Analysis of Islet Function in Dynamic Cell Perifusion System
IIDP-HIPP
Abstract
This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is based on the Vanderbilt Human Islet Phenotyping Program (HIPP) Islet Functional Analysis. This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is based on the Vanderbilt Human Islet Phenotyping Program (HIPP) Islet Functional Analysis. This SOP provides HIPP procedure for dynamic perifusion and hormone secretion measurement to assess islet function. This SOP provides HIPP procedure for dynamic perifusion and hormone secretion measurement to assess islet function.
This SOP defines the assay method used by the Human Islet Phenotyping Program (HIPP) for qualitative determination of the Purified Human Pancreatic Islet product, post-shipment, manufactured for use in the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)-sponsored research in the Integrated Islet Distribution Program (IIDP).
The goal of this SOP is to define the method for quantitative determination of insulin released after glucose stimulation for proving the potency of the human islet preparation shipped by the IIDP.
Steps
Procedures
General Perifusion Startup
Fill water bath with deionized water to about 1 inch from the top, and set the temperature to 37°C .
Label perifusion tubes with date, islet type, and any other identifying information, position the fraction collector trays for perifusion, and load the tubes.
Rinse the tubing with deionized water at max pump speed for 15 minutes, then place new frit into the islet chamber.
Preparation of Base Perifusion Medium and Secretagogues
Prepare Base Perifusion Medium by combining compounds below in a 1-liter Erlenmeyer flask. Add 1L of deionized water and mix for at least 15 minutes until dissolved.
2.1.1 3.2g NaHCO³
2.1.2 0.58L -Glutamine
2.1.3 0.11g Sodium Pyruvate
2.1.4 1.11g HEPES
2.1.5 1 bottle DMEM for 1L of media
2.1.6 1g RIA-Grade BSA
Prepare16.7 mM Glucose Medium with 100 µM IBMX
2.10.1 Weigh out around 10mg IBMX
2.10.2 Make 100 mM Stock IBM by dividing the IBMX weight in mg by 22.22 and add “X” mL of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO). Caution: Wear gloves and avoid spilling any DMSO on skin.
2.10.3 Make 100 µM Final Concentration (1:1000) by adding 100µL of Stock into 100mL of 16.7 mM Glucose medium.
Check the pH of the solution and adjust to 7.3 to 7.5 using either 1N NaOH or 1N HCl as necessary.
Add 70mg Ascorbate, Sigma A5960
Use a vacuum-filtration system to filter medium, transfer to a side-arm flask, and de-gas at 37°C for at least 30 minutes.
Prepare 1.7 mM Low Glucose Medium (for use with Epinephrine)
2.5.1 Add 0.0613g glucose to 200mL Base perifusion medium to 250mL bottle and mix until dissolved.
2.5.2 Wait 30 min and check glucose levels using a glucose meter.
Prepare 5.6 mM Glucose Medium
2.6.1 Add 0.5549g glucose to 550mL Base perifusion medium to 500mL bottle and mix until dissolved.
2.6.2 Wait 30 min and check glucose levels using a glucose meter.
2.6.3 Reserve some 5.6mM medium in a 50mL conical tube for islet loading and unloading.
Prepare 16.7 mM High Glucose Medium
2.7.1 Add 0.7522g glucose to 250mL Base perifusion medium to 250mL bottle and mix until dissolved.
2.7.2 Wait 30 min and check glucose levels using a glucose meter.
Prepare 1.7 mM Glucose plus 1µM Epinephrine/HCl (Store at -20°C )
2.8.1 Prepare 200mM Epi Stock by adding 0.043934g Epinephrine in 1mL 1.7 mM Glucose medium.
2.8.2 Prepare 0.4 mM Intermediate Epi Dilution (1:500): Dissolve 20µL 200 mM Epi stock into 10mL 1.7 mM Glucose medium.
2.8.3 Prepare 1µM Final Epi Concentration (1:400). Dissolve 250µL Intermediate Epi Dilution into 100mL 1.7mM Glucose medium.
Prepare 5.6 mM Glucose plus 20mM KCl
2.9.1 Add 0.149g KCl to 100mL 5.6 mM Glucose medium.
Setup of Secretagogues in Perifusion Water Bath
Place the bottles of media in the water bath to warm up for at least 10 minutes before beginning the perifusion.
Replace Pyrex orange caps with 4-Luer (+1) caps on every bottle of media to be used, and tape over the holes so that gas cannot escape.
Turn on gas (95% O², 5% CO²), and place one gas catheter into each of the bottles with the new caps. Put tape over the other holes on the caps. Make sure that gas catheter is suspended above the media, and not inside the liquid.
Place intake catheters into baseline media bottle, making sure that they reach to the bottom of the bottle. Run the media through the chambers for about 10 minutes while islets are being aliquoted for perifusion, disposing of media .
Preparing Islets for Perifusion
On the day of islet receipt , plate a half of islet shipment (1000 - 5000 IEQs) in 10-cm non-tissue culture treated Petri dish and culture in CMRL-1066 plus 10% FBS media at 37°C/5% CO² for 2 hours prior to perifusion .
Label a 1.5mL clear Eppendorf tube for islets.
Place petri dish with cultured islets on the stage of inverted microscope and view the islets under 4x objective. Use the micrometer in the 10x eyepiece to size the islets.
Place the dish containing islets on the stage of a stereomicroscope equipped with a high-resolution camera and swirl until all islets are in the camera field of view at 10x magnification. Capture brightfield images at approximately 12-ms exposure and darkfield images at approximately 1.2-s exposure, each at 10x magnification. Ensure all islets are present in image. Save all image files.
Transfer all islets from the center of the dish to a labeled 1.5mL clear Eppendorf tube for loading into perifusion chamber.
Open the darkfield image in the cellSens software. Using the manual HSV threshold function, segment the islet tissue channel.
Use the custom Count and Measure algorithm to determine islet count and mean islet diameter. Split adjacent but discrete islets using the Manually Split Objects tool to get an accurate islet count and mean diameter measurements.
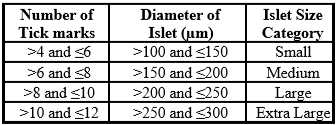
Use the mean diameter measurements to assign islets to a diameter group using the chart provided in 4.4 above.
Islet Loading into the Perifusion Chamber
Turn off the pump.
Turn on the pump, set the fraction collector to 3 minutes and flip the collector arm so that it is over the first collection tube. Press “Start” on the collector to start the timer.
Tighten column end pieces, and end fittings, and make sure there are no leaks.
Lower the column mounting rack into the water bath, and tighten the clamp to prevent wobbling.
Turn the stopcock on the air bubble uptake lines so that the waste pathway is open, and close the stopcock on the outlet line at the fraction collector.
Remove the chamber from its mounting, turn it upside down, and remove the red end piece (inlet).
Remove and discard two thirds of the media from the chamber.
Using a 1mL pipette set to 700µL transfer the slurry of islets from the Eppendorf tube to the perifusion chamber. Rinse the tube at least 3 times with 700µL of baseline medium, and transfer to the chamber.
Place the chamber back onto the mounting, and fill it up with baseline medium until there is a convex meniscus. Tap the sides of the column lightly to dislodge air bubbles from the walls, and collect and discard any bubbles from the top of the meniscus.
When all the bubbles have been removed, carefully replace the inlet plunger.
NOTE - make sure that no bubbles are introduced into the chamber during this process; if bubbles get in, remove the plunger, and repeat step 5.6.
Turn the chamber right side up, and put it back on the mounting rack.
Open the outlet line at the fraction collector and close the waste line on the air bubble uptake line.
Fraction Collector Startup and Islet Wash Period
Collect 10 preliminary fractions to synchronize pump speed to deliver 3mL 3-minute fractions, and to rinse the islets.
Record each pump speed on the perifusion worksheet in the perifusion logbook.
Collection of Perifusate Fractions
Begin to collect fractions.
Change secretagogues at predetermined fractions.
As soon as the fraction collector moves, switch off the pump.
Move the needles from one secretagogue to the other, making sure to not tangle the tubing, and inserting the needle all the way to the bottom of the bottle.
When the needles have been moved, restart the pump.
Recovery of Islets from Chamber and Perifusion System Cleanup
At the end of the perifusion raise the mounting rack from the water.
Stop pumps and close all outlets. Wait about 2 minutes, so that the islets can drift down to the bottom of the chamber.
Carefully remove the blue end piece (outlet) from the first chamber.
Pour the medium from the chamber into a 60 mm untreated dish, and rinse out the chamber and the blue column end piece with 1mL of baseline medium 5 times each into the dish.
Rinse the chamber with deionized water, and remove frit with a frit removal stage and tool.
Put the column back together, and run 10% bleach through them at maximum pump speed for about 15 minutes. Make sure that all the tubing gets bleached, including all the waste lines. After the bleach, run deionized water through the entire system at maximum speed for 1.5 hours.
After the system cleanup, turn off the pump using the master power switch , turn off and drain the water bath, and log the perifusion in the notebook.
Perform any scheduled maintenance.
Islet Hormone Extraction
After retrieving islets from the perifusion chamber, size and count retrieved islets (step 4.4) to determine IEQ and record islet size and count in Islet Cell Calculation Excel Worksheet . Transfer the islets to a 1.5mL Eppendorf tube.
Note: The average expected retrieval rate is approximately 93%. Lower islet recovery has been observed for islets showing hallmarks of disintegration.
Centrifuge the tubes for 3 minutes at 200 rcf and aspirate the supernatant using a pipette, being careful not to disturb the islet pellet.
Remove as much supernatant as possible from the tube, using a 1mL tip, followed by a 200µL tip and place tube on ice.
Prepare fresh acid alcohol for hormone extraction by adding 50µL of concentrated HCl to 5.5mL of 95% ethanol.
Add 200µL of acid alcohol to tube containing islets.
Incubate sample at 4°C for 24 hours.
Spin samples down for 5 minutes at 3000 rcf, and transfer three 50µL supernatant aliquots into pre-labeled 2mL screwcap tubes and store at -80°C .
Data Storage and Reporting
Data Storage and Reporting
To facilitate data management and ensure data security, the Vanderbilt HIPP uses an institutional server-based platform for data storage and analysis.
Deviations and Resolutions
Deviations and Resolutions
Document any deviations that occurred during this protocol that affect the final results and report with the analysis of the assay.