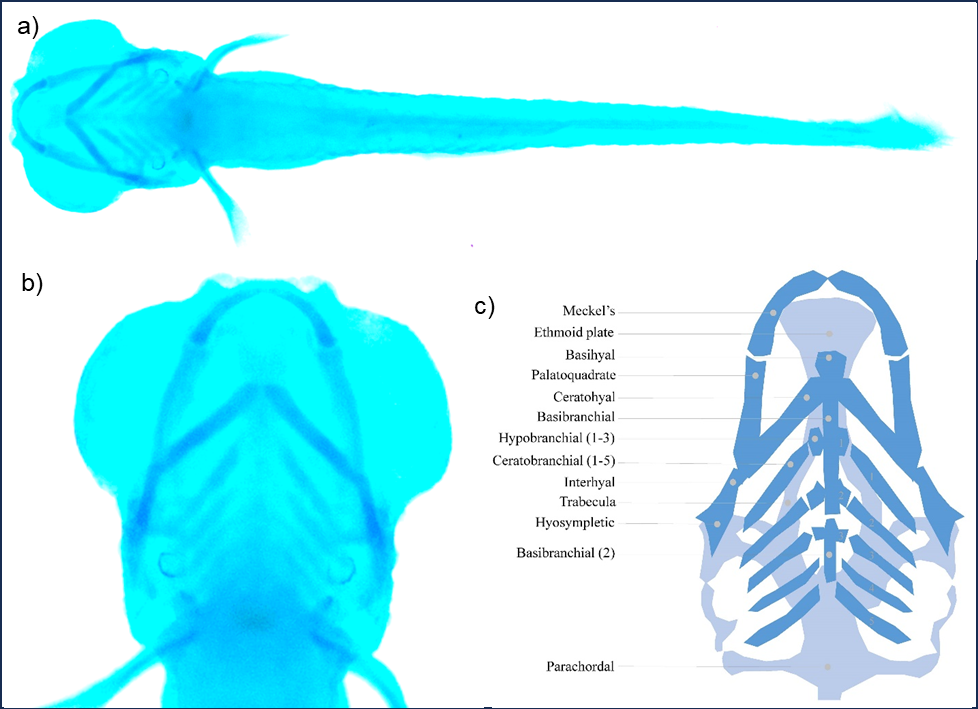
Cartilage staining
Satheeswaran Balasubramanian, Ekambaram Perumal
Abstract
The Alcian blue staining technique is widely used among developmental biologists to observe the development of cartilage and bone in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Alcian blue is a positively charged dye that stains the cartilage through an electrostatic interaction with negatively charged acidic mucopolysaccharides in the presence of magnesium ions (Scott et al. 1996).
Before start
Every protocol needs to be validated in the laboratory when first introduced. The present protocol describes validation steps that were taken in the Molecular Toxicology lab, at Bharathiar University. 1. Always wear personal protective equipment.
- All the steps are optimized in a 24-well plate for multiple groups such as control and treated.
Steps
Larval fixation
At the desired stage, take the zebrafish larvae and wash in PBS for 5 minutes.
Euthanize the larvae using the cold shock method (Keep at 4oC for 5-10 minutes).
Transfer the euthanized larvae into 4% PFA and keep it in the rocker for 2 hours at room temperature (if required, it can be kept overnight at 4oC).
Wash the fixed larvae with PBST for 5 minutes, two times.
Dehydrate the larvae using 50% ethanol and keep it in the rocker for 10 minutes at room temperature.
Staining
Add 1 ml of alcian blue staining solution to the dehydrated larvae and keep it in a rocker overnight at room temperature.
Bleaching
Rinse the stained larvae once using PBST.
Transfer the larvae to a bleach solution and incubate in dark at room temperature. Assess the bleaching process (using a microscope) and stop the reaction when the larvae become transparent (approximately 20-30 min for 4 dpf and above).
Clearing
Remove the bleach solution and rinse once using PBST.
Clear the beached larvae with 25% glycerol and 0.25% KOH. Keep them in a rocker at room temperature for 30 minutes to overnight.
Replace the solution with 50% glycerol and 0.25% KOH. Keep them in a rocker at room temperature for 2 hours to overnight.
Storage
Store larvae in a solution of 50% glycerol and 0.1% KOH at 4oC. Avoid long-term storage as it will diminish the stain. Capture images of the cartilage using any bright field microscope (preferably a stereo microscope).